Intel Corporation is an American multinational corporation and technology company headquartered in Santa Clara, California. It is the world’s largest semiconductor chip maker by revenue, and it has been a major player in the computer industry for over 50 years.
Intel was founded in 1968 by Gordon Moore and Robert Noyce, two engineers who had worked at Fairchild Semiconductor. The company’s name is a combination of the words “integrated” and “electronics”.
Intel has been a major player in the semiconductor industry for over 50 years, and it has a long history of innovation. The company has developed many groundbreaking products, including the 4004 microprocessor and the Core i7 processor. Intel’s first product was the 4004, the world’s first commercial microprocessor. The 4004 was a major breakthrough, and it helped to usher in the era of the personal computer.

Intel has continued to innovate in the semiconductor industry, and it has developed a wide range of products, including microprocessors, chipsets, and memory chips. The company’s products are used in a wide variety of devices, including computers, smartphones, and servers.
Intel is a major player in the global economy, and it has a significant impact on the technology industry. The company employs over 100,000 people worldwide, and it has a market capitalization of over $140 billion. Intel has a global reach, with operations in over 100 countries. The company’s products are used in a wide variety of devices, from personal computers to smartphones to servers.
Intel is committed to research and development, and it invests heavily in new technologies. The company has a number of research and development facilities around the world.
Founding History of Intel
The founding history of Intel Corporation is a tale of innovation, entrepreneurship, and technological advancements that played a crucial role in shaping the modern computing industry. The company was founded by two visionary individuals, Robert Noyce and Gordon Moore, and their journey laid the foundation for Intel’s eventual dominance in the semiconductor industry.
In the 1950s and 1960s, the field of electronics was rapidly evolving, and the demand for smaller, faster, and more reliable electronic components was growing. Semiconductors, which could function as switches and amplifiers, were emerging as a promising technology. Robert Noyce and Gordon Moore were two talented engineers who were deeply involved in this field.
In 1968, Noyce and Moore, along with fellow engineer Andy Grove, decided to leave their positions at Fairchild Semiconductor, a pioneering semiconductor company, to start their own venture. They founded Intel Corporation on July 18, 1968, with the initial goal of producing semiconductor memory products.

Intel’s first major breakthrough came with the invention of the microprocessor. In 1971, Intel introduced the Intel 4004, the world’s first commercially available microprocessor. Developed by Marcian “Ted” Hoff, the 4004 was a revolutionary integrated circuit that combined the functions of a central processing unit (CPU) on a single chip. This innovation marked the beginning of the digital era, as microprocessors became the building blocks of modern computers and electronic devices.
Gordon Moore’s famous observation, known as Moore’s Law, was a prediction he made in 1965 that the number of transistors on a semiconductor chip would double approximately every two years. This prediction became a self-fulfilling prophecy, guiding Intel’s research and development efforts. The relentless pursuit of smaller transistor sizes and increased chip performance led to significant advancements in semiconductor manufacturing technology.
Throughout its history, Intel faced fierce competition, technological challenges, and economic fluctuations. However, the company’s commitment to innovation and its ability to deliver cutting-edge products allowed it to stay at the forefront of the industry. Intel’s processors became the industry standard for personal computers, and its “Intel Inside” marketing campaign helped establish the brand’s recognition among consumers.
In addition to microprocessors, Intel diversified its product portfolio over the years. It developed a wide range of semiconductor products, including memory chips, graphics chips, networking hardware, and more. The company’s processors powered not only personal computers but also servers, workstations, and eventually mobile devices.
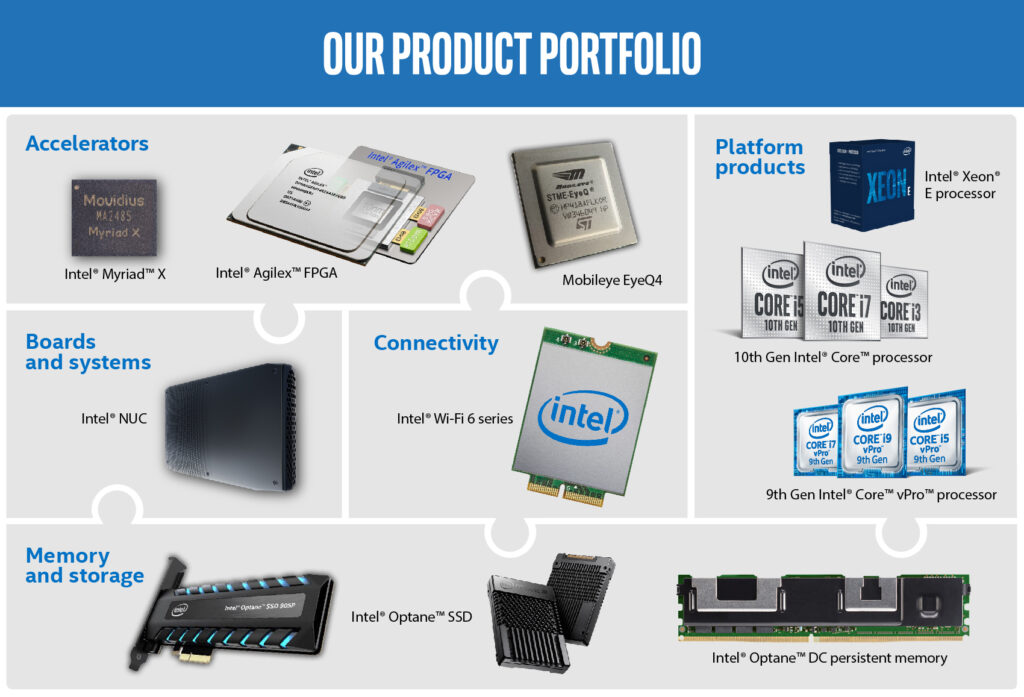
Intel’s innovations had a profound impact on the development of computing technology. Its microprocessors enabled the creation of faster and more capable computers, leading to advancements in fields such as scientific research, business operations, entertainment, and communication.
The founding principles of innovation, entrepreneurship, and technological leadership continue to shape Intel’s legacy. The company’s contributions to the semiconductor industry and the broader technology landscape have left an indelible mark.
In recent years, Intel has faced challenges from competitors and shifts in technology trends. This includes the rise of mobile computing and the increasing importance of energy efficiency. While the company’s dominance in certain areas has been challenged, its legacy and ongoing innovations continue to play a significant role in the evolution of computing and technology.
Marketing Strategy of Intel
Intel has employed various marketing strategies over the years to establish its brand, promote its products, and maintain its position in the competitive technology market. The company’s marketing strategy encompasses a combination of product innovation, brand building, customer engagement, and industry partnerships.
1. Branding and Positioning:
Intel’s “Intel Inside” branding strategy is one of the most iconic and successful campaigns in the technology industry. Launched in 1991, this strategy involved co-branding with computer manufacturers to highlight the presence of Intel processors inside their devices. This approach helped consumers recognize the importance of Intel’s technology and associate it with quality and performance.
2. Product Innovation:
Intel’s marketing strategy revolves around showcasing its commitment to innovation. The company regularly introduces new generations of processors and other semiconductor products, emphasizing improved performance, energy efficiency, and capabilities.
Intel excels at creating groundbreaking products that push the boundaries of what’s possible in computing technology. Their product innovation strategy involves continuous investments in R&D, partnerships with industry leaders, and a keen eye towards emerging trends and opportunities. Here are some specific ways Intel pursues product innovation:
Research & Development (R&D): Intel allocates significant resources toward advancing microprocessor design and fabrication processes. They employ thousands of engineers and scientists focused solely on improving existing architectures and inventing entirely new ones. This dedication enables Intel to introduce trailblazing features like hyperthreading, multi-core support, and adaptive clock speeds.
Manufacturing Capabilities: Developing state-of-the-art chips requires equally impressive production facilities. Intel operates some of the most sophisticated cleanrooms and fabrication plants worldwide. These sites use cutting-edge equipment and techniques to craft increasingly smaller transistors and higher-density memory cells. Such improvements directly translate into better performing and more compact electronic devices.
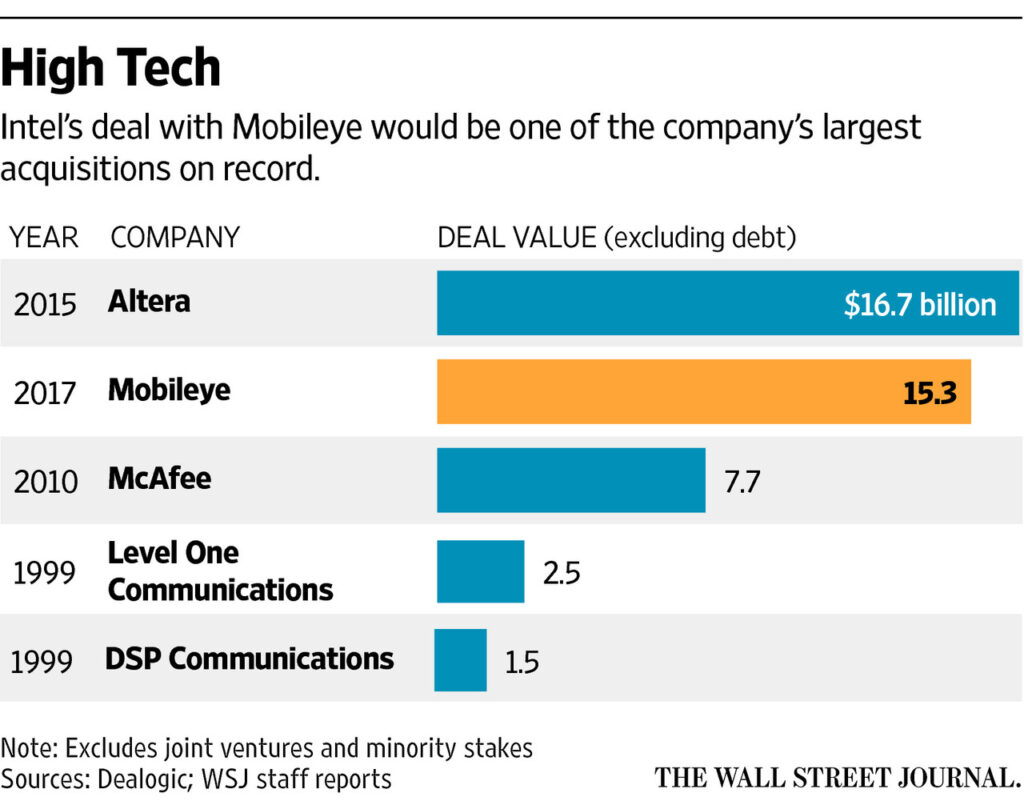
Acquisitions and Joint Ventures: Realizing the importance of expanding expertise beyond pure silicon, Intel actively acquires companies or forms alliances with complementary businesses. Notable acquisitions include Altera (FPGA maker), McAfee (security software), and Wind River Systems (embedded systems). Meanwhile, joint ventures like IM Flash Technologies with Micron Technology ensure continued leadership in flash storage manufacturing.
Emerging Market Opportunities: Identifying untapped potential in burgeoning areas helps Intel diversify its portfolio and maintain growth momentum. For instance, the company entered the Internet of Things (IoT) space early by offering low-power Quark processors suitable for connected devices. Similarly, Intel’s RealSense technology brings depth sensing capabilities to cameras and paves the way for applications like Windows Hello face authentication or RoomAlive immersive gaming experiences. Additionally, Project Athena represents an ambitious initiative aimed at accelerating innovation for high-performance mobile PCs.
3. Content Marketing:
Intel has invested in content marketing to educate and engage its target audience. Intel leverages content marketing to educate audiences, build thought leadership, and foster engagement around their brand. By sharing valuable insights and stories related to technology and innovation, they attract and retain customers while solidifying their status as experts within their industry. Here are some examples of how Intel executes content marketing effectively:
Thought Leadership through Whitepapers and Case Studies: Intel regularly publishes whitepapers discussing topics relevant to their target audience. These papers delve deep into technical subjects like artificial intelligence, cloud computing, cybersecurity, etc., providing readers with comprehensive knowledge and actionable advice. Complementing these whitepapers are case studies detailing successful implementations of Intel solutions in real-world scenarios. Both types of materials help establish Intel as a go-to resource for IT professionals seeking guidance on complex challenges.
Video Content: Creating visually appealing multimedia assets has become essential for captivating modern consumers. Intel capitalizes on this trend by publishing informative videos covering a wide range of tech domains. From “Chip Shots” explaining processor architecture to “Behind the Scenes” footage revealing the making of Extreme Tech Challenge, Intel offers a mix of educational and entertaining clips. By doing so, they cater to varied interests among viewers and encourage repeat visits to their channels.
This approach helps build brand authority and fosters a sense of community around technology enthusiasts.
4. Sponsorships and Partnerships:
Intel recognizes that forming strong relationships with other organizations can amplify their impact and reach new customer segments. They leverage sponsorships and partnerships to associate themselves with reputable brands, support worthwhile causes, and create unique opportunities for collaboration. Below are several instances of Intel’s effective implementation of this strategy:
Sports Industry Collaborations: As a major player in the technology sector, Intel understands the significance of associating itself with popular sports teams and events. Their involvement includes:
- NFL (National Football League): Intel serves as the official provider of football data analytics and supplies the league with wearable technology to enhance performance analysis and broadcast presentations.
- NBA (National Basketball Association): Intel works closely with the NBA to optimize the fan experience through VR streaming, NextVR game replays, and courtside augmented reality features during live games.
- Esports: Intel supports esports competitions globally, including the Intel® Extreme Masters and IEM Expo, featuring top professional gamers battling it out in popular titles like Dota 2, Street Fighter V, and Fortnite.
Cultural Institutions and Nonprofits: Intel values cultural institutions and nonprofit organizations working towards positive societal change. Their partnerships span museums, science centers, environmental groups, and humanitarian foundations. This allows them to promote education, scientific discovery, sustainability, and community development while aligning with their own core values.
Artificial Intelligence and Machine Learning Initiatives: To further advance research and adoption of AI and ML technologies, Intel backs projects focused on developing explainable models, ethical considerations, and interdisciplinary approaches. Supported programs include OpenAI, LAION e.V., and MIT (Massachusetts Institute of Technology) to explore novel computing architectures capable of handling machine learning workloads more efficiently. Additionally, they partner with Google Brain to accelerate deep learning research using specialized chips called Tensor Processing Units (TPUs). These efforts contribute to advancing AI capabilities and democratizing access to powerful tools for developers worldwide.
These partnerships help Intel reach specific target demographics and showcase its technology in real-world applications.
5. Customer Engagement and Support:
Intel prioritizes building meaningful connections with customers to ensure their satisfaction throughout all stages of product ownership. From initial interest to post-purchase assistance, Intel employs multiple tactics to foster long-term loyalty and brand advocacy. Let’s dive deeper into their methods:
Online Communities and Resources: Intel maintains dedicated websites and discussion boards designed specifically for customers seeking technical advice, troubleshooting tips, and peer insights. These resources facilitate self-service options and enable users to help one another, reducing strain on Intel’s support staff and encouraging knowledge sharing within the community.
Personalized Communication Channels: Customers appreciate when companies listen actively and respond appropriately. To achieve this balance, Intel offers tailored communication paths based on individual preferences and needs. Options include email, phone calls, chatbots, and social media messaging.
Educational Content and Training Programs: Intel acknowledges that some customers require guidance beyond basic troubleshooting steps. Therefore, they provide extensive educational materials covering topics ranging from CPU architecture to programming best practices. Additionally, Intel runs training sessions and webinars to equip users with essential skills required for optimizing system performance and achieving desired results.
Proactive Monitoring and Preventative Maintenance: Intel proactively monitors device health and sends notifications regarding potential issues before they become critical problems. This preemptive approach minimizes downtime and reduces the need for reactive repairs. Moreover, Intel shares maintenance recommendations and optimization suggestions to prolong equipment longevity and improve overall user experience.
Seamless Repair and Replacement Services: When necessary, Intel ensures smooth repair or replacement processes by offering hassle-free warranty claims, loaner devices during repairs, and expedited shipping services. By simplifying these procedures, Intel alleviates frustration associated with product failures and demonstrates commitment to keeping customers satisfied.
Positive customer experiences can contribute to word-of-mouth marketing and brand loyalty.
6. Market Segmentation:
Intel recognizes the diversity of its target audiences and customizes its offerings accordingly. The company utilizes several segmentation strategies to cater to distinct customer groups and meet their unique requirements. Below are the primary ways Intel segments its markets:
Geographic Segmentation: Geographic location plays an integral role in determining Intel’s marketing strategy. The company divides its global presence into regions such as North America, Latin America, Europe, Middle East & Africa, Asia Pacific, and Japan. Each region receives tailored advertising campaigns, promotions, and distribution channels optimized for local cultures, languages, and economic conditions.
Demographic Segmentation: Demographics refer to characteristics such as age, gender, income level, occupation, education, family status, etc. Intel leverages this information to create targeted marketing messages and develop products suited to specific audience profiles. For instance, the company designs processors aimed at students, professionals, and gamers differently than those intended for enterprise servers or data center applications.
Psychographic Segmentation: Behavioral traits, interests, attitudes, lifestyles, and values shape consumer behavior and influence purchasing decisions. Intel takes note of psychographic factors like technology affinity, gaming habits, work intensity, and environmental consciousness to craft appealing product features and marketing content. By understanding what motivates different customer groups, Intel can better connect with them emotionally and persuade them to choose its products over competitors’.
Product Attributes Segmentation: Product attributes involve distinguishing physical or functional characteristics that distinguish Intel’s offerings from others available in the marketplace. Intel categorizes its products according to processor type (desktop vs laptop), number of cores/threads, cache size, memory controller, graphics integration, power consumption.
Intel’s marketing strategy goes beyond promoting products; it’s a carefully orchestrated symphony of branding, innovation, engagement, and responsibility. Through its “Intel Inside” campaign, continuous product innovation, strategic partnerships, and digital engagement, Intel has built a brand that is synonymous with technological excellence. By learning from Intel’s multifaceted marketing approach, businesses in the technology sector can draw inspiration for creating their path to success in a dynamic industry.
Marketing Mix of Intel
The 4Ps of marketing, also known as the marketing mix, are a fundamental framework that businesses use to create a comprehensive marketing strategy. They represent four key elements that need to be carefully considered when designing and implementing marketing initiatives. Let’s delve into how Intel, as a technology company, applies the 4Ps of marketing:
Product:
In the case of Intel, the “Product” aspect primarily refers to the semiconductor products it develops, with microprocessors being the most significant. Intel invests heavily in research and development to create cutting-edge processors that offer improved performance, energy efficiency, and innovative features. The company releases a range of processor models tailored for various market segments, such as consumer laptops, desktop computers, servers, and emerging technologies like artificial intelligence and IoT devices. By continually introducing new generations of processors with enhanced capabilities, Intel keeps its product portfolio relevant and aligns with consumer and industry demands.
Price:
Intel employs a value-based pricing strategy. The company’s processors are positioned as premium products, commanding higher prices due to their superior performance and technology. The pricing strategy takes into account factors such as production costs, competition, and perceived value. Intel often offers a range of processor options at different price points, catering to various customer segments. Additionally, Intel’s pricing is influenced by market trends, product innovation cycles, and the perceived value of its technology.
Place (Distribution):
The “Place” element refers to how Intel’s products reach its customers. Intel’s distribution strategy involves multiple channels, including:
- OEMs (Original Equipment Manufacturers): Intel collaborates with computer manufacturers to have its processors integrated into their devices. This aligns with the “Intel Inside” co-branding strategy, making the presence of Intel technology visible to consumers.
- Retailers: Intel products are available through various retailers, both physical and online. Consumers can purchase standalone processors for upgrades or building custom computers.
- Distributors: Intel works with distributors who supply its products to smaller manufacturers, system integrators, and resellers, ensuring a wider distribution reach.
- Online Channels: Intel’s official website serves as an online store where customers can directly purchase products, access information, and receive support.
Intel’s strategic distribution channels ensure that its products are accessible to both consumers and businesses globally.
Promotion:
Promotion encompasses the various marketing activities that Intel undertakes to create awareness, generate interest, and encourage purchase. Intel’s promotion strategies include:
- Advertising: The “Intel Inside” campaign is a prime example of Intel’s advertising efforts. The campaign showcases Intel’s technology as an essential component of computing devices.
- Content Marketing: Intel produces informative content, including articles, videos, and tutorials, to educate customers about its technology and innovations.
- Trade Shows and Events: Intel participates in industry events, conferences, and trade shows to showcase its latest products and share its technological vision.
- Digital and Social Media: Intel maintains an active presence on various social media platforms, engaging with its audience and providing updates about products, technologies, and industry insights.
- Strategic Partnerships: Collaborations with gaming events, eSports tournaments, and other technology-focused platforms help Intel demonstrate its products’ capabilities in real-world scenarios.
Intel’s promotion strategies focus on conveying its brand values, innovation, and technological leadership to a diverse set of stakeholders.
By carefully considering and integrating the 4Ps of marketing, Intel has effectively positioned itself as a leader in the semiconductor industry. Its focus on innovative products, value-based pricing, strategic distribution, and multifaceted promotion has contributed to its brand recognition, market share, and sustained growth.
STP (Segmentation, Targeting and Positioning) of Intel
In the competitive landscape of the technology industry, Intel Corporation has emerged as a trailblazer with its innovative products and strategic marketing. Central to its marketing success is the meticulous implementation of the Segmentation, Targeting, and Positioning (STP) framework. This article delves into the intricacies of Intel’s STP approach, showcasing how the company identifies market segments, selects target audiences, and positions its offerings to resonate with consumers’ needs and preferences.
Segmentation: Understanding the Market Diversity
Segmentation refers to dividing a larger market into smaller subsets of customers with similar wants, needs, or characteristics. This allows companies to tailor their marketing efforts and offerings to better match each group’s preferences and purchase behaviors. Intel applies segmentation principles to identify potential buyers and design appropriate solutions for them.
Here are some examples of how Intel segments its market:
Geographical Segmentation:
Intel differentiates its marketing efforts based on regional differences around the globe. It creates country-specific advertising campaigns, sponsorship opportunities, and distribution networks to accommodate cultural nuances and local regulations. This helps Intel build stronger connections with diverse communities worldwide.
Demographic Segmentation:
Intel targets various age groups, genders, ethnic backgrounds, occupations, educational levels, household sizes, and other demographic categories when developing its marketing plans. By doing so, the company ensures its messaging resonates with people from various walks of life and encourages engagement with its brand.
Psychographic Segmentation:
Intel considers personality traits, interests, hobbies, values, and lifestyle choices when defining its target audience. These dimensions help Intel understand why certain customers might favor particular features or use cases in their computers or devices. By aligning its offerings with these preferences, Intel fosters greater emotional attachment between users and its brand.
Behavioral Segmentation:
Intel examines how customers interact with technology and makes assumptions about their future actions. This analysis guides Intel’s product development, packaging, and promotion strategies to encourage desired user behaviors and maximize brand loyalty.
Usage Segmentation:
Intel categorizes its customers based on how they employ technology in their daily lives. Whether for personal or professional purposes, gaming, content creation, data processing, scientific simulations, cryptography applications, AI model training, distributed ledger management, etc.) can benefit from Intel’s robust and feature-rich CPUs.
Benefit Segmentation:
Intel promotes its products using benefits-oriented language to attract customers seeking specific outcomes from their computer equipment. For instance, business owners may appreciate Intel’s vPro platform for enhanced security, remote manageability, and flexible automation features that streamline operations and reduce downtime risks. Similarly, creators may opt for Intel’s i9 Extreme Edition processors due to their exceptional multithreading capabilities ideal for tasks such as video editing, 3D rendering, complex simulation runs, and other resource-intensive workloads common among professionals operating at the bleeding edge of their respective industries.
Targeting the various customer segments
Targeting involves selecting specific segments of the overall market that Intel believes will generate significant revenue growth or profits. By focusing resources on appealing to these chosen groups, Intel optimizes its marketing efforts and increases the likelihood of converting prospects into satisfied customers. Here’s an overview of Intel’s targeting approach:
Gamers:
Intel targets avid video game enthusiasts who require powerful hardware capable of delivering smooth frame rates during intense action sequences or realistic graphics when streaming games online. To cater to these individuals, Intel develops premium gaming CPUs like the Core i9-10900K and Core i7-1185G1, boasting up to 12 cores/24 threads and improved memory latency for smoother performance.
Content Creators:
Intel addresses digital media professionals producing videos, podcasts, blog posts, etc., who desire reliable platforms supporting multitasking, fast rendering times, and efficient storage handling. Accordingly, Intel crafts robust laptops and desktops equipped with high-end components like the Core i9-11900K and Optane memory modules optimized for content creation tasks.
Data Center Operators:
Intel serves large organizations operating massive server farms hosting critical applications and sensitive information. These clients require scalable solutions guaranteeing consistent uptime, reduced latency, and cost efficiency. Therefore, Intel engineers Xeon Scalable processors with built-in security features, support for higher density DIMMs, and enhanced AI acceleration capabilities ideal for artificial intelligence and machine learning deployments.
Enthusiasts:
Intel appeals to tech aficionados interested in pushing the boundaries of computing technology beyond basic necessity. These individuals seek out innovative advancements like overclocking headroom, novel form factors, and futuristic interfaces. Hence, Intel produces experimental products like the HEDT platform using the new Tiger Lake architecture and Thunderbolt 4 interface expansion slot.
By focusing on these discrete user categories, Intel ensures its marketing messages and product development align closely with each audience’s particular wants and needs.
Positioning of Intel
Positioning refers to the strategic process of creating a distinct and favorable perception of a brand, product, or company in the minds of consumers relative to its competitors. In the case of Intel, positioning has been a critical component of its marketing strategy, helping the company establish itself as a leader in the semiconductor industry. Let’s delve into the positioning strategies that Intel has employed:
Performance Leadership:
One of Intel’s primary positioning strategies is centered around performance leadership. The company has consistently emphasized the superior performance of its processors. This strategy is grounded in the fact that Intel’s processors are often at the forefront of technological advancements, offering higher speeds, increased processing power, and enhanced capabilities. By positioning its products as high-performing and cutting-edge, Intel creates an association with top-tier technology and innovation.
Reliability and Quality:
Intel has successfully positioned itself as a brand associated with reliability and quality. The iconic “Intel Inside” campaign, launched in the early 1990s, played a pivotal role in this positioning. By partnering with computer manufacturers and displaying the “Intel Inside” logo on devices, Intel assured consumers that their devices were powered by a trustworthy and high-quality processor. This strategy established a sense of trust and credibility in Intel’s products, contributing to its reputation for reliability.
Technological Leadership:
Intel has positioned itself as a technological leader in the semiconductor industry. Through continuous innovation, the company has been able to push the boundaries of what is possible in terms of processor performance, energy efficiency, and feature integration. By consistently introducing new technologies and breakthroughs, Intel reinforces its positioning as an industry pioneer, driving the evolution of computing technology.
Diverse Applications:
Intel has positioned its products as versatile and applicable to a wide range of use cases. This approach allows Intel to target different market segments, from consumer electronics to enterprise solutions. By highlighting the diverse applications of its processors, Intel ensures that its technology is relevant to a broad spectrum of industries, from gaming to data centers to artificial intelligence.
Industry Collaboration:
Intel’s collaborations with industry partners, such as software developers and hardware manufacturers, further reinforce its positioning as a technology enabler. By working closely with partners to optimize software and hardware interactions, Intel enhances its products’ performance and value, positioning itself as an essential component of a larger technological ecosystem.
Intel’s strategic implementation of the STP framework demonstrates its deep understanding of market dynamics and consumer behavior. By segmenting the market, carefully selecting target audiences, and positioning itself as an industry leader, Intel ensures that its marketing messages resonate with diverse consumers. This approach has not only fueled Intel’s growth and market leadership but also serves as a blueprint for businesses seeking to establish a strong and impactful market presence in the technology sector.
Also Read: Marketing Strategies and Marketing Mix of Accenture
To read more content like this, subscribe to our newsletter