Siemens is a name synonymous with cutting-edge technology and industrial progress. As the largest industrial manufacturing company in Europe and a global leader in automation and software, Siemens boasts a rich history dating back to 1847. From its humble beginnings as a telegraph manufacturer, Siemens has continuously evolved, shaping industries and transforming the way we live and work.
Founded in Berlin by Werner von Siemens and Johann Georg Halske, the company initially focused on telegraphy, a revolutionary communication technology at the time. Their innovative approach, using a needle system instead of Morse code, laid the foundation for future advancements. Siemens’ entrepreneurial spirit didn’t stop there. The company quickly expanded its reach, establishing the first long-distance telegraph line in Europe, stretching from Berlin to Frankfurt. This pioneering spirit of connecting people and places became a hallmark of Siemens’ future endeavors.

Throughout the 20th century, Siemens continued to push boundaries. They became a major player in the electrification revolution, developing power generation and transmission technologies. Their contributions extended to transportation, with the creation of the first electric locomotive in 1879. Siemens’ influence transcended national borders, establishing a global presence with branches opening across Europe and beyond.
The latter half of the 20th century saw Siemens diversify its offerings. They ventured into medical engineering, building a reputation for high-quality diagnostic and therapeutic equipment. The company also embraced the information age, becoming a leader in telecommunications systems. This period also witnessed strategic acquisitions and spin-offs, allowing Siemens to streamline its focus on core competencies.
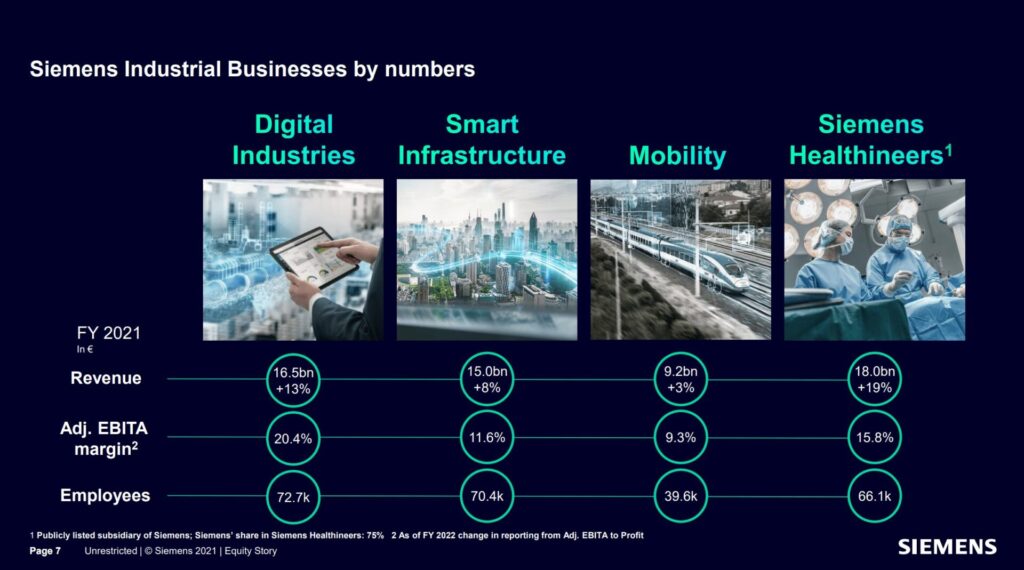
Today, Siemens operates under four major divisions: Digital Industries, Smart Infrastructure, Mobility, and Healthineers. Digital Industries offers automation solutions and software that empower businesses to optimize their operations. Smart Infrastructure focuses on intelligent building technologies and grid solutions that enhance efficiency and sustainability. Mobility delivers a range of transportation solutions, including high-speed trains and efficient railway systems.
Siemens’ commitment to research and development remains unwavering. The company is consistently ranked among the world’s largest patent holders, a testament to its dedication to innovation. Looking ahead, Siemens is at the forefront of shaping the future of industry. They are heavily invested in areas like digitalization, automation, and sustainable solutions, aiming to create a more efficient, connected, and environmentally responsible world.
In conclusion, Siemens’ story is one of continuous innovation and adaptation. From its early days as a telegraph pioneer to its current role as a global technology leader, Siemens has consistently pushed the boundaries of what’s possible. With a focus on digitalization, automation, and sustainability, Siemens is well-positioned to play a pivotal role in shaping the industries of tomorrow.
What’s new with Siemens?
Siemens has reported positive financial results for the first quarter of fiscal 2024, ending December 31, 2023. The company achieved a record high profit of €2.7 billion, showcasing continued strong performance. This positive financial standing allows Siemens to invest in future endeavors and partnerships.
On the business development front, there are interesting updates. Siemens AG is considering separating its energy division, Siemens Energy, into an independent company with a potential listing in India. Additionally, Siemens Energy might sell a portion of its stake in Siemens Ltd., valued at roughly $3.4 billion. These strategic moves could unlock further growth potential for both Siemens and Siemens Energy.
Siemens is also forging key partnerships to drive innovation across various sectors. A collaboration with Microsoft focuses on bringing generative AI to different industries, potentially revolutionizing design and manufacturing processes. In another partnership, Siemens, ubitricity, and Redbridge Council are working together to expand the electric vehicle charging network in Redbridge, UK. Similarly, Siemens’ data platform is assisting Northumbrian Water in tackling household leaks, demonstrating their commitment to sustainable solutions. Furthermore, Siemens hosted Greater Manchester schools for COP28, aiming to inspire the next generation of sustainability leaders. These collaborations highlight Siemens’ commitment to progress across various technological and environmental fields.
In the realm of product development, Siemens PLM Software’s NX software boasts a new feature called Performance Predictor. This innovative tool allows for real-time simulation of parts under stress, empowering engineers to make informed decisions regarding material durability.
Marketing Strategies of Siemens
Siemens operates in various sectors including industry, energy, healthcare, and infrastructure. Its marketing strategies encompass a blend of traditional and modern approaches, tailored to each business segment and geographic region. Here’s a detailed breakdown of Siemens’ marketing strategies:
1. Segmentation and Targeting
Siemens leverages segmentation and targeting to deliver impactful marketing messages to distinct customer groups. The company meticulously divides its vast product portfolio into categories that cater to specific industry needs. This strategic segmentation allows Siemens to tailor its marketing efforts and resonate more effectively with each target audience.
For instance, Siemens’ medical imaging division targets hospitals and healthcare providers. Their marketing emphasizes the exceptional quality, reliability of their equipment, and the improved patient care these solutions enable. In contrast, Siemens’ industrial automation division targets manufacturing companies. Their messaging highlights the efficiency and productivity gains manufacturers can achieve by utilizing their automation solutions.
By understanding the unique requirements of each customer segment, Siemens crafts targeted marketing messages that address their specific pain points and desired outcomes. This approach ensures their marketing efforts resonate with the right audience, ultimately driving sales and brand loyalty. The success of Siemens’ segmentation and targeting strategies is evident in their position as a global leader within the electrical engineering and automation industries.
2. Product Innovation and Differentiation
Siemens stands out as a leader in driving both product innovation and differentiation within the industrial landscape. For over two decades, they have been a significant force in digitalization and software advancements, consistently transforming ideas into tangible products for the future. A key differentiator for Siemens is their embrace of open innovation. This decentralized approach fosters collaboration and allows Siemens to capture valuable ideas from a wider pool, ultimately benefiting both the company and its customers.
Siemens Digital Industries Software empowers organizations of all sizes with a comprehensive digital toolkit. This suite, encompassing software, hardware, and services under the Siemens Xcelerator umbrella, facilitates digital transformation. By leveraging Siemens’ software and the power of digital twins, companies can optimize design, engineering, and manufacturing processes. This translates to efficient creation of sustainable products that address the needs of tomorrow.
Siemens’ innovation strategy is not merely about ideation; it’s about bringing those ideas to life and nurturing an ecosystem that fosters impactful technologies for the energy transition. Their broad-based approach focuses on multiple pathways, with digitalization, electrification, automation, and sustainability at the forefront. Siemens’ leadership in digitalizing industries allows them to provide software and services that enhance efficiency and productivity for their customers. Furthermore, their electrification efforts, including electric vehicles and charging infrastructure, contribute to a greener future by reducing emissions and improving air quality. Automation solutions enhance safety and workplace productivity, while their commitment to sustainable technologies through products and services helps minimize environmental impact.
3. Brand Positioning
Siemens has strategically crafted a brand position centered around leveraging digital technologies to tackle real-world challenges faced by society. Their brand purpose, “make real what matters,” underlines this commitment and translates into three key focus areas: electrification, automation, and digitization. This focus on impactful solutions resonates with customers and positions Siemens as a leader in shaping a better future.
“Ingenuity for life” serves as Siemens’ new brand slogan, effectively capturing their essence. “Ingenuity” represents their engineering expertise, entrepreneurial spirit, and unwavering dedication to innovation, all channeled towards societal benefit. “Life” signifies the positive impact Siemens’ products and services have on people’s lives.
Furthermore, Siemens revamped their brand experience to align with their new positioning. They implemented a “truly digital design system” – flexible, responsive, and optimized for screens. This bold and dynamic design ensures they stand out in the digital landscape. The success of this approach is evident in the positive customer reception and recognition Siemens has received for both their sound branding and employer branding efforts. The latter specifically targets changing the perception of Siemens from a traditional engineering company to a forward-thinking leader in the digital age. In essence, Siemens’ brand positioning effectively communicates their commitment to using cutting-edge technology to create a positive impact on the world.
4. Thought Leadership
Siemens has actively cultivated a thought leadership position within various industries. Their commitment to research and development, coupled with a focus on innovation that addresses real-world challenges, positions them as a trusted authority. Siemens consistently pushes boundaries and offers unique perspectives on industry trends, making them a go-to source for thought leadership content.
For instance, Siemens is a frontrunner in the digitalization of industries. Their expertise and software solutions empower businesses to optimize operations and achieve greater efficiency. A real-life example of this is Siemens’ work with Northumbrian Water. By utilizing Siemens’ data platform, Northumbrian Water was able to tackle household leaks, a major concern for water conservation. This not only showcases Siemens’ technological capabilities but also highlights their focus on practical solutions for real-world problems.
Furthermore, Siemens advocates for sustainable practices and plays a key role in the energy transition. Their focus on electrification, automation, and environmentally conscious technologies positions them as a thought leader in shaping a more sustainable future. An example of this leadership is Siemens’ partnership with Redbridge Council to expand the electric vehicle charging network in Redbridge, UK. This initiative directly contributes to reducing reliance on fossil fuels and promoting a cleaner transportation sector.
Siemens amplifies its thought leadership through various initiatives. They host conferences and events that bring together industry leaders to discuss critical issues and potential solutions. Additionally, Siemens publishes thought leadership content, such as articles, white papers, and webinars, that share their insights and expertise with a broader audience. By actively engaging in these activities, Siemens establishes itself as a thought leader at the forefront of industry progress.
5. Partnerships and Alliances
Siemens actively fosters collaboration through partnerships and alliances, strategically joining forces with other industry leaders to drive innovation and growth.
One such example is the alliance with Atos, a global leader in digital transformation. This collaboration combines Siemens’ digital product and software portfolio with Atos’ expertise in digital platforms and services. Together, they focus on accelerating digital transformation and achieving joint business growth for both companies.

Siemens also prioritizes partnerships that push the boundaries of technology. Their strategic partnership with Microsoft aims to unlock the vast potential of Artificial Intelligence (AI) across various industries. By working together, they can empower businesses to leverage AI for increased efficiency and productivity.
These are just a few examples of Siemens’ extensive network of partnerships and alliances. Through these collaborations, Siemens gains access to complementary expertise, expands its market reach, and accelerates the development of cutting-edge solutions that benefit both their partners and their customers.
6. Global Presence and Localized Marketing
Siemens has established a dominant global presence, reflected in its regional sales figures. In fiscal 2022, nearly half (47%) of their sales originated from Europe, the Middle East, and Africa (EMEA), showcasing their strong foothold in that region. The Americas contributed 29%, and Asia/Australia accounted for the remaining 25%, highlighting their well-balanced global reach. This extensive geographic footprint positions Siemens to cater to a diverse customer base across the world.
To ensure market success in each region, Siemens adopts a localized marketing strategy. Their “acting local” principle involves establishing regional headquarters and investing heavily in local R&D. This enables them to customize products, solutions, and services to address the specific needs and preferences of their customers in each market. For example, Siemens boasts a significant presence in over 20 Indian cities, with substantial investments in R&D and local partnerships. This localized approach has cemented their position as a leading player in the Indian market.
By strategically combining a global presence with localized marketing efforts, Siemens has become a true technology leader on a worldwide scale. Their products, solutions, and services cater to a vast customer base across all regions, ensuring their continued success and influence in the global market.