Persuasion marketing is a type of marketing technique that uses human psychology to manipulate how we feel about stuff. This strategy works when firms accurately apprehend how humans thinking is more likely to work. To persuade an audience we need to evoke an emotional response from them.
A persuasion is an approach to design websites and web services that helps in achieving the commercial objectives of the site. It is based on the recognition of user motivations and psychology and then developing the website accordingly to influence users. It applies explicitly to the promotion aspect of the marketing mix and builds on a customer’s impulsive behavior to lead them to purchase.
Example: When a company that prices something at $9.99 is using persuasion marketing. The perception is that a product at this price costs under $10, so we are more likely to buy it on impulse. It is only a penny less.

What are the elements of the Persuasion technique?
Aristotle broke down the essential elements of persuasion into three components: (1) logos or logic, (2) ethos or ethic, and (3) pathos or emotion. All three components (logos, ethos, and pathos) must be woven together if you want to move people and persuade them to your viewpoint.
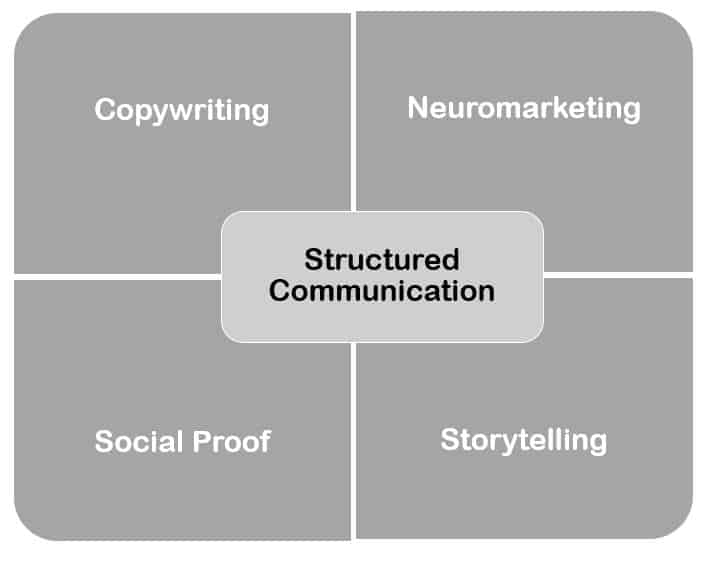
Elements of Persuasion technique
- Structured communication — control the order of a conversation, or how information appears to the consumer
- Storytelling and copywriting
- Testing, measuring, and optimization
- Neuromarketing — market to the 90 percent of the decision-making process not consciously controlled
Types of Customers for persuasion marketing
Several factors contribute to persuading arguments to customer’s sensitivity. To increase the chances of converting a customer; the marketer needs to look for a persuasion window. Some elements of persuasion window are:
- When in a good mood
- When the world does not make sense
- When indebted to a favor
- Can (or must) take immediate action
- Right after a mistake
- Right after being denied a request
Powerful principles for influencing customers
Reciprocity: Give the client something that makes him feel blessed and lucky. If a waiter gives you a sweet together with a bill, you will probably tip him. The tip will become significant if the waiter says, ‘And this is for you because you were such an amazing client’.
Authority: For consumers authority matters. If a person called Jack tries to sell you a residence, you will be less inclined, but if jack introduced to you as a real estate professional with 30 years of experience.
Social proof: Consumers tend to follow what other people do. They follow other people, so it’s better to give them examples.
Commitment: Make people feel they are part of your community by involving them in selling.
Liking: Consumers tend to buy more from people who like who complement and appreciate us.
Scarcity: Consumers love to purchase things other people cannot buy. We tend to rush for things that are scarcely available. Make your product look and feel they are and scarce.
Some persuasive techniques in Advertising
- The Carrot and The Stick
- The Scarcity Principle
- One Message Per Advertisement
- Write in the Second Person
- Give Your Audience a Sense of Control
The Carrot and the sick
Humans are hardwired to move towards pleasure, like a horse towards a carrot, and away from pain, like a donkey avoids a stick. When people read or watch your advertisements, “carrots”, or promises of gain, can fill your prospects with hope and compel them to pursue that potential feeling of pleasure. “Sticks”, possibilities of loss, evoke fear in your prospects, which will compel them to flee from that potential feeling of pain.
The Scarcity Principle
People value experience and objects that are rarely available that is having a product that most people crave but cannot have, boosts their sense of power. “Exclusive offer” or “Limited availability”, evoke a sense of urgency, you can skyrocket your product’s perceived scarcity and consumer demand.
One Message Per Advertisement
To immediately catch attention of people and convince them to read or watch the rest of your commercial, try sticking to only one message. It will be crisp and short, and consumers will be curious to know more.
Write in the Second Person
Pronouns like “you” and “your” can connect customers on a personal level and help them insert themselves in the narrative you are creating and help them envision a future with your product or service improving their lives.
Give Your Audience a Sense of Control
The want for control is a psychological necessity for humans. People like to feel that they have freedom and control over their lives. Don’t force them to buy your product, they will get annoyed and disengage from your message.
Use phrases like “Feel free” or “No pressure” in your advertisements, To give your audience the ability to choose, and in turn, a sense of control.
Persuasive Advertising examples
Nikol
Nikol’s paper towels cannot turn grapes into raisins, but this ad highlights the product’s absorbent powers in such a clear and clever way, they didn’t need to write a single line of copy.

Bic
Bic takes advantage of an unkempt field to highlight the power of their razors. By just mowing a small strip of grass on a field, this ad is an unconventional, simple, and extremely creative way to catch people’s attention and spotlight a razor’s shaving capabilities.

Trident
Every once in a while, you run across an ad that you just can’t forget. Trident’s Facebook ad that appeals to emotions or pathos through some quirky logic as I am sure deodorant won’t taste like spearmint either. Example of emotional and logical appeal in persuasive copy for Trident’s online ads.

If you enjoyed reading this concept, you may also like Guerilla Marketing or Moment Marketing




