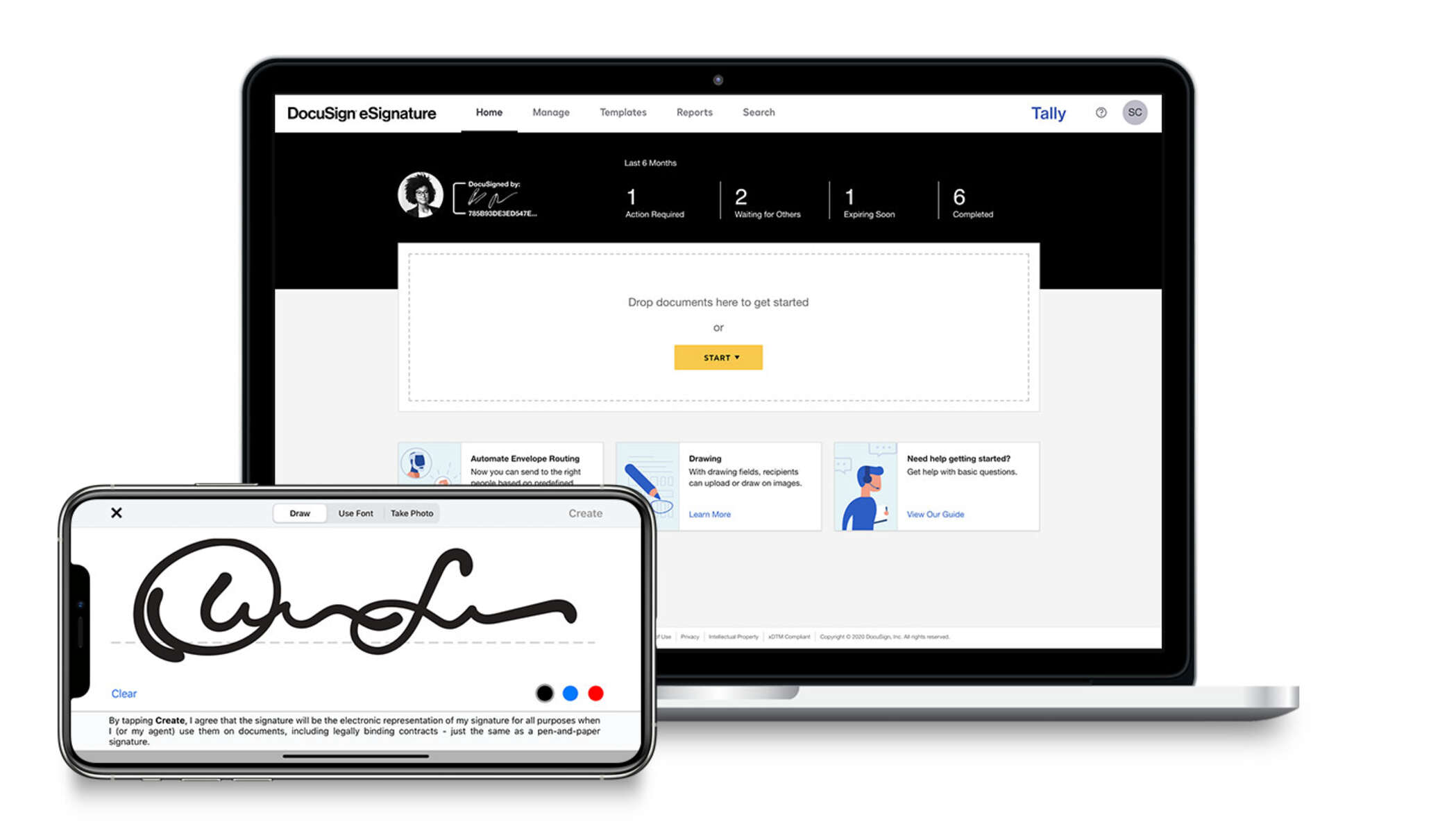
DocuSign is a digital signature and document management platform that was founded in 2003 by Tom Gonser in Seattle, United States. The platform enables users to sign, send, and manage digital documents securely and efficiently. DocuSign has become a popular tool for businesses of all sizes, as well as for individuals who need to sign documents electronically.
Here are some key facts about DocuSign:
- Digital signature technology: DocuSign’s digital signature technology is designed to be legally binding and compliant with e-signature laws around the world. The platform offers a range of signature options, including typed signatures, drawing signatures with a mouse or touchscreen, and uploading a scanned signature image.
- Document management: DocuSign’s platform enables users to upload and manage documents securely. The platform offers a range of document management features, including document storage, version control, and access control.
- Integrations: DocuSign can integrate with a wide range of third-party applications, including popular productivity tools like Microsoft Office, Salesforce, and Google Docs. The platform also offers an API that developers can use to integrate DocuSign’s functionality into their own applications.
- Industry adoption: DocuSign has become a popular tool for businesses in a wide range of industries, including real estate, finance, and healthcare. The platform is used by businesses of all sizes, from small startups to large multinational corporations.
- Growth and funding: DocuSign has experienced significant growth over the years, with the platform now used by millions of people around the world. The company went public in 2018 and has raised over $500 million in funding to support its expansion plans.
Overall, DocuSign has become a popular tool for anyone who needs to sign, send, or manage digital documents. Its digital signature technology is widely regarded as secure and legally binding, and its document management features make it a useful tool for businesses of all sizes.
History of DocuSign
DocuSign was founded in 2003 by Tom Gonser, a tech entrepreneur based in Seattle, Washington. The idea for the company came from Gonser’s personal experience with the challenges of signing and managing paper-based documents.

In the late 1990s, Gonser was working for a startup that was trying to develop an online mortgage application system. One of the biggest challenges the company faced was the process of collecting signatures on the various forms and documents required for a mortgage application. Gonser realized that there was a need for a better solution for signing and managing documents, and he began working on the concept for DocuSign.
Gonser’s initial idea was to create a simple and secure way for people to sign documents electronically. He assembled a team of developers and began working on a prototype of the DocuSign platform. The first version of DocuSign was launched in 2003, and it quickly gained traction among early adopters in the real estate industry.
Over the years, DocuSign has continued to evolve and expand its offerings. The platform now includes a range of document management features, as well as integrations with a wide range of third-party applications. DocuSign has also expanded globally, with offices in cities around the world and users in more than 180 countries.
Despite its growth, DocuSign has remained true to its roots as a company founded on the idea of making it easier for people to sign and manage documents. Today, the company is a leading provider of e-signature and digital document management solutions, with millions of users worldwide.
Business Model of DocuSign
DocuSign operates on a subscription-based business model. The company charges customers a monthly or annual fee to access its digital signature and document management platform. The company offers different pricing plans depending on the number of users and features required.
DocuSign’s platform is designed to be scalable and flexible, making it suitable for businesses of all sizes. Small businesses can opt for basic plans that offer a limited number of signatures and documents per month, while larger enterprises can choose plans with more advanced features and higher usage limits.
In addition to its core subscription-based business model, DocuSign generates revenue from a range of other sources. These include:
Professional services: DocuSign offers a range of professional services, including implementation, training, and support services. These services are designed to help businesses get the most out of the platform and can be a significant source of revenue for the company.
Integrations: DocuSign’s platform integrates with a wide range of third-party applications, including popular productivity tools like Microsoft Office, Salesforce, and Google Docs. The company generates revenue from partnerships and integrations with these applications.
API usage: DocuSign offers an API that developers can use to integrate DocuSign’s functionality into their own applications. The company charges fees for usage of the API.
Transaction fees: DocuSign charges transaction fees for certain types of transactions, such as sending documents for signature.
Overall, DocuSign’s business model is designed to generate recurring revenue from a wide range of customers, including individuals, small businesses, and large enterprises. The company’s scalable and flexible platform, combined with its professional services and integrations, make it a valuable tool for businesses of all sizes.
Also Read: Databricks Success Story- A Data Storage Giant Born Out Of UC Berkeley
Marketing Strategies of DocuSign
DocuSign has a variety of marketing strategies that it uses to attract and retain customers. Here are some examples:
Content marketing: DocuSign publishes a variety of content, such as blog posts, ebooks, and whitepapers, to educate potential customers about the benefits of digital signatures and document management. The company also hosts webinars and events to provide additional educational resources for customers.
Search engine optimization (SEO): DocuSign invests in SEO to ensure that its website ranks well in search engine results pages. The company focuses on keywords related to digital signatures and document management to attract potential customers.
Pay-per-click (PPC) advertising: DocuSign uses PPC advertising to target potential customers who are searching for digital signature and document management solutions. The company uses platforms like Google AdWords to target specific keywords and demographics.
Social media: DocuSign has an active presence on social media platforms like LinkedIn, Twitter, and Facebook. The company shares content and engages with customers and potential customers to build brand awareness and drive traffic to its website.
Account-based marketing (ABM): DocuSign uses ABM to target specific companies and decision-makers with personalized marketing campaigns. The company uses a variety of channels, such as email, social media, and direct mail, to reach these high-value prospects.
Customer advocacy: DocuSign encourages its satisfied customers to share their success stories and recommend the platform to others. The company showcases customer stories on its website and social media channels, and also hosts events and webinars featuring customer speakers.
Overall, DocuSign’s marketing strategies are focused on educating potential customers about the benefits of digital signatures and document management, targeting specific demographics and companies, and building relationships with customers and advocates.
Funding and IPO of DocuSign
Since its founding in 2003, DocuSign has raised over $1.3 billion in funding from a variety of investors. Here are some of the notable funding rounds and investors:
Series F: In 2015, DocuSign raised $233 million in a Series F funding round led by Brookside Capital and Bain Capital Ventures. Other participants in the round included Sigma Partners, Generation Investment Management, and Iconiq Capital.
Series G: In 2018, DocuSign raised $629 million in a Series G funding round led by the Ontario Teachers’ Pension Plan Board and Generation Investment Management. Other participants in the round included ClearBridge Investments, The Baupost Group, and Fidelity Investments.
Initial public offering (IPO): In 2018, DocuSign went public on the NASDAQ stock exchange, raising $629 million in an initial public offering. The company’s shares were priced at $29 each, and the IPO valued the company at $6 billion.
Secondary offering: In 2019, DocuSign raised an additional $461 million in a secondary offering of its shares. The offering was led by Morgan Stanley and J.P. Morgan.
Debt financing: In 2020, DocuSign secured $500 million in debt financing from a group of investors led by BlackRock. The financing was structured as a convertible senior notes offering.
Some of the notable investors in DocuSign include venture capital firms like Sigma Partners and Bain Capital Ventures, as well as institutional investors like BlackRock, Fidelity Investments, and the Ontario Teachers’ Pension Plan Board. The company’s successful IPO and subsequent secondary offering have helped to cement its position as a leading player in the digital signature and document management space.
Growth and Revenue of DocuSign
DocuSign has experienced significant growth and revenue in recent years, driven by the increasing demand for digital signature and document management solutions. Here are some key highlights:
Revenue growth: DocuSign’s revenue has been growing consistently over the past several years. In the fiscal year 2021, the company reported total revenue of $1.5 billion, up 49% from the previous year. The company has also achieved positive cash flow from operations for each of the past three years.
Customer growth: DocuSign has a large and growing customer base, with over 822,000 customers as of the end of the fiscal year 2021. The company has seen strong growth in its enterprise and commercial customer segments, with these segments accounting for 88% of the company’s revenue in the most recent quarter.
International expansion: DocuSign has been expanding its presence in international markets, particularly in Europe and Asia. The company’s international revenue grew 62% year-over-year in the fiscal year 2021, driven by strong growth in the United Kingdom, Germany, and Australia.
Product innovation: DocuSign has been investing heavily in product innovation, developing new features and integrations to expand its capabilities and appeal to a wider range of customers. For example, the company has launched integrations with popular business applications like Salesforce, Microsoft Teams, and Google Drive.
Strategic acquisitions: DocuSign has made several strategic acquisitions in recent years to expand its capabilities and reach. For example, in 2020, the company acquired Seal Software, a provider of contract analytics and artificial intelligence (AI) technology.
Overall, DocuSign’s growth and revenue have been impressive, driven by its strong customer base, international expansion, product innovation, and strategic acquisitions. As the demand for digital signature and document management solutions continues to grow, DocuSign is well-positioned to maintain its leadership position in the market.
Future of DocuSign
The future of DocuSign looks promising as the company continues to innovate and expand its offerings in the digital signature and document management space. Here are some potential areas of growth and development for DocuSign in the coming years:
Expansion into new markets: DocuSign has already made significant progress in expanding its presence in international markets, but there is still room for growth in regions like Asia and Latin America. The company may also consider entering new verticals, such as healthcare, to expand its customer base.
Development of new products and features: DocuSign has been investing heavily in product innovation, and is likely to continue to develop new features and integrations to expand its capabilities and appeal to a wider range of customers. For example, the company may focus on developing new AI-powered tools to streamline document management and contract analysis.
Acquisition of complementary businesses: DocuSign has already made several strategic acquisitions to expand its capabilities, and may continue to pursue acquisitions of complementary businesses to further strengthen its position in the market.
Expansion of eNotary services: DocuSign has already introduced eNotary services in some states in the US, and may continue to expand this offering to other regions. This could help the company to capture a larger share of the real estate and mortgage industries.
Adoption of blockchain technology: DocuSign has already begun exploring the use of blockchain technology to enhance the security and authenticity of its digital signatures. In the future, the company may further develop blockchain-based solutions for document management and contract execution.
Overall, the future of DocuSign looks bright, with many opportunities for growth and innovation in the digital signature and document management space. As the demand for secure, efficient, and convenient digital solutions continues to grow, DocuSign is well-positioned to continue to be a leader in the market.
To read more content like this, subscribe to our newsletter