FedEx Corporation (NYSE: FDX) is one of the world’s largest transportation and logistics companies, providing a broad portfolio of services that includes express package delivery, freight forwarding, and supply chain management. With annual revenue of nearly $90 billion, FedEx operates in more than 220 countries and territories and employs over 520,000 people worldwide.
FedEx was founded in 1971 by Fred Smith, who had the vision of creating a global transportation network that could deliver packages overnight. FedEx quickly became a leader in the express delivery market, and in the years since, the company has expanded its portfolio of services to include a wide range of other transportation and logistics solutions.

The name “FedEx” is a condensed form of the company’s original air division, Federal Express, used from 1973 to 2000. FedEx is widely recognized today for its air delivery service, FedEx Express, renowned for being among the first major shipping companies to introduce overnight delivery as its flagship offering. Over the years, FedEx has expanded its services to include FedEx Ground, FedEx Office (formerly known as Kinko’s), FedEx Supply Chain, FedEx Freight, and more, often in response to its primary competitor, UPS.
With a workforce of approximately 547,000 employees, FedEx stands as the fifth-largest American-headquartered employer globally. Furthermore, it holds a prominent role as one of the primary contractors for the U.S. government and actively contributes to the transportation of certain United States Postal Service packages through their Air Cargo Network contract.
FedEx is committed to providing its customers with the highest quality of service. The company’s global network of facilities and vehicles allows it to deliver packages quickly and reliably, even to the most remote locations. FedEx also offers a wide range of value-added services, such as tracking and tracing, insurance, and customs clearance.
Marketing Strategies of FedEx
FedEx, a global logistics and delivery services company, has developed a comprehensive marketing strategy to maintain its position as a leader in the industry. Here’s a detailed explanation of FedEx’s key marketing strategies:
1. Service Diversification
Service diversification is a marketing strategy used by companies like FedEx to expand their offerings beyond their core products or services. In the case of FedEx, the company has diversified its services significantly over time to become a comprehensive logistics and delivery solution provider. Here are some examples of how FedEx has diversified its services:
Express Services: FedEx started as an express shipping company but has since expanded its services to include international express delivery options, same-day delivery, and even Sunday delivery. These additional services allow FedEx to provide faster and more convenient delivery options for its customers.
Ground Shipments: While FedEx initially focused solely on express shipments, it later introduced ground shipping services to compete directly with UPS (United Parcel Service) and USPS (US Postal Service). This expansion allowed FedEx to capture a larger share of the domestic shipping market.
Freight Forwarding: To further diversify its services, FedEx acquired several freight forwarding companies, which enabled the company to handle large, heavy shipments and provide end-to-end supply chain solutions for its clients.
Logistics Services: FedEx has developed a suite of logistics services, including warehousing, inventory management, customs brokerage, and trade documentation assistance. These services help customers manage complex global supply chains and optimize their operations.
E-commerce Fulfillment: Recognizing the growth potential of e-commerce, FedEx launched fulfillment services to support online sellers and small businesses. These services include order processing, picking and packaging, and last-mile delivery.
Specialized Services: FedEx has also created specialized services for specific industries, such as healthcare, automotive, and aviation. These services are tailored to meet the unique requirements of each industry and provide value-added solutions for customers.
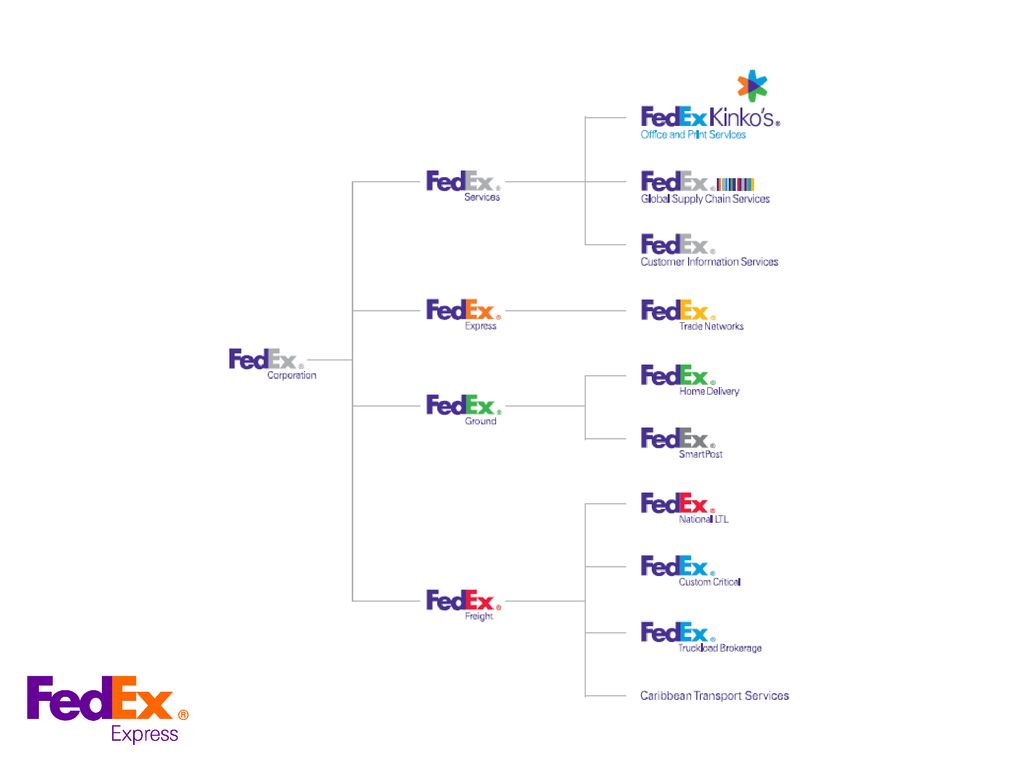
By diversifying its services, FedEx can offer comprehensive logistics solutions to its customers while differentiating itself from competitors. This approach has helped FedEx maintain its leadership position in the shipping and logistics industry and adapt to changing market conditions.
2. Brand Recognition
Brand recognition is a critical aspect of any successful marketing strategy, and FedEx has leveraged brand recognition effectively to build a strong reputation among consumers and businesses alike. Here are some ways FedEx uses brand recognition as a marketing strategy:
Iconic Purple and Orange Color Scheme: One of the most recognizable elements of the FedEx brand is its distinct color scheme of purple and orange. These colors have been consistently used across all touchpoints, creating instant brand recognition for customers.

Simple yet Memorable Tagline: “When it absolutely, positively has to be there overnight” is one of the most famous taglines in advertising history. It perfectly encapsulates the essence of FedEx’s speedy delivery promise and has been etched into public consciousness.
Consistent Visual Identity: From its logo to its website, FedEx maintains a consistent visual identity across all channels. This helps reinforce the brand’s image and makes it easier for customers to recognize the company at a glance.
Advertising Campaigns: FedEx regularly runs high-profile advertising campaigns featuring celebrities like Peyton Manning and Morgan Freeman. These ads showcase the company’s expertise in logistics and emphasize its ability to reliably deliver packages around the globe.
Sponsorships and Partnerships: FedEx sponsors major sporting events like the Super Bowl and the Olympics, as well as cultural institutions like the Smithsonian National Air and Space Museum. These partnerships help raise brand awareness and associate FedEx with excellence and innovation.
3. Technology and Innovation
Technology and innovation play significant roles in FedEx’s overall marketing strategy. By embracing cutting-edge technologies, FedEx seeks to enhance its operational efficiency, improve customer satisfaction, and gain a competitive edge in the shipping and logistics industry. Here are some examples of how FedEx utilizes technology and innovation as a marketing strategy:
Automation and Robotics: FedEx has incorporated advanced robotics and automation systems in its sorting centers and distribution hubs. These technologies enable faster and more accurate handling of packages, reducing manual labor costs and improving delivery times. The use of these technologies positions FedEx as an innovative leader in the industry, attracting tech-savvy customers who appreciate the benefits of modernization.

Mobile Applications: FedEx offers mobile applications that allow customers to track their shipments, request quotes, schedule pickups, and access other useful tools. These apps make it convenient for customers to interact with FedEx and streamline their shipping processes, fostering greater brand loyalty and positive word-of-mouth recommendations.
Big Data Analytics: FedEx collects vast amounts of data from various sources within its operations, including package scanning information, weather patterns, traffic congestion, and customer behavior. Leveraging big data analytics, FedEx optimizes its routes, reduces fuel consumption, and minimizes delays, enhancing its overall performance and reputation. Sharing insights derived from this data can demonstrate FedEx’s commitment to transparency and strengthen trust among stakeholders.
Electric Vehicle Fleet: FedEx has made substantial investments in electric vehicles (EVs), aiming to reduce greenhouse gas emissions and promote sustainability. Its growing fleet of EVs sends a clear message about FedEx’s environmental stewardship, resonating with customers who prioritize corporate responsibility and eco-friendliness when making purchasing decisions.
4. E-commerce Solutions
FedEx utilizes e-commerce solutions as part of its comprehensive marketing strategy to stay ahead in today’s digital landscape. Here are some ways FedEx incorporates e-commerce into its approach:
Integrated Shipping Platforms: FedEx offers seamless integration with popular e-commerce platforms like Amazon, Magento, WooCommerce, and Shopify. This allows merchants to easily manage shipping labels, track packages, and streamline order fulfillment processes within their existing workflows.
International Expansion: FedEx recognizes the growing importance of cross-border trade in e-commerce and has invested heavily in expanding its international capabilities. The company’s suite of customizable shipping options, duty calculations, and tax compliance tools enable small and medium-sized enterprises (SMEs) to tap into foreign markets without incurring excessive overhead costs or navigating complex regulations alone.
Omnichannel Customer Experience: FedEx understands the significance of creating a consistent shopping experience across all channels. To achieve this goal, the company offers features like real-time tracking updates via email/text messages, flexible delivery options (e.g., signature confirmation, drop-off location preferences), and easy returns processing.
5. B2B and B2C Marketing
FedEx employs both Business-to-Business (B2B) and Business-to-Consumer (B2C) marketing strategies to cater to various segments of its target audience. Here are some examples of how FedEx approaches these two distinct marketing methods:
B2B Marketing:
- Targeted Campaigns: FedEx develops personalized campaigns aimed at specific industries or business types, highlighting relevant solutions such as supply chain optimization, international trade support, and technology integrations. These efforts help build stronger relationships with clients and demonstrate a deeper understanding of their unique challenges.
- Thought Leadership Content: FedEx creates informative blog posts, whitepapers, webinars, and infographics addressing topics germane to B2B audiences. For instance, they might discuss trends in industrial manufacturing, best practices for managing inventory, or insights into emerging technologies impacting logistics. Such content helps position FedEx as a valuable source of information and expertise within its core client base.
- Networking Opportunities: FedEx organizes events and sponsorships focused on connecting decision-makers from various industries. Through face-to-face interactions, panel discussions, and networking sessions, FedEx can establish meaningful connections with prospective clients, reinforce existing relationships, and gather feedback on how to improve its service offering.
B2C Marketing:
- User-Friendly Website and App: FedEx maintains a clean, intuitive interface for its online platform, designed to make it simple for individual consumers to navigate and find what they need. The company also provides a mobile application for convenient access to essential features like tracking, estimated delivery times, and account management.
- Emotional Storytelling: FedEx occasionally shares heartwarming stories about how its services bring people together during important life moments, such as birthdays, holidays, or family reunions. These narratives humanize the brand and create an emotional connection between FedEx and its end users.
- Promotions and Discounts: FedEx runs seasonal promotions, limited-time discounts, and referral programs to attract new customers and encourage repeat business. These initiatives may be tailored specifically for residential deliveries or applicable to select services used by SMEs.
- Collaborations and Partnerships: FedEx collaborates with other companies that complement its offerings or share similar values. For example, the company has teamed up with e-commerce platforms, retail giants, and innovative startups to provide enhanced solutions for joint customers. These partnerships not only enhance FedEx’s product portfolio but also broaden its reach and reputation among diverse consumer groups.
6. Institutional Relationships
FedEx leverages institutional relationships as part of its overall marketing strategy to strengthen its presence in different regions and better serve its global customer base. Some ways FedEx utilizes institutional relationships include:
Government Affairs: FedEx engages in government affairs through lobbying, advocacy, and public policy development. By working closely with policymakers and regulatory agencies, FedEx seeks to shape laws and regulations affecting the transportation and logistics sector. This collaboration helps ensure a favorable operating environment for the company and contributes to the growth of the industry as a whole.
Trade Organizations: FedEx is involved in several trade organizations, including the International Air Transport Association (IATA) and the National Retail Federation (NRF). Membership in these associations enables FedEx to stay informed about industry trends, network with peers, and contribute to the advancement of best practices. Additionally, participation in trade shows and conferences organized by these groups provides opportunities for FedEx to showcase its products and services to potential customers.
Nonprofit Partnerships: FedEx supports numerous nonprofits worldwide, focusing on areas such as disaster relief, education, healthcare, and sustainability. By partnering with reputable charitable organizations, FedEx demonstrates its commitment to corporate social responsibility and fosters positive brand perception among stakeholders. Moreover, these alliances often lead to co-branding opportunities, which further amplify FedEx’s visibility and community involvement.
In summary, FedEx’s marketing strategies revolve around diversification of services, brand recognition, innovation, customer-centricity, global reach, e-commerce solutions, sustainability, and corporate responsibility. These strategies help FedEx adapt to evolving customer needs, stay competitive in the logistics industry, and continue to be a trusted partner for businesses and individuals worldwide.
Marketing Mix of FedEx
FedEx effectively deploys the marketing mix, also known as the 4Ps (Product, Price, Place, and Promotion), to achieve its business goals. Below, I’ll provide a detailed explanation of how FedEx employs each element of the marketing mix:
Product
-
- Wide Range of Services: FedEx offers an extensive portfolio of services, including FedEx Express for international and time-sensitive shipments, FedEx Ground for domestic deliveries, FedEx Freight for heavy freight shipments, and specialized solutions for e-commerce, healthcare, and more. FedEx offers a comprehensive suite of shipping and logistics services, encompassing:
- FedEx Express: For international and time-sensitive deliveries.
- FedEx Ground: For domestic shipments.
- FedEx Freight: For heavy and large shipments.
- Specialized Services: Including FedEx Custom Critical, FedEx Cross Border, FedEx Supply Chain, and more.
- Customization: FedEx tailors its services to cater to the specific needs of diverse customer segments, providing solutions for businesses, individuals, and various industries.
- Wide Range of Services: FedEx offers an extensive portfolio of services, including FedEx Express for international and time-sensitive shipments, FedEx Ground for domestic deliveries, FedEx Freight for heavy freight shipments, and specialized solutions for e-commerce, healthcare, and more. FedEx offers a comprehensive suite of shipping and logistics services, encompassing:
Price
-
- Value-Based Pricing: FedEx employs a value-based pricing strategy, where the pricing of services is determined by the perceived value they offer to customers. Customers pay rates based on factors like shipment size, weight, destination, and delivery speed.
- Variable Pricing: Pricing can vary depending on several variables, including shipping distance, package weight, delivery speed, and the selection of additional services such as package insurance, signature confirmation, and tracking.
Place (Distribution)
-
- Global Network: FedEx boasts an extensive global network, with a presence in more than 220 countries and territories. They strategically position hubs, sorting facilities, distribution centers, and offices to efficiently serve customers worldwide.
- Local Partnerships: FedEx collaborates with local agents and partners in various regions to extend its reach and effectively serve customers in remote or challenging-to-reach areas. This local presence ensures a seamless logistics network.
Promotion
-
- Advertising and Branding: FedEx invests in advertising campaigns across multiple media channels, including television, print, online, and social media. Their branding, featuring the distinctive purple and orange color scheme and the iconic FedEx logo with a hidden arrow, reinforces brand visibility and recognition.
- Sponsorships: FedEx sponsors major sports events and organizations, such as the FedExCup in golf and the NFL, to enhance brand recognition and connect with a wide audience.
- Content Marketing: FedEx produces educational content, thought leadership articles, and industry insights to engage with business customers. They provide valuable information on shipping and logistics, positioning themselves as experts in the field.
In conclusion, FedEx’s 4Ps strategy involves offering a diverse range of services tailored to customer needs, employing value-based pricing, maintaining a global distribution network, and implementing comprehensive promotional efforts to strengthen its brand presence and provide valuable information to its target audience. These strategies have contributed to FedEx’s success as a leading global logistics and courier delivery services provider.
Also Read: From Memphis to the World: The Rise of FedEx as a Global Logistics Giant
To read more content like this, subscribe to our newsletter






