SAP SE, an acronym for Systems, Applications, and Products in Data Processing, is a global leader in enterprise resource planning (ERP) software and related enterprise applications. Founded in 1972 by five former IBM employees in Mannheim, Germany, SAP has grown to become one of the world’s leading providers of software solutions that facilitate effective data processing and information flow across organizations.
SAP’s software products are used by companies of all sizes to improve their operational efficiency, data management, and decision-making processes. The company’s core product is SAP ERP, the system that allows businesses to integrate all of their processes into one comprehensive system. This integration enables more streamlined operations and better visibility into the organization’s activities, which in turn leads to enhanced productivity and profitability.
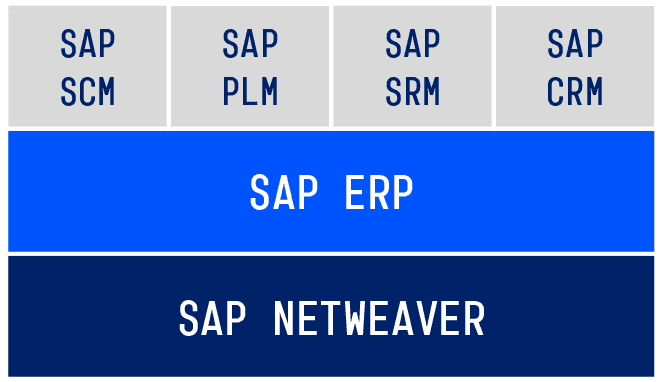
The breadth of SAP’s product offerings extends beyond just ERP. They include solutions for supply chain management, customer relationship management, product lifecycle management, and human capital management. Each solution is designed to be flexible and scalable, accommodating the growth and evolving needs of businesses across various industries. Furthermore, SAP is at the forefront of the latest technological advances, incorporating AI, machine learning, and Internet of Things (IoT) into their solutions to better serve their customers.
SAP operates worldwide, with more than 440,000 customers in over 180 countries. The company’s global presence is supported by more than 100,000 employees, and it boasts one of the largest ecosystems of partners, developers, and service providers who specialize in its software. This extensive network ensures that SAP solutions are supported and enhanced continuously, providing a high level of service to its users.
Financially, SAP is also a powerhouse. As a publicly traded company on both the Frankfurt Stock Exchange and the New York Stock Exchange, it consistently reports strong earnings and revenue growth. This financial stability allows SAP to invest heavily in research and development, ensuring that its technology remains at the cutting edge and maintains its competitive advantage in the market.
Innovation is a key component of SAP’s strategy. The company invests significantly in new technologies and business models, particularly through SAP Labs networks located around the world. These labs focus on developing new products that anticipate the future needs of businesses. SAP also embraces a strong sustainability ethos, aiming to empower not only economic success but also environmental and social progression through its technology.
SAP’s commitment to customer success is reflected in its comprehensive support system, which includes training, certification programs, and post-implementation support services. The company also fosters a large community of users, developers, and partners, collectively known as the SAP Community Network (SCN). This network is an invaluable resource for collaboration and learning, offering a platform for sharing expertise and best practices among its members.
Through continuous innovation and a deep commitment to its customers, SAP remains at the forefront of business technology systems. Its integrated solutions suite has proven essential for companies navigating the complex business landscape of the 21st century. As businesses continue to undergo digital transformation, SAP’s role as an enabler of that transformation becomes ever more crucial. By providing robust software solutions that streamline operations and enhance decision-making, SAP helps businesses to not only survive but thrive in an increasingly digital world.
SAP’s Top Competitors and Alternatives
SAP is a global leader in the enterprise resource planning (ERP) market and related enterprise applications, but it faces stiff competition from several other software giants. Here’s a detailed look at SAP’s top competitors and alternatives, each offering their own unique strengths and focusing on different segments of the market:
1. Oracle

Website – https://www.oracle.com/
Oracle is perhaps the most direct competitor to SAP, especially in the ERP space. Both companies offer comprehensive ERP systems that are favored by large enterprises worldwide. Oracle’s ERP Cloud is renowned for its scalability, robust functionality, and strong integration capabilities, making it a popular choice for businesses looking to manage their finances, operations, and human resources efficiently. Oracle also offers a wide range of cloud applications for finance, HR, and supply chain management, directly competing with similar SAP offerings.
2. Microsoft Dynamics 365

Website – https://www.microsoft.com/en-us/dynamics-365
Microsoft Dynamics 365 is another significant competitor, offering ERP and CRM solutions that integrate seamlessly with other Microsoft products like Office 365 and Azure. This integration provides a compelling option for businesses already entrenched in the Microsoft ecosystem. Dynamics 365 is known for its flexibility and is suitable for companies of all sizes, from small businesses to large enterprises, making it a versatile competitor to SAP.
3. Infor

Website – https://www.infor.com/
Infor is a key player in the ERP market, known for its industry-specific solutions that are tailored to meet the unique needs of various sectors such as manufacturing, healthcare, retail, and hospitality. This focus on industry-specific solutions sets Infor apart from SAP, which offers more generalized solutions. Infor’s CloudSuite, powered by Amazon Web Services, offers robust capabilities in cloud-based ERP solutions, directly challenging SAP’s S/4HANA and Business ByDesign.
4. Workday

Website – https://www.workday.com/
Workday specializes in human capital management (HCM) and financial management applications. While it started primarily in the HCM space, Workday has expanded into financial management, planning, and analytics, positioning itself as a comprehensive cloud solution for enterprise applications. Workday’s strength in usability and customer satisfaction makes it a strong alternative to SAP, particularly for companies focusing on HR and finance.
5. Salesforce

Website – https://www.salesforce.com/
While primarily known for its customer relationship management (CRM) software, Salesforce has expanded its offering to include a wider range of business applications through its cloud ecosystem. Salesforce’s platform now covers marketing, sales, service, and commerce, which intersects with some of SAP’s business applications. With its acquisition of Tableau and MuleSoft, Salesforce has strengthened its capabilities in business intelligence and data integration, areas that are also significant to SAP’s business model.
6. Epicor Software

Website – https://www.epicor.com/en/
Epicor provides tailored ERP solutions focused on specific industries such as manufacturing, distribution, retail, and services. Epicor’s emphasis on customizable and scalable ERP solutions makes it a favorable option for mid-sized businesses, challenging SAP’s ERP market share in these sectors.
7. IFS

Website – https://www.ifs.com/
IFS offers applications for enterprise resource planning, enterprise asset management, and field service management, with a strong focus on industries like manufacturing, construction, and services. IFS is known for its agility and user-friendly interface, making it a competitive alternative for businesses that require flexible and easily adaptable solutions.
Each of these competitors and alternatives brings different strengths to the table, from Oracle’s robust data capabilities and Microsoft’s integration with its own products to Workday’s user-friendly applications and Salesforce’s leadership in CRM. The choice among these platforms often depends on specific business needs, industry focus, existing IT infrastructure, and budget considerations.
For businesses evaluating ERP and CRM solutions, the decision extends beyond just features and price; it also involves considering the ecosystem, support, integration capabilities, and the long-term roadmap of the product. SAP, with its extensive portfolio and deep integration capabilities, continues to hold a significant position in the market but must continually innovate to stay ahead of these formidable competitors.
Also Read: Who are Oracle’s Top Competitors and Alternatives?
To read more content like this, subscribe to our newsletter




