Boeing, often referred to as “The Boeing Company,” stands as an iconic American multinational corporation. This aerospace powerhouse is renowned worldwide for its prowess in designing, manufacturing, and globally distributing an impressive array of products. From airplanes and rotorcraft to rockets, satellites, telecommunications equipment, and missiles, Boeing’s innovation knows no bounds. Beyond crafting these technological marvels, Boeing extends its reach by providing leasing services and comprehensive product support.
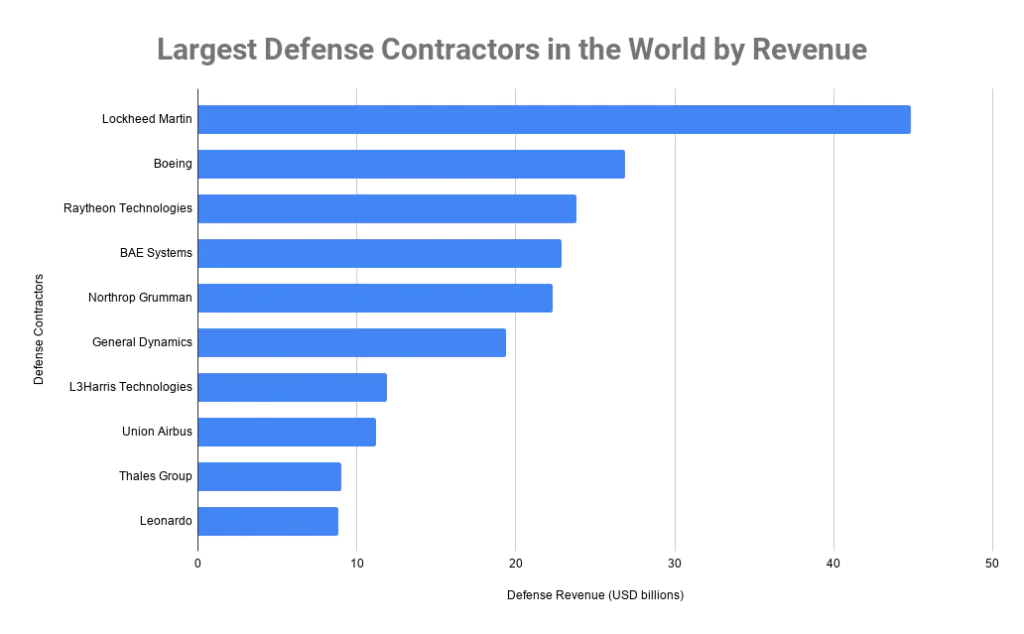
Boeing’s prominence in the global aerospace arena is hard to overstate. As one of the largest aerospace manufacturers on the planet, it holds the remarkable distinction of being the second-largest defense contractor by revenue in 2020. Furthermore, Boeing proudly bears the mantle of the United States’ foremost exporter, valued by the dollar.
The story of Boeing traces back to its founding by William Boeing in Seattle, Washington, on July 15, 1916. Over the decades, Boeing’s trajectory has been marked by transformative milestones, including the pivotal merger with McDonnell Douglas on August 1, 1997. This union saw Philip M. Condit, then-chairman and CEO of Boeing, take the helm of the merged entity, while Harry Stonecipher, former CEO of McDonnell Douglas, assumed the roles of president and COO.
Fast forward to 2023, and the Boeing Company has established its corporate headquarters in the Crystal City neighborhood of Arlington, Virginia. The organization operates through four primary divisions, each contributing to its multifaceted success: Boeing Commercial Airplanes (BCA), Boeing Defense, Space & Security (BDS), Boeing Global Services, and Boeing Capital. In terms of financial prowess, Boeing demonstrated its mettle in 2021 by recording a staggering $62.3 billion in sales.
However, Boeing’s journey has not been without its share of challenges. In 2019, the company faced turbulence in its global reputation and commercial business, compounded by a financial rating setback. This turbulent period followed the grounding of the entire 737 MAX fleet worldwide, stemming from two tragic crashes in late 2018 and early 2019.
Marketing Strategies of Boeing
Boeing employs a range of marketing strategies to maintain its global prominence and drive growth in a competitive industry. These strategies are designed to address various aspects of its business, from commercial airplanes to defense and space systems. Here are some key elements of Boeing’s marketing strategies:
1. Diverse Product Portfolio
Boeing, the world’s largest aerospace company, effectively employs this strategy by offering a wide range of products and services that cater to various customers in the aviation industry.
One of the key ways Boeing diversifies its product portfolio is by offering both commercial and defense aircraft. Its commercial aircraft division produces planes for passenger airlines, such as the 737 Max, 787 Dreamliner, and 747-8 Intercontinental. These planes cater to different customer segments, including low-cost carriers, full-service airlines, and cargo operators. On the other hand, Boeing’s defense division produces military aircraft, such as the F-15 fighter jet, KC-46 tanker, and P-8 maritime patrol plane. By offering both commercial and defense aircraft, Boeing can tap into different markets and reduce its reliance on any single segment.
Another way Boeing diversifies its product portfolio is through its subsidiaries and partnerships. For example, it owns Aurora Flight Sciences, a leading provider of autonomous systems and advanced robotics. This acquisition allows Boeing to expand its offerings beyond traditional aircraft manufacturing and tap into emerging technologies like unmanned aerial vehicles (UAVs) and urban air mobility solutions. Additionally, Boeing has formed strategic partnerships with suppliers and other industry players to develop new products and services. For instance, it collaborated with Safran, a French aerospace company, to create a joint venture called CFM International, which produces engines for commercial aircraft. By diversifying its product portfolio, Boeing can adapt to changing market conditions, attract new customers, and maintain its position as an industry leader.
2. Innovation and Technology Leadership
Innovation and technology leadership are essential components of Boeing’s marketing strategy. The company continuously invests in research and development to stay ahead of the competition and meet evolving customer needs. Boeing’s commitment to innovation is evident in its significant investments in cutting-edge technologies, such as artificial intelligence, autonomous systems, and advanced materials. By developing and integrating these technologies into its products and services, Boeing can differentiate itself from competitors, improve customer experience, and maintain its position as a global leader in the aerospace industry.
One notable example of Boeing’s innovative spirit is the development of the 787 Dreamliner. This revolutionary aircraft features lightweight composite materials, advanced flight controls, and a host of other cutting-edge technologies that provide unparalleled fuel efficiency, comfort, and safety. The 787 Dreamliner has been a game-changer in the aviation industry, setting new standards for passenger travel and establishing Boeing as a leader in next-generation aircraft design. Another example is Boeing’s development of autonomous systems, such as the Phantom Express spacecraft and the NeXt generation air traffic management system. These innovations not only demonstrate Boeing’s technical prowess but also highlight its commitment to addressing pressing challenges in areas like space exploration and sustainable transportation.
Boeing’s focus on innovation and technology leadership extends beyond its products. The company has established a robust ecosystem of research partnerships, startup accelerators, and internal research centers to foster collaboration and drive advancements in fields relevant to its business. Boeing’s Research & Development organization works closely with universities, government agencies, and private sector partners to explore emerging technologies and their potential applications. Through these efforts, Boeing gains early access to disruptive ideas and can integrate them into its products and services before they become mainstream. This approach enables Boeing to maintain its edge over competitors while providing customers with the most advanced and efficient solutions available.
3. Global Reach and Presence
Global reach and presence are critical components of Boeing’s marketing strategy. As a multinational corporation with a diverse portfolio of products and services, Boeing operates in more than 150 countries around the world. This widespread presence allows the company to tap into various markets, better understand local customer needs, and tailor its offerings to meet unique regional requirements. By having a strong global footprint, Boeing can effectively serve its customers, respond quickly to changing market dynamics, and capitalize on growth opportunities in emerging regions.
One way Boeing achieves its global reach and presence is through strategic partnerships and collaborations. The company has formed numerous alliances with local businesses, governments, and organizations to strengthen its position in international markets. For instance, Boeing has partnered with India’s Tata Advanced Systems Limited to produce Apache helicopter fuselages and with Brazil’s Embraer to develop a new line of commercial jets. These partnerships not only help Boeing access new markets but also enable it to leverage local expertise and resources to enhance its offerings. Moreover, Boeing has established a vast network of supply chain partners and distributors worldwide, ensuring timely delivery of parts and services to its global customer base.
Another means by which Boeing maintains its global presence is through its extensive sales and marketing efforts. The company has dedicated teams focused on specific regions and markets, allowing it to tailor its messaging and outreach to local cultures and languages. Boeing regularly participates in major trade shows and exhibitions worldwide, showcasing its latest products and technologies to potential customers and reinforcing its brand visibility.
Furthermore, the company invests heavily in digital marketing initiatives, enabling it to connect with customers and stakeholders across the globe. From social media campaigns to targeted advertising, Boeing leverages modern communication channels to promote its brand, products, and services to a worldwide audience.
4. Brand Reputation
As one of the largest and most recognizable companies in the aerospace industry, Boeing understands the importance of building and maintaining a positive brand image. A strong brand reputation helps Boeing to establish trust with customers, attract top talent, and weather challenges during times of crisis. By focusing on ethical practices, quality products, and excellent customer service, Boeing has developed a reputation as a reliable and innovative provider of aerospace solutions.
One way Boeing builds and maintains its brand reputation is through effective communication and transparency. During times of crisis, such as the 737 Max crashes, Boeing has faced intense scrutiny and criticism. However, the company has taken steps to address concerns and reassure stakeholders by being open and honest about its actions and intentions. For example, Boeing has provided regular updates on its progress towards returning the 737 Max to service, including details on software updates and pilot training programs. Additionally, the company has made significant investments in safety and quality control measures to ensure that its products meet the highest standards.
Another way Boeing promotes its brand reputation is through corporate social responsibility (CSR) initiatives. The company believes that CSR is an integral part of its business model and has implemented various programs aimed at supporting education, environmental conservation, and community development. For instance, Boeing’s “Dream Learn Soar” program provides educational resources and scholarships to students interested in STEM fields. Similarly, the company’s “Global Engagement” initiative supports environmental projects and disaster relief efforts around the world. By demonstrating a commitment to responsible business practices, Boeing enhances its brand reputation and solidifies its position as a respected industry leader.
5. Customization and Flexibility
As a leading aerospace company, Boeing understands that each customer has unique needs and preferences. Therefore, the company offers customized solutions tailored to meet the specific requirements of its clients. By providing flexible and adaptable products, Boeing sets itself apart from competitors and creates long-term relationships with its customers.
One way Boeing offers customization and flexibility is through its diverse product portfolio. The company produces a range of aircraft models, each designed to cater to different customer needs. For instance, Boeing’s 787 Dreamliner is a state-of-the-art passenger jet offering unparalleled fuel efficiency and comfort. On the other hand, its 747-8 Intercontinental is a luxury airliner designed for long-haul flights and features a spacious interior and cutting-edge technology. By providing a variety of options, Boeing allows customers to choose the best fit for their operations, thereby increasing customer satisfaction and loyalty.
Boeing also demonstrates flexibility in its willingness to modify existing products or design new ones to meet customer demands. In 2019, the company announced plans to launch a new midsize airplane, the NMA (New Midsize Airplane), in response to growing demand for a more efficient and capable aircraft in the middle-market segment. This move illustrates Boeing’s commitment to listening to customer feedback and adapting its offerings accordingly. Additionally, the company’s dedication to research and development ensures that it remains at the forefront of aviation technology, enabling it to deliver cutting-edge solutions that meet evolving customer needs. Overall, Boeing’s focus on customization and flexibility strengthens its market position and fosters enduring relationships within the aerospace industry.
6. Strategic Alliances and Partnerships
By teaming up with other companies, organizations, and government agencies, Boeing can expand its reach, improve its offerings, and enhance its reputation. These collaborations allow Boeing to access new markets, technologies, and customers, while also sharing risks and costs. For instance, Boeing has partnered with NASA to develop the Space Launch System (SLS), a heavy-lift rocket designed to take humans deeper into space. This partnership not only helps Boeing gain access to NASA’s expertise and resources but also allows the company to showcase its capabilities in space exploration.
Another significant partnership for Boeing is its joint venture with Lockheed Martin, called United Launch Alliance (ULA). ULA produces the Atlas V and Delta IV rockets, which are used to launch military, civil, and commercial payloads into space. By partnering with Lockheed Martin, Boeing can offer a broader range of launch services to its customers, while also benefiting from the shared resources and expertise of both companies. Moreover, Boeing has also partnered with several suppliers and subcontractors to improve its supply chain efficiency, reduce costs, and enhance the quality of its products. For example, Boeing has partnered with Spirit AeroSystems to produce fuselage sections for its 737 and 787 aircraft.
Overall, strategic alliances and partnerships play a vital role in Boeing’s marketing strategy by enabling the company to expand its offerings, improve its capabilities, and build strong relationships with customers and partners. By collaborating with other companies and organizations, Boeing can achieve mutually beneficial goals, share risks and costs, and stay ahead of the competition in the aerospace industry.
7. After-Sales Support
After-Sales Support is a critical component of Boeing’s marketing strategy, aimed at building long-term relationships with customers and enhancing their overall experience with the company’s products. Boeing understands that its customers require comprehensive support throughout the lifecycle of their aircraft, and therefore offers a range of after-sales services that cater to their diverse needs. From maintenance and repair to technical support and training, Boeing’s after-sales support services are designed to ensure that its customers receive the highest level of service and support, thereby building trust and loyalty.
One of the primary objectives of Boeing’s after-sales support strategy is to provide timely and effective solutions to its customers’ issues. The company operates a vast network of service centers, spare parts depots, and field service representatives across the globe, allowing it to respond quickly to customers’ requests. For instance, if an airline experiences a technical issue with one of its Boeing aircraft, the company can dispatch a team of experts to assist with repairs or provide replacement parts promptly. By offering such responsive support, Boeing not only minimizes downtime for its customers but also demonstrates its commitment to their satisfaction.
8. Government Relations
Boeing’s business is heavily regulated, and government policies can significantly impact its operations, procurement processes, and ability to secure contracts. Effective government relations help Boeing navigate complex regulatory environments, shape policy outcomes favorable to its interests, and foster collaboration with government entities to advance its business objectives.
To execute this strategy effectively, Boeing engages in various activities, including lobbying, public affairs, and thought leadership initiatives. The company maintains a robust presence in Washington, D.C., and works closely with lawmakers, congressional staff, and executive branch officials to advocate for policies that support its business priorities. For instance, Boeing has been actively involved in shaping U.S. trade policy, particularly with regard to international agreements like the Trans-Pacific Partnership and the Export-Import Bank charter renewal. The company also invests in research and development projects aligned with government priorities, such as sustainability and advanced manufacturing, to demonstrate its commitment to national interests.
In addition, Boeing collaborates with foreign governments to promote its products and services, facilitate market entry, and cultivate local industrial partnerships. For example, the company has worked closely with the Japanese government to secure defense contracts, develop next-generation aircraft programs, and establish a robust supply chain network within Japan. Similarly, Boeing has partnered with Indian authorities to develop a domestic aerospace ecosystem, investing in local talent development and infrastructure projects to support India’s aspirations for self-reliance in defense production. Through these efforts, Boeing not only advances its own interests but also contributes to the economic growth and security of the countries where it operates. By integrating government relations into its marketing strategy, Boeing ensures that its voice is heard in the policymaking process and that its actions align with the needs of the communities it serves.
In summary, Boeing’s marketing strategies revolve around diversification, customer-centricity, innovation, and global reach. By continuously adapting to market dynamics and customer needs, Boeing has managed to maintain its leadership position in the aerospace industry. Additionally, a focus on sustainability and strategic partnerships ensures that Boeing remains competitive and relevant in an ever-changing world.
Marketing Mix of Boeing
Boeing employs an intricate marketing mix strategy, also known as the 4Ps (Product, Price, Place, and Promotion). Here’s a detailed explanation of Boeing’s marketing mix:
Product
-
- Aircraft Portfolio: Boeing’s core product line consists of commercial airplanes. They offer a diverse array of aircraft, including the popular 737, 747, 767, 777, and 787 families. These aircraft serve various market segments, from regional flights to long-haul international travel.
- Defense and Space Systems: Boeing designs, manufactures, and sells military aircraft, satellites, and space exploration systems. This segment caters to the defense and space exploration markets.
- Services: Boeing provides a comprehensive suite of services to support its products throughout their lifecycle. These services include maintenance, repair, training, and spare parts support.
Price
-
- Custom Pricing: Boeing employs a tailored pricing strategy for its commercial airplanes. The price of each aircraft is determined based on various factors, such as the specific type of aircraft, configuration, and customer negotiations. Airlines work closely with Boeing to establish pricing and finalize purchase agreements.
- Government Contracts: In the defense and space sector, Boeing often competes for government contracts, where pricing is determined through competitive bidding processes.
- After-Sales Services: Boeing charges airlines and defense customers for maintenance and support services. The pricing structure for these services is influenced by factors like the level of support required and the duration of service agreements.
Place
-
- Global Manufacturing and Supply Chain: Boeing operates a vast global network of manufacturing facilities, supply chain partners, and service centers. Key manufacturing sites are situated in the United States, while assembly and service centers are strategically located worldwide to cater to international markets.
- Distribution Channels: Boeing primarily sells its commercial airplanes directly to airlines. However, in some instances, leasing companies may act as intermediaries. In the defense and space sector, sales often involve government procurement agencies and intermediaries.
- Online Presence: Boeing maintains a robust online presence through its official website. This online platform serves as a critical hub for customers and stakeholders, providing easy access to product information, news, and support resources.
Promotion
-
- Advertising: Boeing conducts advertising campaigns to promote its products and services. These campaigns often highlight the advanced features, performance, and reliability of Boeing aircraft. They target both airline customers and the broader aerospace industry.
- Public Relations: Boeing actively manages its public image and reputation through media relations and press releases. The company communicates its accomplishments, innovations, and contributions to the aerospace industry.
- Trade Shows and Events: Boeing participates in major aerospace and aviation trade shows and events worldwide. These platforms enable Boeing to showcase its products, innovations, and capabilities to a global audience and establish industry connections.
- Corporate Responsibility: Boeing emphasizes its commitment to sustainability and corporate responsibility in its promotional efforts. Initiatives related to environmental sustainability and community engagement are highlighted to demonstrate Boeing’s dedication to responsible business practices.
In summary, Boeing’s marketing mix is a multifaceted strategy tailored to the complex aerospace industry. Boeing’s ability to offer a wide range of products and services, adapt to customer needs, and maintain a global presence through its manufacturing and distribution networks contributes to its continued success. Moreover, its focus on building and promoting its brand reputation and its dedication to sustainability further enhance its marketing mix.
Also Read: Navigating the Aerospace: Exploring Boeing’s Top Competitors
To read more content like this, subscribe to our newsletter
Go to the full page to view and submit the form.

