Management consultant, Dr. William Edwards Deming developed a method known as PDCA cycle/Shewhart Cycle in the 1950s to identify why some products or processes do not function as expected. His strategy, used by many different types of organizations, has since become a popular strategy tool. It makes it possible for them to formulate theories about what needs to change and then test them in a “continuous feedback loop.”
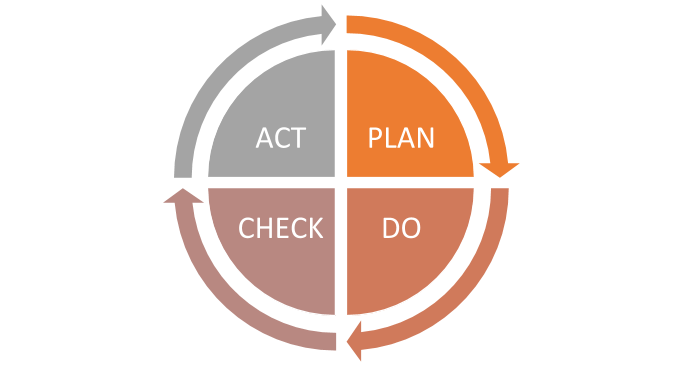
We use this strategy tool to serve the purpose of a continuous growth plan in the organization. This cycle consists of 4 phases:
Plan- At this point, you can simply schedule what needs to be done. Based on the project’s scale, preparation will take a big part of the team’s efforts. Usually, it would consist of smaller steps so that you can create a proper strategy and fewer failure chances.
Here you need to answer some basic issues and then you can move to the next phase.
- What are the core issues that need to be addressed?
- What are resources are we going to use?
- What are the best solutions we have while considering the availability of our resources?
- What are the ways of fixing problems with minimal expense?
Always keep in mind that plan is an important primary stage you cannot proceed if you are not sure about the plan, try to be as precise as you can before going to the next phase. Gather all important parameters information.
Do- Now you have a plan for all your work that needs to be done. You need the best possible method to implement your plan. You are going to implement here everything that you considered in the planning phase.
Here you need to be aware of unpredicted problems and uncertainties during implementation. First, let’s say try to do it on a smaller scale & controlled environment and then try on a bigger one.
When you are doing then keep a record of all steps and standardize it then after successful implementation.
Check- What did you do? What are the outcomes? Here comes your audit phase that your initial plan and implementation worked and you get the best outcomes than previous solutions. Find the root cause of the problems after implementation.
The most important phase of the PDCA cycle where you need to check the alignment of your plan and implementation, avoid repetitive mistakes, and improve by the continuous feedback loop.
Act- last phase Act, you have planned, done, checked your work now comes the phase of the act on what you have analyzed so far. In this stage, if everything seems perfect then you can proceed with your initial plan and achieve your target.
The repeated methodology allows the team to identify and validate and enhance solutions through a waste-reducing loop.
A required dedication to quality improvement is included in the PDCA process, and it can have a significant effect on effectiveness and performance.
Finally, bear in mind that a certain amount of time is required for the PDCA model, and it may not be ideal for solving immediate problems.
If you like this concept, you can also read A/B Testing and The Hedgehog Concept.