The product life cycle is divided into four phases, namely introduction, growth, maturity, and decline. Product planning is done based on these steps.
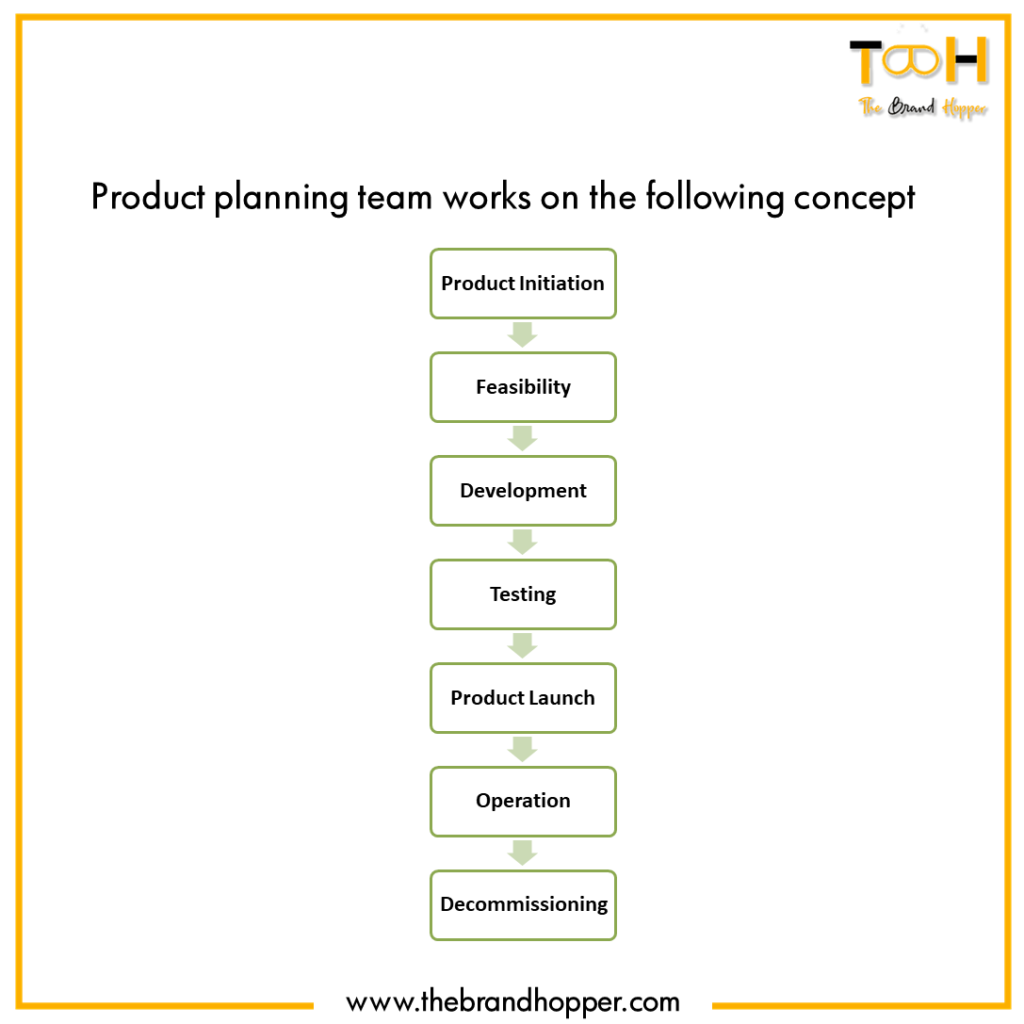
Product Initiation: In a product initiation phase, a request comes up for a new product or a modification in the existing product. Various management teams review these requests and study them in the context of the internal needs and external environment. If the product aligns with the companies objectives, the required funding is granted and it moves to the next stage.
Feasibility study: Here, the feasibility of the project is assessed in greater detail. The engineering and product management team evaluates the technical feasibility, and a general outline of the project is proposed. A time and cost estimates are made, and thus here, the team decides if they should move ahead with the project or not.
Design and Plan Phase: At this stage, all cross-functional teams prepare documents related to the product like marketing service description, technical service descriptions, and Customer Care works on specifying their requirements for supporting the service. All these documents are approved and confirmed by the project manager, and then the project moves into the development phase.
Development Phase: All the engineering work is completed here. Documentation to support Customer Care, Training, Vendors, and Clients is created during this phase. The Quality Assurance (QA) Group prepares for the testing handoff by documenting Test Plans and Test Specifications. A decision gate ensures that all pieces required for testing have been completed. The following are requirements to pass through the decision gate:
- Ready for Testing Phase from a System Integration Test perspective
- Documentation Complete
- Test Environment Complete
- Code Complete
- Vendor Requirements met
- Integration Testing & Results Complete.
Once the Project Team has approved the readiness of the service, the Development Checklist is compiled, and then comes the Testing Phase.
Testing Phase: In this stage, software and hardware changes are made to the service. The service is tested in a lab environment. Operations Readiness is tested, and then the service may undergo field trials. The Testing Phase Decision Gate is based on the QA Test Results, Operations Test Results, Field Verification, Change Requests, and Business Needs. A ‘go’ decision at the gate authorizes the launch of the service.
Product Launch Phase: The product launch phase deploys the new service. Other support processes are initiated, and then the final service check is done to ensure stability.
Operation Phase: The Operation Phase is typically the longest of the phases. The team tracks problems and bugs and responds to customer issues regarding the product in a timely and cost-effective manner.
Decommissioning Phase: This is the end stage of the product life cycle. It is where a decommission plan is prepared and executed to address all aspects of the archiving, transferring and disposing of product or service components.
Explore more concepts:




