Cargill, Incorporated is a multinational commodity trading and processing company that has been in operation for over 150 years. Founded in 1865 by William W. Cargill, the company has grown to become the largest privately held company in the United States in terms of revenue. With headquarters in Minnetonka, Minnesota, and incorporated in Wilmington, Delaware, Cargill operates in 66 countries and employs over 155,000 people worldwide.

The company’s core businesses include trading, purchasing, and distributing grain and other agricultural commodities such as palm oil, as well as trading in energy, steel, and transport. Additionally, Cargill raises livestock and produces feed, and manufactures food ingredients like starch, glucose syrup, vegetable oils, and fats for use in ultra-processed foods and industrial applications. The company also boasts a significant financial services arm, which manages financial risks in the commodity markets. In 2003, Cargill created Black River Asset Management, a hedge fund with approximately $10 billion in assets and liabilities.
Cargill’s impact on the global food industry cannot be overstated. The company is responsible for 25% of all United States grain exports and supplies around 22% of the US domestic meat market. Notably, Cargill imports more products from Argentina than any other company and is the largest poultry producer in Thailand. Furthermore, all the eggs used in US McDonald’s restaurants pass through Cargill’s plants, solidifying the company’s position as a dominant force in the food industry. Cargill is also the sole producer of Alberger process salt, a crucial ingredient used in the fast-food and prepared food sectors.
Despite its massive size and influence, Cargill remains a family-owned business. The descendants of the founder, from the Cargill and MacMillan families, collectively own over 90% of the company. This continuity of ownership has allowed Cargill to maintain a long-term perspective and invest heavily in research and development, ensuring its continued relevance and growth in an ever-changing marketplace.
In January 2023, Brian Sikes was appointed as the company’s president and CEO, becoming the 10th CEO in Cargill’s 158-year history. Under his leadership, the company continues to evolve and adapt to the changing needs of the global food industry, while remaining committed to its core values of sustainability, innovation, and customer satisfaction.
With a rich history, diverse portfolio, and commitment to excellence, Cargill is poised to remain a leader in the global food industry for generations to come. Its unwavering dedication to quality, efficiency, and sustainability has earned it the trust of customers, suppliers, and partners worldwide, solidifying its position as a true giant in the agribusiness landscape.
History of Cargill
The company was founded in 1865 by William W. Cargill, who had a vision of building a business that would bridge the gap between the rural farmer and the urban consumer.
William Cargill was born in 1822 in New York state and grew up in a family of modest means. He began his career in the grain trade, working for a company in Buffalo, New York. However, he soon realized that there were opportunities to be had in the Midwest, where the railroads were expanding and the agricultural industry was growing rapidly.
In 1865, Cargill moved to La Crosse, Wisconsin, where he established his first grain elevator. The location was strategic, as it was situated near the confluence of the Mississippi and La Crosse rivers, making it an ideal spot for transporting grain. Over time, Cargill expanded his operations, building more grain elevators and establishing relationships with farmers and traders throughout the region.
In the late 1800s, Cargill made a bold move by investing in the development of the Great Northern Railway. The railway connected the Midwest to the Pacific Northwest, opening up new markets for Cargill’s grain. The company’s business flourished, and by the early 1900s, Cargill was one of the largest grain traders in the country.
Diversification and Expansion
Under the leadership of William Cargill’s son, John, the company began to diversify its operations. In 1911, Cargill entered the meatpacking industry with the acquisition of a packing plant in Chicago. The company quickly became a major player in the industry, and by the mid-1920s, it was operating plants in several cities across the United States.
Cargill continued to expand its operations during World War II, when it began to supply food and other goods to the military. After the war, the company shifted its focus to international trade, establishing offices in Europe, South America, and Asia.
In the 1960s and 1970s, Cargill experienced rapid growth under the leadership of John’s son, Whitney. The company acquired several other firms, including a soybean processor, a corn miller, and a sugar refiner. By the 1980s, Cargill had become a multinational corporation with operations in over 30 countries.
Challenges and Adaptations
Like many companies, Cargill faced challenges in the latter half of the 20th century. The farm crisis of the 1980s hit the company hard, as declining crop prices and high interest rates led to a sharp decline in profits. However, Cargill adapted by diversifying further into areas such as financial services and risk management.
In the 1990s, Cargill continued to expand its operations, acquiring several other companies, including Continental Grain, Nutrena, and Provimi. The acquisitions helped the company strengthen its positions in the animal nutrition, pet food, and aquaculture markets.
Sustainability and Innovation
In recent years, Cargill has focused on sustainability and innovation. The company has invested heavily in renewable energy, including wind and solar power, and has implemented measures to reduce its carbon footprint. Cargill has also launched several initiatives aimed at promoting sustainable agriculture practices among farmers and ranchers.
In addition, the company has turned its attention to developing new technologies and products. Cargill has invested in startups working on alternative protein sources, such as lab-grown meat and plant-based alternatives. The company has also developed new products, such as biodegradable plastics and advanced materials, designed to replace traditional fossil fuel-based materials.
Cargill Family
The Cargill family, officially known as the Cargill-MacMillan family, boasts a storied legacy deeply entrenched in the annals of American business history. Descendants of William Wallace Cargill, the visionary founder of Cargill Inc., and his son-in-law John H. MacMillan Sr., the family has maintained a steadfast presence in the agribusiness giant for over 140 years. William Cargill established the company in 1865 as a modest grain storage business in Iowa, navigating the challenges of the post–Civil War era. After William’s passing in 1909, John MacMillan Sr. adeptly led the company out of a debt crisis, securing its stability and setting the stage for enduring success.
As of 2019, the Cargill-MacMillan family, comprised of 23 members, held a staggering 88% ownership of Cargill Inc., a privately held corporation that reported an impressive $113.5 billion in revenue that year. The family’s estimated net worth, primarily derived from their holdings in Cargill Inc., reached $38.8 billion, making them the 4th wealthiest family in the United States. Notably, the family strategically reinvests 80% of Cargill Inc.’s net income annually for sustained growth.
Despite their immense wealth, the Cargill-MacMillan family maintains a low profile, with 6 family members serving on the company’s 17-member board. However, since 1995, family members have not actively participated in the day-to-day operations of Cargill. Whitney MacMillan, who served as Cargill’s chairman and CEO since 1976, stepped down from the executive role in 1995, marking a shift in the family’s direct involvement in running the company.
In addition to their influence over Cargill, the family was the majority owner of The Mosaic Company, a major player in the production of potash and phosphate fertilizer in the United States. In 2011, they divested their sixty-four-percent stake in Mosaic for a substantial $24.3 billion, further solidifying their financial prowess. The Cargill-MacMillan family’s impact extends beyond business, with the late Margaret Anne Cargill earning recognition as one of America’s most generous donors in 2012. Posthumously awarded the top spot in the Chronicle of Philanthropy’s annual list, Margaret Anne’s bequest to non-profits, totaling around $6 billion, added a philanthropic chapter to the family’s multifaceted legacy.
Businesses of Cargill
Cargill is a massive global corporation with a diverse range of businesses, spanning the entire food and agriculture value chain. Let’s delve into the key segments that define Cargill’s operations:
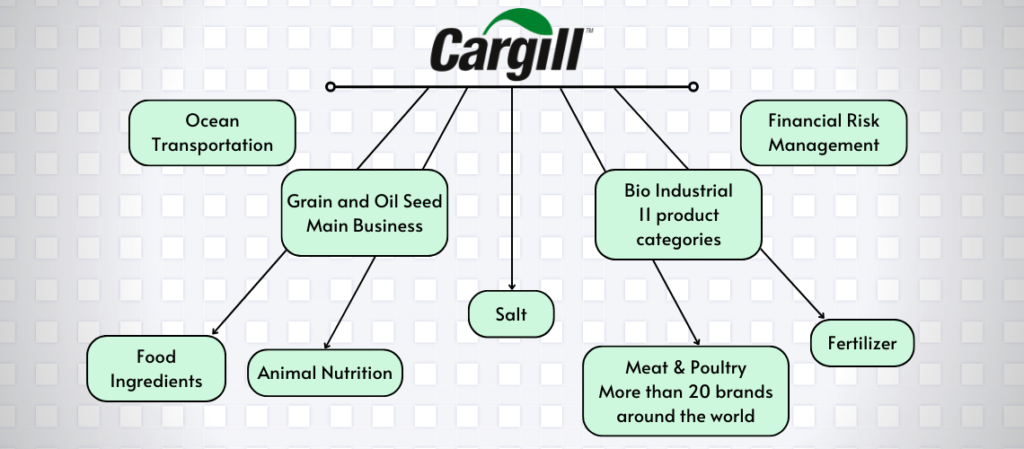
1. Food Ingredients & Products
This segment encompasses the processing and production of food ingredients, such as starches, sweeteners, oils, and proteins, derived from grains, oilseeds, and other agricultural commodities. These ingredients are essential components of various food products, including bread, pasta, confectionery, and beverages.
2. Food Distribution & Merchandising
This segment involves the sourcing, trading, and distribution of food products, ranging from grains and oilseeds to processed foods and animal nutrition products. Cargill’s global network facilitates the movement of these products from producers to consumers worldwide.
3. Animal Nutrition & Protein
Cargill plays a crucial role in providing feed ingredients and premixes for livestock and poultry production. This segment ensures the availability of high-quality animal nutrition to support the growing demand for meat, eggs, and dairy products.
4. Industrial & Financial Services
Cargill extends its expertise beyond food and agriculture into industrial applications and financial services. The industrial segment produces biodiesel, biolubricants, and de-icing fluids, while the financial services segment provides risk management and financing solutions to agribusinesses and other clients.
5. Origination & Processing
This segment forms the backbone of Cargill’s operations, encompassing the procurement, transportation, processing, and storage of grains and oilseeds. Cargill’s expertise in logistics and supply chain management ensures efficient movement of these commodities across the globe.
6. Trade & Risk Management
Cargill’s global trading activities play a critical role in connecting producers and consumers, facilitating price discovery, and managing risk in the agricultural markets. The company’s risk management expertise helps mitigate price fluctuations and ensures stable supply chains.
7. Specialty Products & Solutions
Cargill’s diverse portfolio extends to specialty products and solutions tailored to specific industries. This includes ingredients for personal care and beauty products, bioindustrial products for various industrial applications, and data asset solutions for optimizing agricultural practices.
Through its diverse range of businesses, Cargill plays a pivotal role in the global food and agriculture system, connecting farmers to consumers, ensuring food security, and contributing to sustainable agricultural practices. The company’s commitment to innovation, sustainability, and social responsibility positions it as a leader in the ever-evolving food and agriculture industry.
Growth of Cargill in 2023
Cargill has demonstrated robust growth, achieving a historic revenue milestone in 2023 with a reported $177 billion, marking a noteworthy 7% increase from the preceding year. This remarkable financial achievement aligns with Cargill’s strategic focus on three key pillars: value, volume, and optimization. The company’s commitment to delivering exceptional value is evident in its efforts to bring capabilities to the market that align with evolving sensory trends. Simultaneously, Cargill is amplifying its production capacity at European plants to bolster volume and meet the escalating demand. The optimization pillar underscores Cargill’s dedication to operational efficiency, ensuring a high service level for its diverse customer base.
Beyond revenue growth, Cargill’s financial success is evident in its 2022 performance, reporting a gross revenue of $165 billion, reflecting a substantial 23% increase from the previous year. The company’s profitability is underscored by a net profit of just under $5 billion in 2021. Cargill’s global impact is further highlighted by its extensive workforce, employing over 155,000 individuals across 66 countries. With responsibility for 25% of all United States grain exports, Cargill’s influence is pivotal in the agricultural commodities sector.
The company’s growth strategy extends beyond financial metrics, encompassing diverse initiatives such as manufacturing dielectric fluid in India using Cargill’s patented technology, providing warehousing and logistics services, and specializing in handling identity-preserved and differentiated products. These multifaceted efforts position Cargill as a prominent player in the dynamic landscape of agricultural commodities.
Future of Cargill
While predicting the future of any company involves uncertainties, Cargill is poised for a dynamic and impactful trajectory based on its strategic initiatives and industry trends. As of 2023, Cargill’s robust expansion strategy, emphasizing value, volume, and optimization, sets the stage for continued growth. The company’s commitment to aligning capabilities with sensory trends and increasing production capacity at European plants reflects a proactive approach to evolving market demands. Cargill’s focus on optimization, ensuring operational efficiency and a high service level for customers, positions the company to navigate challenges and capitalize on emerging opportunities in the global agricultural and commodities markets. Additionally, Cargill’s dedication to sustainability and innovation, exemplified by ventures such as manufacturing dielectric fluid in India using patented technology, showcases its forward-looking approach to addressing environmental concerns and embracing technological advancements.
Furthermore, Cargill’s diversified portfolio, which includes offering warehousing and logistics services and handling identity-preserved and differentiated products, positions the company as a versatile player in the agribusiness sector. As the world grapples with the increasing demand for food security, sustainable practices, and innovative solutions, Cargill is likely to play a pivotal role in shaping the future of the agricultural industry. Leveraging its extensive global presence, commitment to responsible business practices, and ongoing investments in technology and sustainability, Cargill is well-positioned to adapt to changing market dynamics and contribute to the evolving landscape of the global agribusiness sector in the years to come.
Also Read: From Retail Pharmacy to Healthcare Giant: Story of CVS Health
To read more content like this, subscribe to our newsletter




