Amazon is an American multinational technology company specializing in e-commerce, cloud computing, digital streaming, and artificial intelligence (AI). It was founded by Jeff Bezos in 1994 as an online bookstore and has since become one of the most valuable companies in the world. Amazon is the world’s largest online retailer, offering a wide range of products, including books, electronics, music, movies, home goods, clothing, toys, and food.
Amazon’s primary business is e-commerce, but the company also has a number of other businesses. These include:
- Amazon Web Services (AWS): AWS is a cloud computing platform that provides businesses with a wide range of services, including storage, computing power, and networking.
- Amazon Prime: Amazon Prime is a subscription service that offers a number of benefits, including free two-day shipping, access to Amazon Prime Video, and exclusive deals.
- Amazon Kindle: The Kindle is an e-reader that allows users to read books, magazines, and other digital content.
- Amazon Echo: The Echo is a smart speaker that can be used to play music, make hands-free calls, and control other smart home devices.
Amazon has had a significant impact on the world. The company has revolutionized the way people shop, and it has also had a major impact on the retail industry. Amazon has also been a pioneer in the development of cloud computing, and its AWS platform has become the industry standard.
Success Story of Amazon
In the ever-evolving world of e-commerce, one name stands out as a pioneer and a global giant: Amazon. Founded in 1994 by Jeff Bezos, Amazon began as an online bookstore in a garage in Bellevue, Washington. Over the years, it has transformed into the world’s largest online marketplace, offering a vast array of products and services. This success story is a testament to Bezos’ visionary leadership, relentless pursuit of innovation, and Amazon’s ability to adapt to changing market dynamics.
The Genesis of Amazon:
Jeff Bezos, a former Wall Street hedge fund executive, embarked on the journey of building Amazon with a clear vision – to deliver any book to any reader anywhere. The company’s humble beginnings in a garage highlight the entrepreneurial spirit and determination that would later define its success. In 1995, Amazon.com went live, focusing initially on the sale of books due to their logistical convenience and high order value.
The Journey to Profitability:
Amazon’s early years were marked by intense efforts to establish a robust online platform. Despite facing skepticism and not turning a profit until 2001, Bezos remained steadfast in his belief in the vast growth potential of the internet. The company went public in 1997, with an IPO that priced its stock at $18 a share and a market capitalization of approximately $438 million. Bezos instilled a “Get Big Fast” culture, prioritizing revenue growth and customer acquisition over short-term profitability.

Diversification Beyond Books:
As Amazon expanded internationally in 1998, its product offerings grew beyond books to include music and videos. Acquiring small online bookstores in the UK and Germany, Amazon broadened its reach and solidified its status as an all-purpose online store. The company’s product range expanded further in 1999 to include consumer electronics, video games, software, home-improvement items, toys, and more.
Milestones in Amazon’s Success:
Several key milestones marked Amazon’s journey to becoming an e-commerce behemoth:
- 1995: Launch of amazon.com
- 1999: Amazon becomes the world’s largest online sales platform
- 2005: Introduction of Prime Membership
- 2007: Launch of the Kindle, Amazon’s first consumer product
- 2017: Acquisition of Whole Foods Market, Inc., entering the grocery industry
- 2018: Amazon becomes the largest bookseller and the third-largest smart devices seller in the US
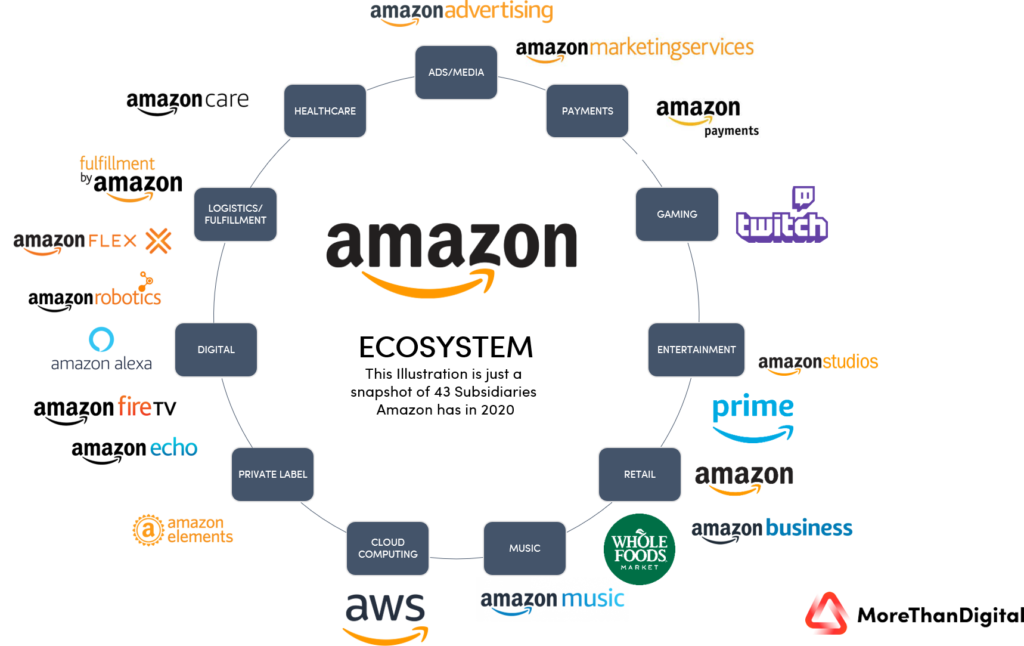
The Power of Expansion and Acquisition:
Amazon’s massive growth can be attributed to its strategic expansion into new markets and acquisitions. The company’s foray into cloud computing with Amazon Web Services (AWS) in the late 2000s revolutionized the tech industry. AWS’s powerful computing systems became the backbone for countless businesses, establishing Amazon as a world leader in computing services.
Tech Devices and Innovation:
Amazon’s ventures into technology devices, such as the Kindle, Fire HD, and Fire TV, demonstrated its commitment to innovation. The launch of Alexa, a smart assistant, further solidified Amazon’s presence in the tech world. By allowing developers to build upon Alexa and offering machine learning tools, Amazon positioned itself at the forefront of the technology revolution.
Entertainment and Streaming Services:
In 2010, Amazon entered the entertainment industry with the launch of Prime Video and Amazon Studios. The acquisition of Twitch in 2014 marked its entry into the world of video game streaming. Today, Prime Video stands as the world’s second-largest online streaming platform, with notable achievements like an Oscar-nominated film.
Grocery Services and Beyond:
Amazon’s interest in online grocery services dates back to 1999, with investments in HomeGrocer.com. The launch of Amazon Fresh in 2007 and the acquisition of Whole Foods in 2017 strengthened its position in the grocery market. Amazon’s relentless pursuit of disruption is evident in its focus on expanding its grocery delivery services.
The Future of Amazon
As Amazon continues its relentless pursuit of growth, entering new markets and disrupting traditional industries, the global impact of this e-commerce giant is undeniable. However, concerns about market inflexibilities and potential pricing issues loom on the horizon. Nevertheless, Amazon’s success story remains an inspiration for aspiring entrepreneurs worldwide, showcasing the transformative power of vision, innovation, and relentless determination.
Success Factors of Amazon
Amazon has revolutionized the way people shop and do business online. Founded in 1994 by Jeff Bezos, Amazon has grown from a small startup to a global powerhouse with over $1 trillion in Market Cap. The company’s success can be attributed to several key factors, which have contributed to its dominance in the digital marketplace. Let’s explore the success factors of Amazon in detail, providing insights into the company’s strategies, strengths, and innovations that have made it a household name.
1. Customer Obsession
Amazon’s primary focus has always been on customer satisfaction. The company’s mission statement reads, “Our vision is to be Earth’s most customer-centric company, where customers can find and discover anything they might want to buy online.“ To achieve this goal, Amazon has implemented various initiatives aimed at enhancing the customer experience. For instance, the company offers personalized product recommendations based on users’ browsing history and purchase behavior. Additionally, Amazon’s customer service is known for being responsive and helpful, ensuring that customers receive prompt assistance whenever needed.
2. Continuous Innovation
Amazon has consistently invested in research and development (R&D), leading to numerous innovations that have disrupted traditional retail models. Some notable examples include:
- 1-Click ordering: Introduced in 1997, this feature allows customers to make purchases quickly and easily without re-entering their payment information.
- Fulfillment by Amazon (FBA): Launched in 2006, FBA enables third-party sellers to store and ship products directly from Amazon’s warehouses, streamlining logistics and reducing delivery times.
- Prime membership program: Debuted in 2005, Amazon Prime offers perks like free two-day shipping, access to streaming services, and other benefits, fostering customer loyalty and encouraging repeat business.
3. Diversification & Expansion
Amazon has expanded beyond its core e-commerce business, exploring new markets and opportunities. Key diversification efforts include:
- Cloud computing: Amazon Web Services (AWS) was launched in 2006 and has since become a leading cloud infrastructure platform, offering data storage, analytics, machine learning, and security solutions to businesses.
- Digital media: Amazon has developed a robust digital media presence through its subsidiary, Amazon Studios, producing original content for Amazon Prime Video, including critically acclaimed shows like “The Grand Tour” and “The Marvelous Mrs. Maisel.”
- Physical stores: Amazon has opened brick-and-mortar locations, such as bookstores and grocery stores, blending its online capabilities with offline experiences.

4. Artificial Intelligence (AI) Integration
Amazon has leveraged AI technology to enhance various aspects of its operations, including:
- Product recommendation algorithms: Amazon uses advanced algorithms to suggest products based on user preferences, improving customer satisfaction and driving sales.
- Natural Language Processing (NLP): Alexa, Amazon’s virtual assistant, utilizes NLP to understand voice commands, allowing users to interact with devices and access information hands-free.
- Predictive analytics: Amazon employs predictive modeling to forecast demand, optimize inventory management, and streamline supply chain processes.
5. Strategic Partnerships & Acquisitions
Amazon has formed partnerships and acquired companies to expand its offerings and reach new audiences. Notable collaborations include:
- Retail partnerships: Amazon has partnered with major retailers like Target and Kohl’s, allowing customers to order products online and pick them up in-store or return items purchased from Amazon at these retail locations.
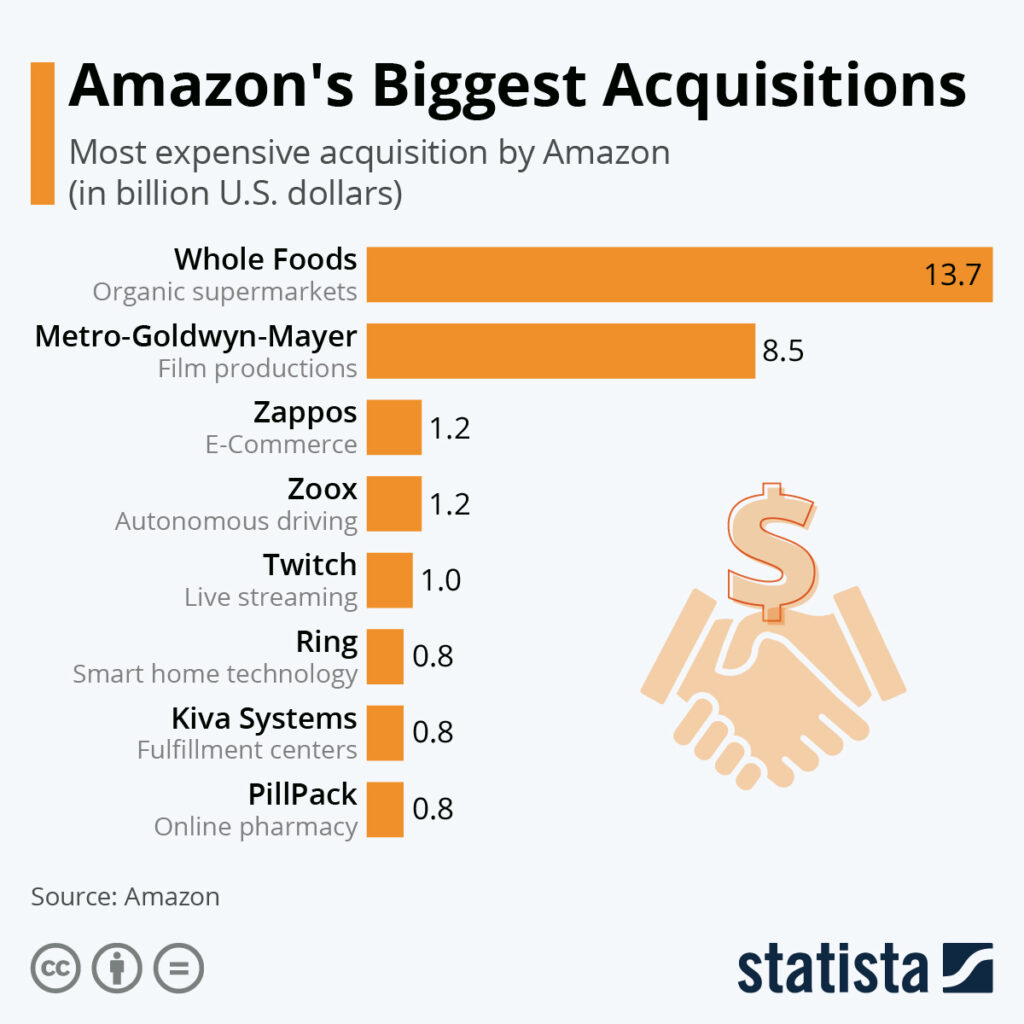
- Whole Foods Market acquisition: In 2017, Amazon acquired the upscale grocery chain, integrating its Prime Now delivery service and introducing new technologies like smart shopping carts and augmented reality displays.
- Twitch acquisition: In 2014, Amazon bought Twitch Interactive, a live streaming platform popular among gamers, expanding its reach into the gaming community and offering new monetization opportunities for content creators.
6. Logistical Efficiency & Infrastructure
Amazon has invested heavily in building a robust logistics network, enabling fast and reliable deliveries. Key initiatives include:
- Network expansion: Amazon has established a vast network of fulfillment centers, distribution centers, and sortation centers across the globe. These facilities are strategically located near highways, airports, and transportation hubs to ensure efficient transportation and delivery.
- Automated warehouse management: Amazon uses automated systems and robotics in its warehouses to streamline inventory management, picking, packing, and shipping processes. This helps reduce errors, increases efficiency, and enables faster order fulfillment.
- Last-mile delivery: Amazon has introduced various last-mile delivery solutions, such as Amazon Flex, Amazon Lockers, and Amazon Key, to provide customers with flexible and convenient delivery options.
7. Data-Driven Decision Making
Amazon collects and analyzes vast amounts of data on customer behavior, preferences, and transactions. This data is used to inform decision making, improve customer experiences, and drive business growth. Key applications of data analysis include:
- Personalized recommendations: Amazon uses machine learning algorithms to suggest products based on individual customer preferences, purchase history, and browsing behavior.
- Supply chain optimization: Amazon analyzes data on inventory levels, demand patterns, and shipping routes to optimize its supply chain and minimize costs.
- Marketing strategy: Amazon uses data to identify customer segments, tailor marketing campaigns, and measure advertising effectiveness.
8. Disruptive Business Models
Amazon has disrupted multiple industries by introducing innovative business models that challenge traditional ways of doing business. Examples include:
- Subscription-based services: Amazon Prime, which offers free two-day shipping, streaming, and other benefits, has transformed the retail landscape by creating a loyal customer base willing to pay annually for premium services.
- Online marketplaces: Amazon Marketplace allows third-party sellers to list and sell products directly to customers, eliminating intermediaries and increasing competition.
- Payment processing: Amazon Pay, a digital payment service, simplifies checkout processes for customers and reduces transaction fees for merchants.
9. Sustainability and Social Responsibility
Amazon has taken steps towards sustainability and social responsibility, recognizing the impact of its large scale operations on the environment and society. Efforts include:
- Renewable energy: Amazon has pledged to use 100% renewable energy sources by 2030, investing in wind farms, solar panels, and hydroelectric power.
- Sustainable packaging: Amazon promotes eco-friendly packaging materials, reduced packaging waste, and ‘frustration-free’ packaging designed to minimize damage during transit.
- Employee welfare: Amazon has faced criticism for worker treatment in its warehouses but has responded by implementing measures to improve working conditions, increase minimum wage, and provide training programs for employees.
10. Continuous Learning and Improvement
Amazon fosters a culture of continuous improvement, encouraging experimentation, risk-taking, and learning from failures. This mindset is reflected in practices such as:
- Customer feedback: Amazon solicits customer feedback extensively, using it to refine products, services, and overall customer experience.
- Innovation labs: Amazon operates secretive labs focused on developing cutting-edge technologies, like drone delivery and augmented reality, to stay ahead of competitors.
- Failure tolerance: Amazon embraces failure as a necessary step in the innovation process, with CEO Jeff Bezos famously stating, “If you’re going to take bold bets, you have to be willing to fail.”
By focusing on these ten factors, Amazon has created a powerful ecosystem that continues to disrupt industries and set new standards for customer expectations. As the company evolves and expands into new areas, it’s likely that these principles will remain central to its success.
Also Read: Marketing Strategies, Marketing Mix and STP of Amazon
To read more content like this, subscribe to our newsletter



