Tesla, Inc. is a renowned American company headquartered in Austin, Texas, known for its groundbreaking innovations in the automotive and clean energy sectors. Tesla’s primary focus is on designing and manufacturing electric vehicles, ranging from cars to trucks, as well as producing stationary battery energy storage solutions for both homes and large-scale grid applications. Additionally, the company offers solar panels, solar shingles, and a range of related products and services.
Tesla Energy, a subsidiary of the company, plays a significant role in the installation of photovoltaic systems and ranks among the world’s leading providers of battery energy storage systems, with an impressive 6.5 gigawatt-hours installed in 2022.
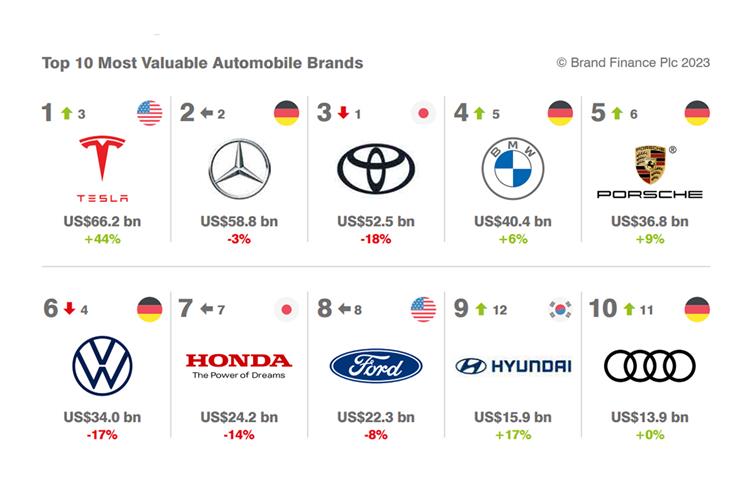
As of 2023, Tesla stands as the world’s most valuable automaker and one of the most highly esteemed companies globally. In 2022, it took a prominent position in the battery electric vehicle market, holding an impressive 18% market share.
Tesla’s journey began in July 2003 when it was incorporated as Tesla Motors by Martin Eberhard and Marc Tarpenning, paying homage to the renowned inventor and electrical engineer, Nikola Tesla. A pivotal moment arrived in February 2004 when Elon Musk, through a substantial $6.5 million investment, became the company’s largest shareholder. Musk took on the role of CEO in 2008, leading Tesla into its mission to accelerate the world’s transition to sustainable energy.
Over the years, Tesla has unveiled a series of groundbreaking vehicle models, including the iconic Roadster sports car in 2008, the Model S sedan in 2012, the Model X SUV in 2015, the widely acclaimed Model 3 sedan in 2017, the Model Y crossover in 2020, and the innovative Tesla Semi truck in 2022.
The company’s future holds exciting prospects, with plans to introduce the Cybertruck light-duty pickup truck in 2023. Notably, the Model 3 stands as the world’s all-time bestselling plug-in electric car, reaching the historic milestone of 1 million units sold globally in June 2021. In 2022, Tesla experienced a remarkable 40% increase in deliveries, totaling around 1.31 million vehicles, with cumulative sales surpassing 4 million cars as of April 2023.
Tesla’s influence extends beyond its impressive product lineup, as the company briefly reached a market capitalization of $1 trillion in October 2021, a feat achieved by only a handful of companies in U.S. history.
Despite its undeniable success, Tesla has also faced its share of challenges, including lawsuits, regulatory scrutiny, and criticism from the media. These issues have arisen from allegations of whistleblower retaliation, concerns related to worker rights, product defects, and the often-controversial statements made by Tesla’s outspoken CEO, Elon Musk.
Tesla Success Story
Humble Beginnings
Tesla, as we know it today, has a fascinating origin story that began in 2003 when it was incorporated as Tesla Motors by two visionaries, Martin Eberhard and Marc Tarpenning, in San Carlos, California. What inspired them to start this groundbreaking company was a critical moment in the automotive world: General Motors had recalled and subsequently destroyed all of its EV1 electric cars in 2003. This event, coupled with their realization that electric vehicles could offer both high performance and superior fuel efficiency, spurred Eberhard and Tarpenning to take action.
Another pivotal influence on Tesla’s early days was the AC Propulsion tzero, which served as inspiration for the company’s first vehicle, the iconic Roadster. Eberhard’s vision went beyond just building cars; he aimed to create a car manufacturer that was also a technology company, with a strong focus on three core technologies: the battery, computer software, and a proprietary motor.
Tesla’s journey received a significant boost when Ian Wright joined the team as the third employee a few months later. The trio embarked on a venture capital (VC) funding hunt in January 2004 and, in February of that year, crossed paths with Elon Musk. Musk played a pivotal role by contributing an impressive $6.5 million in the initial Series A funding round of $7.5 million. He also assumed the position of chairman of the board of directors and later became the CEO, making him a central figure in Tesla’s evolution.
In the following months, J.B. Straubel joined as the fifth employee, adding another dimension to Tesla’s talented team. A significant moment occurred in September 2009 when a lawsuit settlement allowed all five individuals (Eberhard, Tarpenning, Wright, Musk, and Straubel) to be recognized as co-founders.
Elon Musk, with his visionary thinking, consistently emphasized Tesla’s long-term goal: to create affordable electric vehicles for the mass market. The strategy was to begin with a premium sports car aimed at early adopters and then expand into more mainstream vehicle categories, including sedans and affordable compacts.
Musk’s relentless commitment to Tesla’s success was evident in his Series A investment in February 2004, which involved several private investors. Over the years, he continued to secure substantial investments and played a vital role in steering the company’s course.
In 2006, Tesla’s master plan included a partnership with SolarCity, focusing on co-marketing photovoltaic solar panels. This innovative move allowed Tesla to explore renewable energy solutions beyond just electric cars.
Tesla underwent changes in leadership throughout its early years, with Elon Musk ultimately assuming the CEO position in October 2008. This transition included restructuring and workforce reductions as the company worked to stabilize its finances.
Despite these challenges, Tesla continued to attract investments and support from key players in the industry. In May 2009, Daimler AG acquired an equity stake in Tesla, ensuring the company’s survival during a critical period.
In July 2009, Abu Dhabi’s Aabar Investments further bolstered Tesla by acquiring a significant interest, solidifying the company’s position as a leading innovator in the electric vehicle and clean energy space. This marked the beginning of Tesla’s journey towards becoming a global powerhouse in sustainable transportation and energy solutions.
United States Department of Energy Loan for Tesla
In 2009, Tesla’s journey into the electric vehicle world received a significant boost when it was approved to receive a substantial loan of US$465 million from the United States Department of Energy. This funding was part of the Advanced Technology Vehicles Manufacturing Loan Program, which aimed to support the engineering and production of the groundbreaking Model S sedan.
Additionally, Tesla intended to use these funds to further develop commercial powertrain technology. It’s worth noting that this low-interest loan program, initiated during the George W. Bush administration, was separate from the “bailout” funds that General Motors and Chrysler received, as well as distinct from the 2009 economic stimulus package. Tesla made history by fully repaying this loan, including an interest of US$12 million, in May 2013. In doing so, Tesla became the first car company to accomplish this feat, setting an impressive standard.
The company’s journey toward profitability reached a significant milestone in August 2009 when Tesla announced that it had achieved corporate profitability for the month of July 2009. This marked a turning point for the company, as it earned approximately US$1 million on revenue totaling US$20 million. Much of this profitability was attributed to improved gross margins on the 2010 Roadster, the second iteration of Tesla’s award-winning sports car. During that period, Tesla experienced a surge in new Roadster purchases, contributing to its overall financial success. In September 2009, Tesla announced a successful funding round of US$82.5 million to accelerate its retail expansion. Notably, Daimler, one of Tesla’s key partners, participated in this funding round to maintain its equity ownership.
Tesla’s Impressive IPO
Tesla’s growth and ambitious plans continued as it filed for an initial public offering (IPO) in January 2010. The IPO, underwritten by prestigious firms like Goldman Sachs, Morgan Stanley, J.P. Morgan, and Deutsche Bank Securities, was launched on June 29, 2010, marking a historic moment for the company. Tesla offered 13,300,000 shares of common stock to the public at a price of US$17.00 per share, raising an impressive US$226 million for the company. This IPO made Tesla the first American car manufacturer to go public since Ford in 1956.
Shortly after its IPO, Tesla announced a strategic partnership with Toyota in May 2010. Toyota agreed to purchase US$50 million in Tesla common stock through a private placement. The two companies expressed their intention to collaborate on the development of electric vehicles, parts, production systems, and engineering support. This partnership paved the way for the development of an electric version of the RAV4 EV, solidifying Tesla’s position as a leading innovator in the electric vehicle industry.
As Tesla moved forward, it faced challenges related to Model S production and financial sustainability. Elon Musk proposed a US$11 billion deal with Google to rescue the company. However, improved production processes and a strong sales push eventually led to Tesla’s first profitable quarter, rendering the deal unnecessary.
Tesla’s journey was not without challenges. In November 2013, after several incidents of Model S fires following high-speed impacts with road debris, Tesla’s stock faced a temporary setback, falling more than 20 percent. Tesla responded by developing a battery protection system as a no-cost retrofit to all Model S vehicles. Despite this, the company remained the top performer on the Nasdaq 100 index in 2013.
By 2014, Tesla had its sights set on expanding its global presence and sales, aiming to sell 40,000 electric vehicles worldwide. This expansion included introducing Tesla vehicles in countries such as China, Hong Kong, Japan, and Australia. However, the company later revised its sales guidance to 33,000 units for 2014.
Tesla’s production efforts commenced at the Tesla Factory in Fremont, California, but in October 2015, the company began negotiations with the Chinese government regarding local production in China. This move had the potential to reduce the prices of Tesla models by a significant margin, making them more accessible to Chinese consumers. Elon Musk clarified that production would remain in the U.S. for the time being, but a factory in China could be a possibility in the future, depending on local demand. Similar considerations were made for potential manufacturing plants in India.
Tesla’s impressive progress continued as it announced record vehicle production numbers in November 2015, including revised sales targets for 2015. The company anticipated producing an average of 1,600 to 1,800 vehicles per week for both the Model S and Model X during 2016, aiming to deliver 80,000 to 90,000 new vehicles in total. This signaled Tesla’s commitment to delivering sustainable transportation to an ever-growing global audience.
Model 3 Rollout and Financial Triumphs
In the electric vehicle revolution, Tesla’s most significant milestone came with the introduction of the Model 3. Unveiled in March 2016, the Model 3 garnered immense attention. Just a week after the unveiling, global reservations for the Model 3 surpassed a staggering 325,000 units, showcasing the immense demand for affordable electric vehicles. In response to this unprecedented demand, Tesla made a bold move in May 2016 by accelerating its annual unit build plan for all models, aiming to reach 500,000 units by 2018. This decision was strategic, allowing more Model 3 buyers to take advantage of the full U.S. tax credit of US$7,500 before it gradually phased out.
The year 2017 brought pivotal changes for the company. On February 1, 2017, Tesla officially changed its name from Tesla Motors to Tesla, signifying its broader focus beyond just automobiles. Furthermore, in March 2017, the tech giant Tencent Holdings Ltd., one of China’s most valuable companies, invested US$1.8 billion to acquire a 5% stake in Tesla. This strategic partnership marked a significant step in Tesla’s global expansion.
Tesla’s remarkable journey was reflected in its stock market performance. In 2017, for a brief period, Tesla surpassed both Ford Motor Company and General Motors in terms of market capitalization, making it the most valuable American automaker. Additionally, Tesla made its debut on the Fortune 500 list in June 2017.
However, the launch of the Model 3 on July 7, 2017, posed certain challenges for Tesla. The company’s stock-market value declined by more than US$12 billion in the week leading up to the Model 3 debut. Several factors contributed to this decline, including the fact that demand for Tesla’s existing luxury models, the Model S and Model X, did not show substantial growth in the second quarter of 2017. Moreover, there were concerns that the introduction of the Model 3 could negatively impact sales of these luxury models. Tesla aimed to achieve annual luxury sales of 100,000 units, which fell below some analysts’ expectations. Furthermore, competition in the electric vehicle market was intensifying, with Volvo Cars committing to introduce only electric and electric-assisted vehicles by 2019.
Tesla faced challenges related to the production timeline for the Model 3. Elon Musk’s initial prediction in 2016 suggested that 100,000 Model 3 units would be sold in 2017. However, production numbers by December fell significantly short of this target, with only about 20,000 units produced. Issues at the Gigafactory, including difficulties with robots on the assembly line and battery manufacturing problems, contributed to production delays. Despite the challenges, Tesla remained committed to overcoming these hurdles.
In April 2018, Elon Musk expressed optimism by increasing the production target to 6,000 Model 3 units per week by the end of June 2018. However, he declined to speculate on reaching a production level of 10,000 units per week.
By 2018, Tesla had made significant strides, selling approximately 140,000 Model 3 vehicles worldwide. In terms of market share and brand recognition, Tesla was on the rise, solidifying its position as a leader in the electric vehicle industry.
Financially, Tesla had used various means to fund its operations, including sales income, stock offerings, and bond sales. These efforts included raising billions of dollars to support growth, research, and development.
Tesla’s brand value was also on the rise. In 2020, Kantar rated Tesla’s brand as worth US$11.35 billion, surpassing all other automakers and reflecting the company’s strong market presence.
Despite its ups and downs, Tesla continued to make headlines and redefine the automotive industry. With innovative products and a commitment to sustainability, the company consistently pushed the boundaries of what electric vehicles could achieve. Tesla’s journey showcased the power of innovation and determination in shaping the future of transportation.
Expansion and Diversification
Following the success of the Model 3, Tesla continued to expand its product lineup and diversify its offerings. In 2020, Tesla introduced the Model Y, another crossover vehicle. The Model Y was designed to be more compact and affordable than the Model X while sharing many components with the Model 3. This strategic move aimed to capture a broader segment of the market.
Sales of the Model Y quickly gained momentum, rivaling those of the Model 3. Elon Musk expressed confidence that the Model Y had the potential to become Tesla’s best-selling model, further solidifying the company’s position in the electric vehicle market.
Looking ahead, Tesla had ambitious plans for the early 2020s. The company announced its intention to release several new models, each pushing the boundaries of electric vehicle technology. Among these exciting prospects was a second version of the Roadster, a legendary sports car that had initially put Tesla on the map. This new Roadster promised to combine high-performance capabilities with cutting-edge electric technology.
Additionally, Tesla had its sights set on the commercial sector. The company unveiled a semi-trailer truck, designed to revolutionize freight transportation by offering long-range electric capabilities. This move aligned with Tesla’s commitment to sustainability and reducing carbon emissions.
Perhaps one of the most talked-about announcements was the introduction of the Cybertruck, Tesla’s take on a pickup truck. The Cybertruck’s design was unlike anything seen before in the automotive industry, featuring a bold and angular aesthetic that sparked both excitement and controversy. Tesla aimed to disrupt the traditional pickup truck market by offering an electric alternative with impressive performance and durability.
As Tesla continued to innovate and expand its product portfolio, the company maintained its commitment to sustainability and the global transition to electric transportation. With a diverse range of vehicles, from compact sedans to rugged trucks, Tesla positioned itself as a leader in the electric vehicle revolution, shaping the future of mobility.
Also Read: PlayStation Success Story: How Sony Revolutionized Gaming
To read more content like this, subscribe to our newsletter
Go to the full page to view and submit the form.

