FedEx is an American multinational delivery services company that is known for its fast and reliable shipping services. The company was founded in 1971 by Frederick W. Smith, who had the idea of creating a system for overnight package delivery that could revolutionize the shipping industry.
FedEx started out as Federal Express, a company that provided overnight air delivery services to 25 cities in the United States. The company’s early success was driven by its innovative approach to package tracking and delivery, which relied on a central hub-and-spoke system that allowed packages to be transported quickly and efficiently across the country.
Over the years, FedEx has expanded its operations and diversified its business to include a range of shipping and logistics services. Today, the company offers a wide range of services, including domestic and international shipping, e-commerce solutions, customs brokerage, and supply chain management.
One of the key factors that has contributed to FedEx’s success is its focus on customer service. The company has developed a reputation for providing fast and reliable shipping services, and it has invested heavily in technology and infrastructure to ensure that its customers receive their packages on time and in good condition.
In recent years, FedEx has also been working to reduce its environmental impact, by investing in more fuel-efficient aircraft and vehicles, and by implementing sustainable practices across its operations.
Overall, FedEx is a major player in the global shipping and logistics industry, with a reputation for innovation, reliability, and customer service. Its continued success in the years ahead will depend on its ability to adapt to the changing needs of its customers and to stay ahead of the curve in terms of technology and innovation.
Founding History of FedEx
FedEx Corporation, commonly known as FedEx, is an American multinational delivery services company. It was founded in 1971 by Frederick W. Smith, who recognized the need for a more reliable and efficient delivery service for businesses.

In the late 1960s, Smith was a student at Yale University, studying economics. While there, he wrote a paper proposing an overnight delivery service that would take advantage of new developments in air transportation. Smith realized that by using airfreight instead of ground transportation, packages could be delivered much faster and more reliably, even over long distances. He believed that such a service would be in high demand among businesses, particularly those in the financial and technology sectors.
After graduating from Yale, Smith enlisted in the U.S. Marine Corps and served two tours of duty in Vietnam. In 1970, he began developing his idea for an overnight delivery service, drawing on his experience in the military and his knowledge of the transportation industry.
To start the company, Smith raised $4 million in venture capital and acquired a fleet of 14 small aircraft. He then set up operations in Memphis, Tennessee, where he established the company’s headquarters and built a hub for sorting and processing packages.
FedEx began operations on April 17, 1973, with 389 employees and 14 aircraft. The company’s first flight was from Memphis to Chicago, carrying 186 packages. The service was an immediate success, with customers impressed by the speed and reliability of the delivery.
Over the next few years, FedEx continued to expand its operations, adding new routes and aircraft, and developing a sophisticated computerized system for tracking and processing packages. By the end of the decade, the company had become a major player in the transportation industry, with annual revenue of over $1 billion.
Today, FedEx is one of the world’s largest delivery services companies, with a global network that spans more than 220 countries and territories. The company employs over 500,000 people worldwide and generates annual revenue of more than $80 billion. It continues to innovate and adapt to changing market conditions, with a strong focus on technology and sustainability.
Why is FedEx a leading global logistics Service provider?
FedEx Creates value by offering “High value-added” package delivery. As their slogan says, “The World On Time,” FedEx emphasizes delivery absolutely, positively being overnight. FedEx also guarantees speed with reliability at a rate higher than 99%.
FedEx has a proper procedure for shipping your courier to door which consists of following steps:
Create an account- The first step is to sign up for FedEx account. From this account, you can order supplies, view the history of your shipment, and track the order.
Transfers cost estimation- After signing up, the system offers cost estimation based on origin, destination, packaging cost, and need of freight or not. These are the most important deciding factors in your shipment cost.
Best possible pickup point- At this step, FedEx offers you an opportunity to try to minimize your shipment by using the best on-time pickup point, and FedEx sends a courier to your selected location.
International shipping guide- Basic guidelines are given in this step about foreign taxes, codes, and customs duties.
Freight shipping- Freight shipping options can be explored by using tools and service options.
Return – If you want to return your product(s), you have to get return label from shipping site, and then you can discover convenient returns
Customer-Centricity is the Core of FedEx Operations
The use of technology by FedEx is for consumer-centricity, rather than for being competitive. With FedEx, companies can, in real-time, assess the status of their shipments at any possible position along the distribution route.
Customers can monitor shipments in three ways: on the Internet through the FedEx website, using the FedEx Ship Manager at fedex.com, or using the FedEx WorldTM Shipping App. FedEx is actively developing new technology to provide time-defined services to customers.
Operational Activities Behind Every Delivery in FedEx
COSMOS (Customer Operations Service Master On-line System) is a computerized package tracking system that monitors every stage of the Federal Express delivery process. FedEx workers continuously upload information into COSMOS through different means. Customer service representatives enter information through computer terminals into COSMOS, notify the dispatcher closest to the pickup or delivery.
Constant tracking allows the company to maintain positive control over shipments every step of the way. It is so integral part of the system that FedEx promises to deliver all packages within one minute of the delivery commitment, or the customer does not pay. The company also offers a second guarantee that is unique to the industry. If a customer cannot be told exactly where their package is, within 30 minutes of their inquiry, FedEx will pay the transportation costs of the box.
From COSMOS and tracking to service guarantees, the Federal Express network is designed to provide 100% customer satisfaction.
FedEx also uses ‘Command and Control,’ the Memphis SuperHub-based satellite to the ground-level operating system that enables FedEx to distribute packages in any weather condition on the quickest, easiest and safest path. It is a worldwide relational database that manages FedEx logistics. Command and control is, in essence, the largest UNIX organization in the commercial world. The program makes use of satellite and computer communication technology to monitor routing and traffic information all in real-time.
Also Read: United Parcel Service (UPS) – The Glorious History of Over 100 Years
FedEx uses NASA weather data and artificial intelligence to plot alternate routes when the weather can disrupt on-time delivery. The program offers the best three alternative transport options for a product, enabling the client to choose the fastest, safest, and most cost-effective route.
The Command and Control network guarantees the seamless operation of inbound and outbound aircraft and thousands of delivery vehicles by linking to more than 750 customer service workstations, over 500 aircraft and traffic hubs across the globe. Though invisible to the consumer, Command, and Control is one of the most significant technical innovations within the business.
Business Model of FedEx
FedEx operates on a business model that focuses on providing fast, reliable, and convenient courier and logistics services to businesses and individuals around the world. The company generates revenue by charging fees for its services, including shipping, freight, and logistics solutions.
FedEx’s business model can be broken down into the following components:
Services: FedEx offers a wide range of services to its customers, including overnight shipping, international shipping, ground shipping, freight services, and logistics solutions. The company’s services are designed to cater to the needs of businesses and individuals, with options for different package sizes, delivery speeds, and destination locations.
Pricing: FedEx’s pricing model is based on a combination of factors, including package weight, dimensions, shipping speed, and destination location. The company offers pricing plans for both businesses and individuals, with discounts available for high-volume shippers.
Infrastructure: FedEx operates a massive infrastructure that includes planes, trucks, and other vehicles, as well as sorting and distribution centers around the world. This infrastructure enables the company to transport packages and shipments quickly and efficiently, while its tracking system provides customers with real-time visibility into the status of their shipments.
Technology: FedEx’s technology solutions play a key role in its business model. The company offers a range of technology tools to help businesses manage their supply chains more efficiently, including warehouse management systems, transportation management systems, and e-commerce solutions.
Customer Service: FedEx places a strong emphasis on customer service and strives to provide fast, reliable, and convenient services to its customers. The company’s customer service team is available 24/7 to assist customers with their shipping and logistics needs.
Overall, FedEx’s business model is built around providing high-quality courier and logistics services to businesses and individuals around the world. The company’s focus on technology, infrastructure, and customer service helps to differentiate it from competitors and maintain its position as a leading global logistics service provider.
How does FedEx earn money? – Revenue Streams of FedEx
FedEx generates revenue primarily through its transportation and logistics services. The company operates in four main segments, which are as follows:
FedEx Express: This segment is the company’s largest revenue generator, accounting for more than 50% of total revenue. FedEx Express offers time-definite delivery services for documents, packages, and freight to customers worldwide. The segment includes several services such as international express delivery, domestic express delivery, and ground delivery services. FedEx Express generates revenue primarily by charging customers based on the weight, size, and distance of their shipments.
FedEx Ground: This segment provides small-package ground delivery services to customers throughout North America. It generates revenue by charging for pickup, transportation, and delivery services. FedEx Ground also offers value-added services such as residential delivery and delivery confirmation at an additional fee. The segment accounts for about 20% of total revenue.
FedEx Freight: This segment provides less-than-truckload (LTL) freight services throughout North America. FedEx Freight generates revenue through shipping fees based on weight, distance, and other factors. The segment accounts for around 15% of total revenue.
FedEx Services: This segment provides sales, marketing, information technology, communications, and other support services to the other three segments. FedEx Services generates revenue by charging fees for its services. The segment accounts for around 10% of total revenue.
Other services: In addition to the main segments, FedEx generates revenue through various other services. For example, its subsidiary, FedEx Office, provides printing and shipping services to customers. FedEx also offers customs brokerage, e-commerce fulfillment, and other specialized logistics services. These additional services account for the remaining 5% of total revenue.
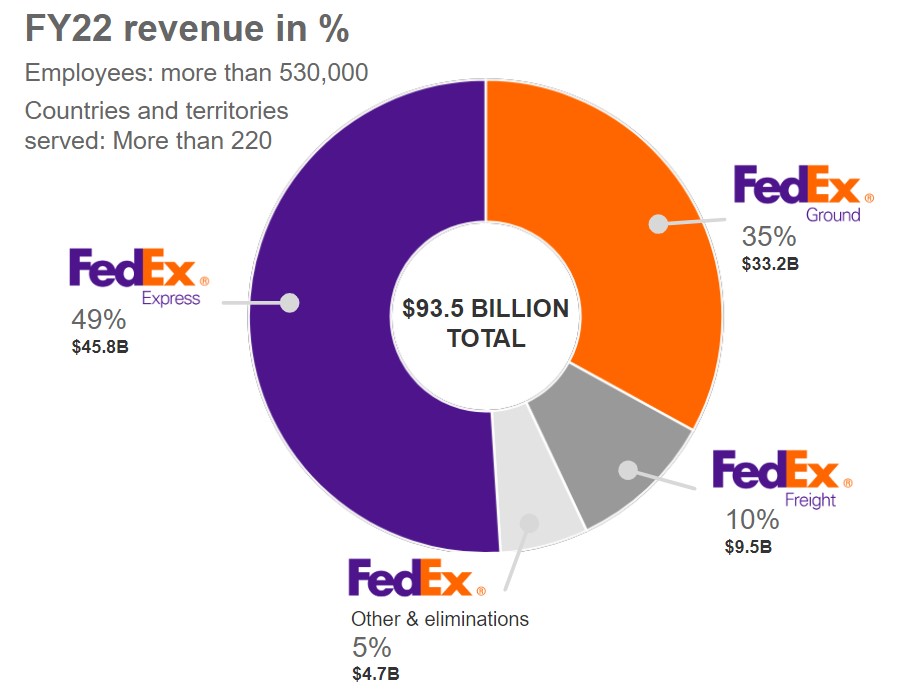
Overall, FedEx’s revenue streams are diversified across different segments and services, which helps the company maintain a strong financial position. By offering a range of transportation and logistics services to customers worldwide, FedEx is able to generate steady revenue and compete effectively in the industry.
Competitors of FedEx
FedEx has several competitors in the transportation and logistics industry. Some of the major competitors of FedEx are:
United Parcel Service (UPS): UPS is one of the largest package delivery companies in the world and provides similar services to FedEx. The company offers express delivery, ground delivery, and freight services to customers worldwide.
DHL: DHL is a global logistics company that provides air and ocean freight forwarding, warehousing, and transportation services. The company also offers express delivery services in some markets, competing with FedEx and UPS.
Amazon Logistics: Amazon Logistics is the logistics arm of e-commerce giant Amazon and provides delivery services to its own customers, as well as third-party sellers on its platform. The company is expanding its logistics capabilities and is increasingly competing with FedEx and other delivery companies.
USPS: The United States Postal Service is a government-run postal service that provides delivery services within the United States. While USPS does not offer the same range of services as FedEx, it is a major competitor in the domestic delivery market.
Regional carriers: There are also many regional carriers that provide delivery services in specific markets or regions. These carriers may compete with FedEx in certain areas, particularly for small package delivery and last-mile delivery services.
Overall, FedEx faces significant competition in the transportation and logistics industry, with many large and well-established companies competing for market share. The company has historically competed on the basis of its reliability, speed, and range of services, as well as its strong brand recognition and global network.
To read more content like this, subscribe to our newsletter




