Apple, a name synonymous with sleek design, cutting-edge technology, and unwavering brand loyalty, has revolutionized the way we interact with technology. Its story, however, begins not in the polished environment of a Silicon Valley headquarters, but in the humble setting of a California garage. Founded in 1976 by Steve Jobs and Steve Wozniak, Apple’s journey is a testament to human ingenuity, visionary leadership, and the power of design to transform industries.
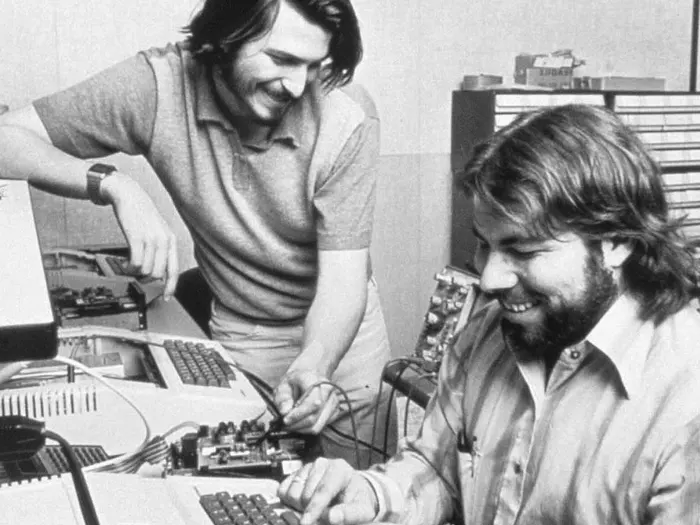

The early days of Apple were fueled by the technical brilliance of Wozniak, an engineer who designed the company’s first product, the Apple I computer. This machine, a basic circuit board aimed at hobbyists, lacked a keyboard, monitor, or case. Yet, it showcased Wozniak’s knack for creating powerful yet affordable computers. Recognizing the potential market, Steve Jobs, with his unparalleled charisma and business acumen, partnered with Wozniak to bring the Apple I to life.
The launch of the Apple II in 1977 marked a pivotal moment. Unlike its predecessor, the Apple II was a fully assembled personal computer, featuring a keyboard, color graphics, and a user-friendly interface. This innovation opened the doors for a wider audience, making computing accessible to not just tech enthusiasts but also educators, businesses, and everyday users. The Apple II became a runaway success, propelling Apple to the forefront of the personal computer revolution.
Throughout the 1980s, Apple continued to push boundaries. The company introduced the revolutionary Macintosh in 1984, boasting a graphical user interface (GUI) and a mouse, a stark contrast to the text-based interfaces dominant at the time. This intuitive design philosophy, now commonplace, was a game-changer, making computers significantly easier to use for the average person. While the Macintosh faced initial challenges due to its high price tag, it laid the foundation for Apple’s future success in user-friendly computing experiences.
The later part of the decade saw Apple grapple with internal struggles and a decline in sales. However, the return of Steve Jobs in 1997 marked a turning point. Jobs, known for his unwavering belief in Apple’s vision, spearheaded a strategic comeback. This period witnessed the launch of the iMac, a vibrantly colored all-in-one computer that revived consumer interest in the Macintosh. Apple’s product line further expanded with the introduction of the groundbreaking iPod in 2001, a portable digital music player that redefined the way people listened to music.
The launch of the iPhone in 2007 truly catapulted Apple into a new era. This revolutionary device, combining a phone, a widescreen iPod, and a web browser with an intuitive touchscreen interface, redefined the mobile phone landscape. The iPhone’s success was followed by the iPad tablet computer in 2010, further solidifying Apple’s position at the forefront of mobile technology.
Today, Apple stands as a global tech titan, consistently recognized for its innovative products, sleek design aesthetics, and a loyal customer base. From its humble beginnings in a garage to its current status as a cultural icon, Apple’s story is a remarkable journey of innovation, design, and the unwavering pursuit of a vision. The company’s impact on the world of technology is undeniable, having shaped the way we communicate, work, and interact with the digital world around us.
Top Apple Competitors and Alternatives
Apple faces competition across various segments of the tech industry, depending on the specific product or service. Here’s a breakdown of some key competitors:
Smartphones:
1. Samsung

Website – https://www.samsung.com/global/galaxy/
Samsung is a major thorn in Apple’s side across multiple product categories. In the smartphone market, Samsung’s Galaxy series directly rivals Apple’s iPhone. These devices boast high-end features and run on the Android operating system, the leading competitor to Apple’s iOS. This creates a choice for consumers between the closed ecosystem of Apple products and the open nature of Android. Beyond smartphones, Samsung competes with Apple in tablets (Galaxy Tab vs. iPad) and smartwatches (Galaxy Watch vs. Apple Watch).
Direct Product Competition:
- Smartphones: Both Apple’s iPhone and Samsung’s Galaxy lines are leading players in the high-end smartphone market. They compete fiercely on features, design, and camera technology.
- Tablets: Apple’s iPad and Samsung’s Galaxy Tab series battle for dominance in the tablet market, offering a range of screen sizes and functionalities.
- Smartwatches: Apple Watch and Samsung Galaxy Watch vie for wrist real estate, boasting fitness tracking, messaging, and app integration.
Beyond the Device: While both companies are leaders in hardware, their competition extends to software and services. Apple prides itself on a tightly controlled ecosystem (iOS, macOS) that integrates seamlessly with its devices. Samsung leverages the open-source Android platform, offering more customization but potentially less user-friendliness.
Here’s a table highlighting the key areas of competition:
| Category | Samsung | Apple |
|---|---|---|
| Smartphones | Galaxy Line | iPhone |
| Tablets | Galaxy Tab | iPad |
| Smartwatches | Galaxy Watch | Apple Watch |
| Operating Systems | Android (Open-Source) | iOS (Closed Ecosystem) |
| Services | Samsung Pay, Bixby | Apple Pay, Siri |
2. Huawei

Website – https://www.huawei.com/en/
Head-to-Head in High-End: Both Huawei and Apple are major forces in the premium smartphone market, constantly innovating and vying for consumer loyalty.
- Flagship Phones: Huawei’s Mate and P series compete directly with Apple’s iPhone in terms of features, design, and camera technology. Both companies push the boundaries in areas like screen quality, processing power, and camera capabilities.
Beyond Smartphones: The competition extends beyond just phones.
- Laptops and Tablets: Huawei’s MateBook laptops and MatePad tablets directly compete with Apple’s MacBook and iPad lines, offering similar functionality at often more competitive price points.
- Smartwatches: Huawei’s Watch GT series competes with the Apple Watch, boasting fitness tracking, messaging capabilities, and app integration.
Innovation Battleground: Both companies invest heavily in research and development (R&D).
- AI Chips: Huawei boasts its own in-house designed Kirin chips with a focus on AI processing, potentially giving them an edge in this rapidly evolving field. Apple utilizes its own Neural Engine for AI tasks within its devices.
- 5G Technology: Both companies are actively involved in developing and implementing 5G technology for their devices, aiming to provide faster connectivity to users.
Ecosystem and Brand Identity: Here’s a key differentiator.
- Open vs. Closed: Huawei leverages the open-source Android platform, offering greater customization for users. Apple, on the other hand, operates within its tightly controlled iOS ecosystem, prioritizing seamless integration between its devices and services.
Here’s a table summarizing the key areas of competition:
| Category | Huawei | Apple |
|---|---|---|
| Smartphones | Mate Series, P Series | iPhone |
| Laptops | MateBook | MacBook |
| Tablets | MatePad | iPad |
| Smartwatches | Watch GT | Apple Watch |
| AI Development | Kirin Chips | Neural Engine |
| Operating Systems | Android (Open-Source) | iOS (Closed Ecosystem) |
| Brand Identity | Openness, Customization | Premium, Integration |
3. Xiaomi, Oppo, and other Chinese brands

Price and Features: Chinese brands like Xiaomi, Oppo, and Vivo (collectively referred to as “Chinese brands” here) compete with Apple primarily on price and features.
- Flagship Killers: These brands offer feature-packed smartphones at significantly lower prices than Apple’s iPhones. They often boast impressive camera systems, powerful processors, and innovative features like fast charging, catering to a budget-conscious and tech-savvy audience.
- Market Share Focus: Chinese brands aggressively target market share, particularly in developing regions like India and Southeast Asia. Their affordability makes them highly attractive to a wider range of consumers compared to Apple’s premium positioning.
Beyond Price: The competition goes beyond just affordability.
- Rapid Innovation: Chinese brands are known for rapid innovation, releasing multiple phone models per year with the latest features. This keeps their offerings fresh and caters to consumers who want the newest technology at a competitive price.
- Offline Market Strength: Chinese brands have a strong presence in the offline retail market, particularly in their home turf of China. This allows them to reach a wider range of consumers who may not be comfortable purchasing online.
Brand Identity: Here’s a key difference.
- Value-Driven: Chinese brands prioritize offering the most features for the price, appealing to a value-conscious market.
- Premium Image: Apple, on the other hand, focuses on cultivating a premium brand image associated with quality, design, and a seamless user experience within its closed ecosystem.
Here’s a table summarizing the key areas of competition:
| Category | Chinese Brands (Xiaomi, Oppo, Vivo) | Apple |
|---|---|---|
| Price Point | More Affordable | Premium |
| Focus | Features, Market Share | Brand Image, User Experience |
| Innovation | Rapid Iteration | Focused Innovation |
| Sales Strategy | Strong Offline Presence | Online & Flagship Stores |
| Brand Identity | Value-Driven | Premium |
Computers:
1. Microsoft

Website – https://www.microsoft.com/en-in
While Microsoft and Apple may seem like distant competitors, they battle for consumer loyalty across several product categories. Here’s a detailed breakdown:
Direct Product Competition:
- Personal Computers: While Apple’s Macs dominate the premium market with a focus on design and user experience, Microsoft caters to a broader audience with various Windows PCs offered by different manufacturers. These PCs provide a wider range of affordability and hardware options.
- Tablets: Microsoft’s Surface tablets directly compete with Apple’s iPads. Surface devices offer a unique 2-in-1 functionality (laptop and tablet) with a focus on productivity and drawing/inking capabilities, while iPads prioritize a sleek design and a strong app ecosystem.
Beyond Devices:
- Operating Systems: Microsoft’s Windows operating system holds a dominant position in the desktop PC market, while Apple’s macOS is exclusive to its Macs.
- Productivity Suites: Microsoft Office (Word, Excel, PowerPoint) remains the industry standard for professional use, while Apple’s free iWork suite (Pages, Numbers, Keynote) offers a good alternative for casual users within the Apple ecosystem.
- Cloud Services: Both Microsoft OneDrive and Apple iCloud offer cloud storage and file synchronization, with each company integrating their services tightly with their respective device ecosystems.
Different Philosophies:
- Integration vs. Openness: Apple prioritizes tight integration between its hardware, software, and services, creating a seamless user experience. Microsoft offers a more open approach, allowing its software (like Office) to work on various devices and operating systems.
Here’s a table summarizing the key areas of competition:
| Category | Microsoft | Apple |
|---|---|---|
| Personal Computers | Windows PCs (Various Manufacturers) | Macs |
| Tablets | Surface (2-in-1) | iPad |
| Operating Systems | Windows (Dominant in Desktops) | macOS (Exclusive to Apple Devices) |
| Productivity Suites | Microsoft Office (Industry Standard) | iWork (Free, Apple Ecosystem) |
| Cloud Services | OneDrive | iCloud |
| Philosophy | Openness, Software on Various Devices | Integration, Seamless User Experience |
2. Dell, HP, Lenovo

While Apple carves a niche for itself in the premium tech market, Dell, HP, and Lenovo (collectively referred to as “PC Makers” here) compete fiercely as value-oriented alternatives. Here’s a breakdown of their rivalry:
Focus on Affordability and Choice:
- Wider Price Range: PC makers offer a vast array of desktops and laptops at various price points, catering to budget-conscious buyers and those seeking specific features without the premium Apple tax.
- Hardware Customization: Unlike Apple’s standardized configurations, PC makers allow for more customization of hardware components like processors, RAM, and storage, giving users greater control over performance and price.
Beyond Price:
- Windows Ecosystem: PC makers rely on Microsoft’s Windows operating system, providing a familiar user experience for many users accustomed to Windows PCs. This familiarity can be a significant advantage for businesses and consumers already invested in the Windows ecosystem of software and peripherals.
- Gaming Market: Many PC makers cater heavily to the gaming market with powerful machines boasting high-performance graphics cards and advanced cooling systems, an area where Apple doesn’t directly compete.
Apple’s Counterpoints:
- Brand Image and Design: Apple holds a strong brand image associated with sleek design, user-friendly software, and a reputation for quality and durability.
- Seamless Ecosystem: Apple offers a tightly integrated ecosystem of devices and services (iPhones, iPads, Macs) that seamlessly work together, creating a smooth user experience not easily replicated by PC makers with various hardware configurations.
Here’s a table summarizing the key areas of competition:
| Category | PC Makers (Dell, HP, Lenovo) | Apple |
|---|---|---|
| Price Point | Wide Range (Budget to High-End) | Premium |
| Customization | More Hardware Customization Options | Standardized Configurations |
| Operating System | Windows | macOS |
| Gaming Focus | Many Cater to Gamers | Not a Focus |
| Brand Image | Value-Oriented, Familiarity | Premium Design, User Experience |
| Ecosystem | Open Windows Ecosystem | Tightly Integrated Apple Ecosystem |
Services:
1. Google

Website – https://abc.xyz/
While Google and Apple may seem like they cater to different audiences, they are fierce competitors across several product categories. Here’s a detailed breakdown of their rivalry:
Direct Product Competition:
- Smartphones: Google’s Pixel line competes directly with Apple’s iPhone in the premium smartphone market. Both offer high-end features, powerful processors, and advanced camera systems. However, Google prioritizes software innovation like AI integration within its Pixel phones, while Apple focuses on a seamless user experience within its closed ecosystem.
- Smartwatches: Google’s Wear OS platform powers various smartwatches from different manufacturers, competing with Apple Watch’s dominance in the smartwatch market. Google aims to offer a wider range of smartwatch options at various price points, while Apple prioritizes tight integration with its iPhones and a curated app selection.
Beyond Devices:
- Operating Systems: Google’s free and open-source Android operating system dominates the mobile market, powering billions of smartphones worldwide. Apple’s iOS, on the other hand, is exclusive to its iPhones and iPads, offering a more controlled and secure user experience.
- App Stores: Google Play Store and Apple App Store are the primary gateways for downloading apps on their respective platforms. Google offers a wider range of apps with potentially looser restrictions, while Apple prioritizes app quality and security through a stricter review process.
- Cloud Services: Both Google Drive and Apple iCloud offer cloud storage and file synchronization, with each company integrating their services tightly with their respective device ecosystems.
Different Philosophies:
- Openness vs. Control: Google operates with a more open approach, allowing its Android OS and services to be used by various manufacturers. Apple prioritizes tight control over its hardware, software, and services, creating a more curated user experience.
- Free vs. Paid: Many of Google’s core services like Search, Gmail, and Maps are free and ad-supported, while Apple often charges premium prices for its hardware and services.
Here’s a table summarizing the key areas of competition:
| Category | Apple | |
|---|---|---|
| Smartphones | Pixel Line (Software Innovation) | iPhone (Seamless Ecosystem) |
| Smartwatches | Wear OS Platform (Variety) | Apple Watch (Dominant Market Share) |
| Operating Systems | Android (Open-Source, Dominant Market Share) | iOS (Exclusive, Secure) |
| App Stores | Google Play Store (Wider Selection) | Apple App Store (Stricter Quality Control) |
| Cloud Services | Google Drive | Apple iCloud |
| Philosophy | Openness, Free Services | Control, Premium Products |
2. Amazon Prime

Website: https://www.primevideo.com/
While seemingly focused on different areas (retail vs. tech), Amazon Prime and Apple compete for customer loyalty through content and subscription services. Here’s a breakdown of their rivalry:
Indirect but Overlapping Competition:
- Streaming Services: Both Amazon Prime Video and Apple TV+ offer ad-supported or subscription-based streaming services with original and licensed content. They compete for viewers’ attention and subscription dollars in the ever-crowded streaming landscape.
- Music Streaming: While Apple Music remains a dominant force, Amazon Music Prime is included with a Prime membership, offering a vast library of music for a potentially lower effective price compared to standalone music streaming services.
Beyond Streaming:
- Convenience and Value: Amazon Prime membership bundles various benefits like free shipping, exclusive deals, and access to streaming services. This creates a perception of value and convenience for frequent online shoppers. Apple, on the other hand, focuses on premium hardware and doesn’t offer bundled services to the same extent.
- Cloud Storage: Both Amazon Prime and Apple offer cloud storage options (with varying capacities depending on subscription tiers). This caters to users’ needs for backing up photos, videos, and documents.
Different Target Audiences:
- Value-Conscious Consumers: Amazon Prime targets value-conscious consumers who shop online regularly and appreciate the bundled benefits of a Prime membership.
- Apple’s Loyal Customer Base: Apple leverages its strong brand loyalty and existing user base to promote its services like Apple Music and iCloud storage.
Here’s a table summarizing the key areas of competition:
| Category | Amazon Prime | Apple |
|---|---|---|
| Focus | Online Retail & Subscription Services | Premium Hardware & Services |
| Value Proposition | Bundled Benefits (Free Shipping, Streaming, etc.) | Premium Products & Services (à la carte) |
| Streaming | Prime Video, Music Prime | Apple TV+, Apple Music |
| Cloud Storage | Amazon Drive | iCloud |
| Target Audience | Value-Conscious Consumers | Apple’s Loyal Customer Base |
Other Competitors:
1. Fitbit, Garmin

While Apple Watch dominates the smartwatch market, Fitbit and Garmin are strong competitors in the fitness tracker and smartwatch space. Here’s a breakdown of how they compete with Apple:
Focus on Fitness:
- Fitness Tracking Expertise: Fitbit and Garmin have a strong heritage in the fitness tracker market, offering a wider range of fitness-focused features like advanced sleep tracking, activity tracking with various metrics (distance, pace, calories burned), and built-in GPS for runners.
- Battery Life: Fitbit and Garmin devices often boast superior battery life compared to the Apple Watch, lasting for several days on a single charge. This appeals to users who prioritize uninterrupted fitness tracking.
Beyond Fitness Tracking:
- Smartwatch Features: While some Fitbit and Garmin models offer smartwatch features like notifications, contactless payments, and music storage, Apple Watch offers a wider range of these functionalities and deeper integration with the iPhone ecosystem.
- Price Point: Fitbit and Garmin tend to offer a wider range of trackers and smartwatches at various price points, catering to budget-conscious users or those who prioritize specific fitness features over extensive smartwatch functionalities.
Apple’s Counterarguments:
- Holistic Health Management: Apple Watch positions itself as a more comprehensive health and wellness device, offering features like heart rate monitoring, fall detection, and integration with health apps.
- Seamless Integration: Apple Watch excels in seamlessly integrating with iPhones, allowing users to make calls, send texts, and access various iPhone functionalities directly from their wrist.
Here’s a table summarizing the key areas of competition:
| Category | Fitbit & Garmin | Apple Watch |
|---|---|---|
| Focus | Fitness Tracking Expertise | Overall Smartwatch Functionality |
| Strengths | Advanced Fitness Tracking Features, Battery Life | Wider Smartwatch Features, iPhone Integration |
| Target Audience | Fitness Enthusiasts, Budget-Conscious Users | Tech-Savvy Users Prioritizing Smart Features |
| Price Point | Wider Range of Prices | Generally More Expensive |
These competitors and alternatives provide consumers with choices across different product categories, driving innovation and competition in the technology and consumer electronics industries.
Also Read: Top Microsoft Competitors and Alternatives
To read more content like this, subscribe to our newsletter