Uber is a company that offers various transportation services, including giving people rides, delivering food, and transporting goods. It’s based in San Francisco and operates in around 70 countries and over 10,500 cities globally. Uber has a massive user base of more than 131 monthly million people who use its services every month, and it also has 6 million active drivers and couriers worldwide. On an average day, Uber arranges about 25 million trips. Since it started in 2010, Uber has facilitated a whopping 42 billion trips, making it the biggest ride-hailing company in the United States.
To use Uber, you need to download the Uber app and set up an account. Once you have an account, you can ask for a ride by telling the app where you want to go and choosing the type of vehicle you want. The app will then give you an estimate of how much your ride will cost and tell you when the closest driver will arrive. When the driver shows up, you can get in the car, and they will take you to your destination.
Uber offers a range of vehicle options, including regular cars, SUVs, luxury cars, and vans. There are also different ride-sharing choices, like UberPool and UberX. With UberPool, you can share your ride with other passengers who are heading in the same direction. If you’re looking for a more affordable ride, UberX is a good choice. On the other hand, UberBlack provides luxury cars and high-end service.
Uber is a popular way to get around because it’s convenient and reasonably priced. The Uber app is user-friendly, and you can see the estimated cost and how quickly a driver will arrive before you request a ride. Moreover, Uber gives you plenty of options for vehicles and ride-sharing, so you can pick the one that suits your needs and budget.
Besides offering rides, Uber also has services for food delivery and moving goods. Uber Eats lets you order food from restaurants and have it delivered to your location. Meanwhile, Uber Freight connects companies that need to transport goods with the trucking companies that can do the job, making sure products get where they need to go.
Marketing Strategies of Uber
Uber has employed a variety of marketing strategies to establish and maintain its position as a leading ride-hailing and transportation network company. These strategies are designed to attract both passengers and drivers, increase brand awareness, and expand its services globally. Here are some of the key marketing strategies Uber has employed:
1. Digital Advertising
Uber leverages digital advertising as one of its primary marketing strategies to attract new riders, retain existing ones, and increase revenue. Here are some key aspects of how Uber uses digital advertising effectively:
Targeted Ads: Utilizing data analytics and machine learning algorithms, Uber creates targeted ads that reach potential customers based on demographics, location, browsing history, and search behavior. For example, Uber may show ride discount promotions to people living in areas where public transportation is scarce or to frequent business travelers searching for airfare tickets.
Dynamic Pricing: Uber adjusts prices dynamically based on real-time traffic conditions, rider demand, and driver availability. By doing so, they can ensure that fares remain competitive while maximizing profits during peak hours or high-demand periods. This pricing model encourages both drivers and passengers to use the platform more frequently, driving increased revenue for Uber.
Cross-Platform Advertising: To capture diverse segments of the population, Uber runs ads across different digital channels, such as Google Search, YouTube, Facebook, Instagram, Snapchat, and LinkedIn. Each platform reaches unique groups of people, ensuring maximum exposure for Uber’s services.
Geo-Targeted Promotions: Uber often partners with local businesses, event organizers, or tourist destinations to create geo-targeted promotions. For instance, Uber might provide discounted rides to concertgoers attending a music festival or offer free first rides to new users within a certain radius of a newly launched restaurant. Such collaborations benefit both parties by boosting foot traffic and generating additional revenue streams.
2. Promotional Discounts and Coupons
Uber utilizes promotional discounts and coupons as an effective marketing strategy to attract new customers, promote loyalty among existing riders, and compete against rival companies. Some key components of this approach include:
New User Acquisition: Offering initial ride discounts or complimentary trips serves as an enticement for potential customers to try Uber’s services. The allure of saving money on their first few rides encourages people to switch from traditional taxi services or alternative mobility solutions.
Customer Retention: Uber periodically offers exclusive discounts or promo codes tailored specifically for returning riders. These special deals reinforce customer loyalty by making Uber a preferred choice over competitors. As customers continue using Uber, they become familiarized with the platform’s ease of use, reliability, and overall value proposition.
Geographic Targeting: Uber sometimes designs region-specific promotions to address local needs or challenges. For example, if a city experiences severe weather conditions, Uber could release promo codes for emergency situations to assist residents in getting home safely. Similarly, Uber might collaborate with local businesses or attractions to offer joint promotions that benefit both parties.
3. Partnerships and Cross-Promotions
As part of their marketing strategy, Uber has formed partnerships and engaged in cross-promotional activities with other companies to expand their reach and attract new customers. Here are some examples:
UberEATS Partnership with McDonald’s: In 2017, Uber partnered with fast food giant McDonald’s to offer delivery services through the UberEATS platform. This allowed Uber to tap into McDonald’s vast customer base and increase demand for their food delivery service.
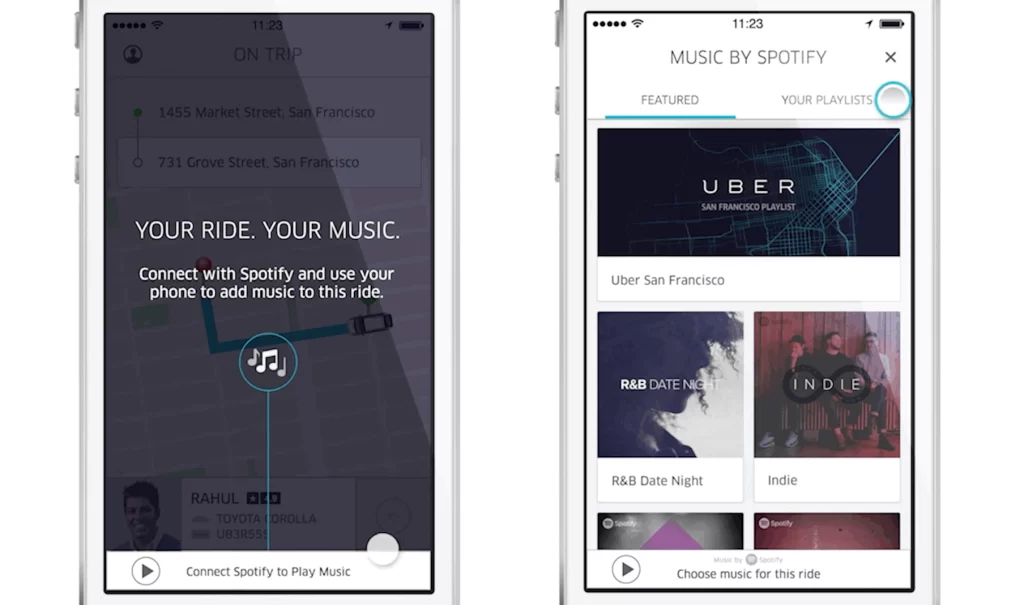
Spotify Integration: Uber integrated Spotify into their app, allowing riders to control the music played during their ride. This not only enhanced the rider experience but also promoted Spotify’s streaming service.
HotelTonight Collaboration: Uber teamed up with hotel booking site HotelTonight to provide discounted rates on hotels for riders who used both services together. This collaboration benefited both companies by driving more business to each other’s platforms.
NFL Partnership: Uber became the official rideshare partner of the National Football League (NFL) in 2018. Through this partnership, Uber offered promo codes and special deals to football fans attending games, which helped drive traffic to their platform.
Visa Checkout Integration: Uber integrated Visa Checkout into their app, making it easier for riders to pay for their trips using their Visa accounts. This partnership increased convenience for users while also promoting Visa’s payment processing services.
Airline Ticket Discounts: Uber has partnered with airlines such as United Airlines and Qantas to offer discounts on flights to passengers who use Uber to travel to the airport. These collaborations benefit both parties by increasing demand for their respective services.
Overall, these partnerships and cross-promotions have helped Uber build brand awareness, expand their user base, and enhance the overall rider experience. By leveraging existing brands and services, they were able to create value for their customers and grow their business.
4. Local Marketing Initiatives
Local marketing initiatives are an essential component of Uber’s broader marketing strategy. Here are some ways Uber implements local marketing initiatives:
Geo-targeted advertising: Uber utilizes geo-location data to serve targeted ads to people in specific locations. This enables them to reach potential riders and drivers in specific neighborhoods or cities.
Sponsored content: Uber works with influencers and bloggers in different cities to create sponsored posts showcasing how easy it is to get around town using Uber. This type of content helps raise awareness about Uber’s services while also providing useful information to readers.
Event activations: Uber participates in local events across the country, setting up booths and handing out swag to attract attention and encourage people to download the app. Events provide opportunities for face-to-face interaction between Uber staff and potential riders/drivers.
Collaborating with local businesses: Uber teams up with small business owners in various cities to offer special deals and promotions to Uber customers. This not only drives more traffic to those businesses but also increases exposure for Uber itself.
Local marketing initiatives allow Uber to adapt their message and approach to fit the unique needs and characteristics of each region. By doing so, they can better connect with potential riders and drivers, ultimately leading to increased usage of the Uber platform.
5. Customer Loyalty and Referral Programs
Uber has developed several programs aimed at building customer loyalty and driving referrals. Here are some examples:
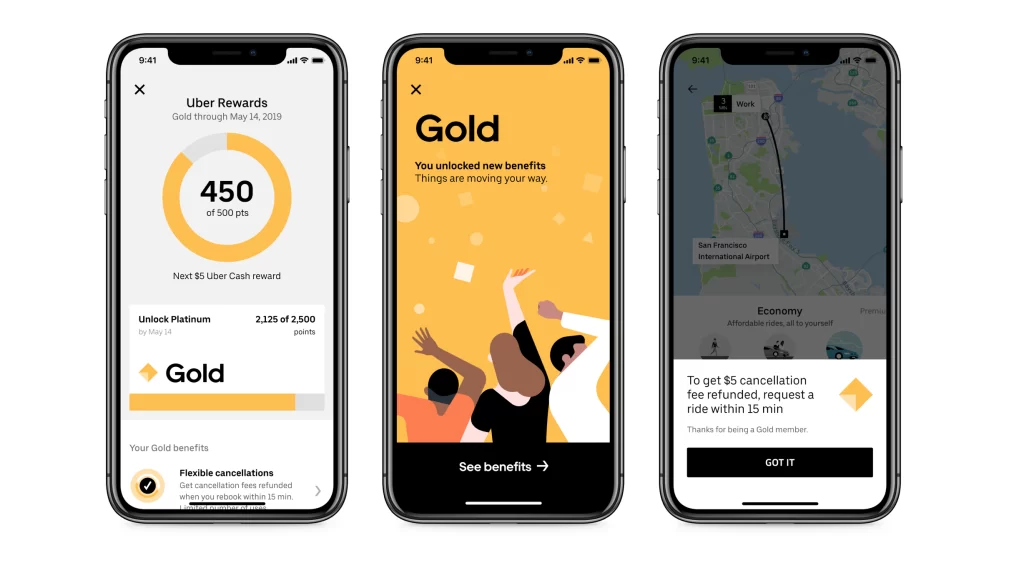
Uber Rewards: Launched in 2018, this program allows riders to earn points for every dollar spent on Uber rides, Uber Eats orders, and other activities such as referring friends to sign up for the service. Users can then redeem these points for benefits like free rides, upgrades to premium vehicles, and priority airport pickup.
Uber Pro: Introduced in 2019, this program targets professional drivers by rewarding them for consistently providing good service. Drivers can qualify for benefits such as accelerated earnings, vehicle maintenance coverage, and exclusive bonuses.
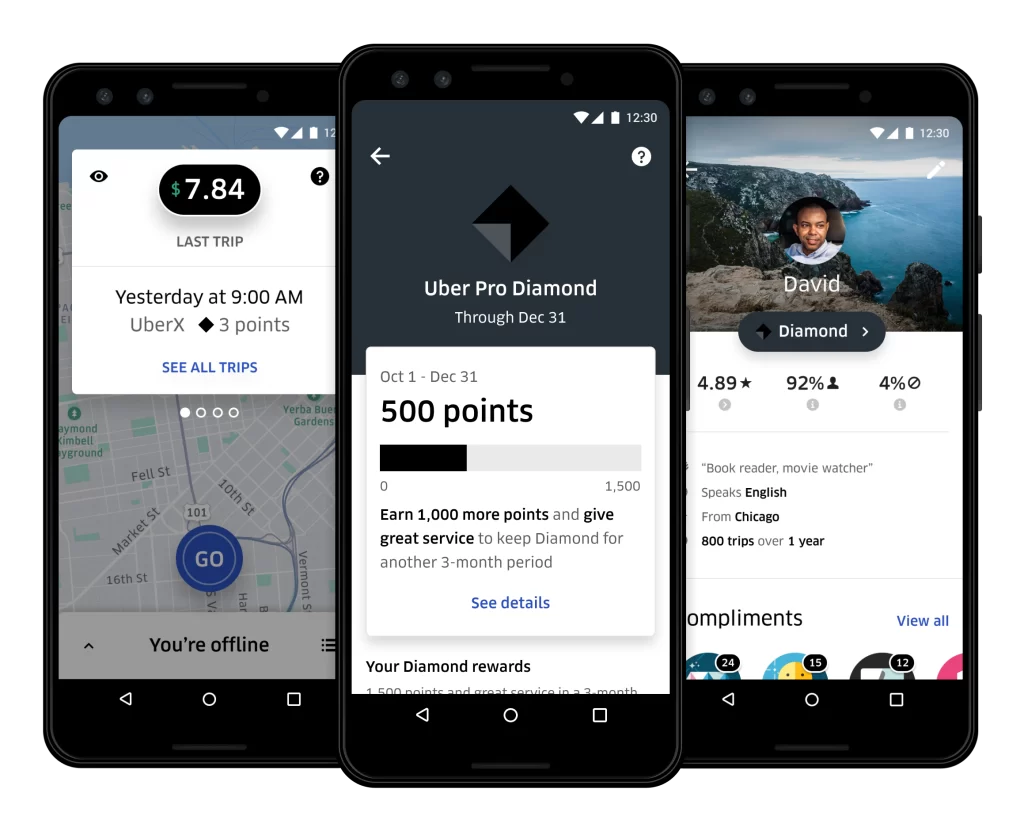
Uber Amplify: Another driver-focused program launched in 2020, Uber Amplify offers tailored rewards and recognition to top performers. Eligible drivers receive personalized communications, access to exclusive experiences, and other perks designed to boost engagement and retention.
Uber Boost: Rolled out in 2021, this feature lets riders request surge pricing without waiting for peak demand periods. It serves both as a convenience enhancement and a means of incentivizing riders during off-peak hours when demand might be lower.
Uber Credits: Available since late 2020, this option allows riders to purchase prepaid credit packs at a discount. Purchases made with Uber Credits accrue points toward future redemptions, helping build long-term loyalty.
Uber Pass: Debuted in 2019, this subscription plan grants riders flat-rate prices on rides within a specified area over a set time frame (e.g., one month). Subscribers also benefit from reduced wait times and no surge charges during peak hours.
Uber Visa Card: Partnering with Barclays Bank, Uber released a co-branded credit card in 2019. Cardholders earn rewards points for purchases made outside of Uber transactions, with the ability to convert accumulated points directly into Uber Cash for use on the platform.
6. Uber for Business
“Uber for Business” is a program offered by Uber that allows companies to manage their employees’ ground transportation needs more efficiently. With Uber for Business, companies can set up centralized billing accounts, track employee trips, and even create custom rules for usage based on factors like time of day or location.
As a marketing strategy, Uber for Business offers several benefits for both Uber and participating companies. Firstly, it helps drive increased demand for Uber’s services by making it easier for businesses to integrate ride-sharing into their daily operations. Secondly, it creates a recurring revenue stream for Uber through subscription fees charged to participating companies. Thirdly, it provides valuable data insights for Uber to better understand how their platform is used by businesses and identify opportunities for further growth.
In terms of implementation, Uber for Business typically involves creating a dedicated portal where companies can sign up for the program and manage their account settings. Companies can then invite their employees to join the program using unique codes or links, which allow them to access the Uber app and charge trips back to the company account. Uber also offers support resources such as webinars and training sessions to help companies get started with the program and maximize its value.
7. Localized Content and Social Media
Localized content and social media have become essential components of Uber’s marketing strategy, allowing the ride-hailing company to connect more effectively with local communities and build stronger relationships with riders and drivers worldwide. Here are several ways Uber leverages localization and social media to achieve its goals:
Tailored Communication: To address regional differences and cultural nuances, Uber creates custom messaging and promotions specific to each city or country where it operates. This personalized approach enables the company to resonate more deeply with users and foster greater trust and understanding. By speaking directly to local needs and preferences, Uber can increase user satisfaction and retention rates.
Hyperlocal Promotions: Uber regularly launches targeted campaigns designed to attract new riders and encourage repeat usage among existing ones. These initiatives might include discount codes for first-time passengers, special deals tied to local events (e.g., music festivals, sports games), or even limited-time offers linked to weather conditions (e.g., rain-sensitive pricing). Such hyperlocal tactics help Uber stand out amid competitors and showcase its commitment to serving distinct neighborhoods and populations.
Community Engagement: Through social media platforms like Facebook, Instagram, Twitter, and LinkedIn, Uber interacts with users on a grassroots level. By responding promptly to comments, questions, and complaints; sharing helpful tips and advice; and highlighting success stories and milestones, Uber cultivates an active dialogue with its audience. This two-way conversation not only improves transparency but also positions the company as a reliable partner dedicated to supporting local communities.
Location-Specific Content: Uber produces regionally focused blog posts, videos, infographics, and other multimedia assets to educate and entertain viewers. From spotlighting beloved landmarks and hidden gems to profiling passionate drivers and fascinating riders, these pieces serve as valuable resources for exploring cities and connecting with fellow residents. By providing such insider perspectives and recommendations, Uber strengthens its role as a go-to resource for navigating urban environments and discovering unique experiences.
Real-Time Adaptation: As circumstances evolve rapidly in different regions, Uber must be prepared to adjust its strategies accordingly. For instance, during major weather events or transportation disruptions, the company may implement surge pricing or alternative services (such as bike rentals) to accommodate changing demand patterns. By remaining flexible and responsive to unforeseen developments, Uber demonstrates its flexibility and resilience, which can bolster consumer confidence and loyalty over time.
8. Expansion and Market Entry
Expansion and market entry represent critical aspects of Uber’s overall growth strategy, allowing the ride-hailing giant to diversify its operations, tap into fresh markets, and solidify its position as a global industry leader. Here are some key approaches Uber employs to expand and enter new territories:
Gradual Rollout: Rather than rushing into unfamiliar territory, Uber typically introduces its service gradually by starting small and then scaling up based on performance metrics and user feedback. This measured approach minimizes potential risks associated with entering foreign markets while ensuring that the company is well-prepared to handle any challenges that arise.
Acquisitions and Partnerships: In addition to organic growth, Uber pursues acquisitions and partnerships to accelerate its expansion efforts. By acquiring complementary businesses or forming alliances with local players, Uber can leverage established networks, expertise, and infrastructure to penetrate new markets faster and more efficiently. Examples of notable acquisitions include Otto (self-driving technology), Careem (Middle Eastern ride-hailing platform), and JUMP Bikes (electric bicycle sharing).
Customization for Cultural Differences: When entering new countries or regions, Uber adapts its offering to align with local norms, regulations, and expectations. This could involve modifying app interfaces, payment options, driver/rider communication protocols, or vehicle types to better fit the prevailing environment. By acknowledging and respecting cultural distinctions, Uber shows respect for local values and increases its chances of gaining traction in those markets.
Lobbying and Government Relations: Given the regulatory complexities involved in operating globally, Uber engages in extensive lobbying and government relations activities to secure favorable policies and avoid legal hurdles. The company collaborates with policymakers, think tanks, and advocacy groups to promote pro-innovation agendas, address concerns related to labor standards, and ensure fair competition within the ride-hailing ecosystem. By actively participating in policy debates and shaping legislative frameworks, Uber protects its interests and expands its opportunities for growth worldwide.
In conclusion, Uber’s marketing strategies are multifaceted and dynamic, adapting to the evolving needs of its users and the competitive landscape of the transportation industry. By employing a combination of digital marketing, incentives, partnerships, and customer-centric approaches, Uber has successfully grown its user base and maintained its presence in markets worldwide.
Also Read: The Rise and Challenges of Uber: A Story of Disruption
To read more content like this, subscribe to our newsletter




