Accenture is a global professional services company that provides services in strategy, consulting, digital transformation, and operations. It is one of the world’s largest consulting firms, with over 733,000 employees in more than 200 cities in 120 countries. Accenture serves more than 9,000 clients—including more than three quarters of the Fortune Global 100 and Fortune Global 500—spanning the full range of industries around the world. Accenture’s clients include some of the world’s largest and most successful companies, as well as governments and other organizations.
Accenture was founded in 1989 as a spin-off from Arthur Andersen, and it has grown rapidly since then. The company has expanded its service offerings and geographic reach over the years, and it is now one of the leading providers of professional services in the world.
Accenture’s services can be broadly divided into two categories: consulting and operations. Consulting services include strategy, innovation, technology, and people consulting. Operations services include business process outsourcing, IT services, and cloud services.
Accenture’s clients use its services to improve their performance, transform their businesses, and create new value for their customers. For example, Accenture has helped clients to improve their customer service, reduce costs, increase revenue, and develop new products and services.
Accenture is a leader in the use of technology to help its clients succeed. The company has invested heavily in research and development, and it has a number of proprietary technologies and solutions. Accenture also has a strong ecosystem of partners, including technology companies, system integrators, and other professional services firms.
Success Story of Accenture
Accenture has cemented its place as a premier consulting firm through a rich history of innovation, evolution, and resilience. In this article, we will delve into the remarkable journey of Accenture, tracing its origins, transformation, and key developments that have shaped it into the industry giant it is today. From its early years as part of Arthur Andersen to its current status as a technology and consulting powerhouse, Accenture’s success story serves as an inspiration for businesses worldwide.
Formation and Early Years
Accenture’s story begins in the early 1950s when it operated as the business and technology consulting division of the renowned accounting firm Arthur Andersen. At this time, Accenture conducted a groundbreaking feasibility study for General Electric, which ultimately led to the installation of a UNIVAC I computer at GE’s Appliance Park in Louisville, Kentucky. This installation is believed to be the first commercial use of a computer in the United States, marking a pivotal moment in the history of technology consulting.
Split from Arthur Andersen
The late 1980s and early 1990s saw increasing tension between Andersen Consulting and Arthur Andersen, with the former paying a significant portion of its profits to the latter while competing through its business consulting service line. This dispute came to a head in 1998 when Andersen Consulting put a 15% transfer payment into escrow, resulting in a breach of contract claim. In 2000, an arbitration process with the International Chamber of Commerce severed all contractual ties between Andersen Consulting and Arthur Andersen. As part of the resolution, Andersen Consulting paid a substantial sum held in escrow to Arthur Andersen, leading to the renaming of the entity as Accenture.
Emergence of Accenture
On 1 January 2001, Andersen Consulting officially adopted the name “Accenture.” The name “Accenture” reflects the company’s vision, derived from the words “Accent on the future.” This new identity signaled a fresh start and a global outlook for the firm, emphasizing its intention to be a leader in the world of consulting.
Public Offering and Expansion
Accenture’s initial public offering (IPO) on 19 July 2001 marked a significant milestone in its history. The IPO was priced at $14.50 per share, and shares began trading on the New York Stock Exchange. On the first day, Accenture raised nearly $1.7 billion. This step towards becoming a publicly traded company symbolized Accenture’s transition into a new era of growth and global expansion.

Moving Headquarters and Tax Controversy
In 2009, Accenture’s board of directors unanimously approved a change in the company’s place of incorporation from Bermuda to Ireland. This shift was accompanied by a rebranding, with the company becoming Accenture plc. The move to Ireland raised questions about corporate taxes, as Accenture paid significantly lower taxes in Ireland than it would have in the United Kingdom. This choice sparked controversy and discussion about tax avoidance practices among multinational corporations.
Healthcare IT Project and Challenges
Accenture made headlines for its involvement in an IT overhaul project for the British National Health Service (NHS) in 2003. However, the project faced significant challenges, leading Accenture to withdraw from the contract in 2006 due to disputes over delays and cost overruns. The UK government later abandoned the project in 2011, citing similar issues. This experience highlighted the complexities and challenges of large-scale government IT projects.
Global Expansion and Technology Leadership
With a presence in over 120 countries, Accenture’s global reach has been instrumental in its success. The company’s diversification into technology services and its focus on innovation have made it a leader in digital transformation. Accenture has consistently stayed ahead of industry trends and emerging technologies, further strengthening its position in the consulting and technology space.
Corporate Social Responsibility and Sustainability
Accenture has also demonstrated a commitment to corporate social responsibility and sustainability. Initiatives like Skills to Succeed reflect the company’s efforts to make a positive impact on society by providing individuals with the skills needed to secure employment and build sustainable careers. Accenture’s sustainability goals, including achieving net-zero emissions by 2025, showcase its dedication to environmental responsibility.
Leadership Changes and Controversies
Over the years, Accenture has witnessed changes in leadership. CEO Pierre Nanterme’s resignation in 2019, citing health reasons, led to the appointment of Julie Sweet as the new chief executive officer. The company has faced controversies related to the working conditions of content moderators and its government contracts, demonstrating the challenges associated with rapid growth and diverse business activities.
Recent Acquisitions and Expansion
Accenture’s growth has continued with a series of acquisitions in various domains, including cybersecurity, data analytics, and digital transformation. These acquisitions have bolstered the company’s capabilities and services, positioning it as a go-to provider in a rapidly evolving technology landscape.
Challenges and Resilience
While Accenture’s journey has seen its share of challenges and controversies, the company’s resilience, adaptability, and commitment to its core values have been central to its success. The ability to navigate economic downturns, address tax-related concerns, and deliver complex projects underscores Accenture’s position as a pioneering consulting firm.
Accenture’s success story is a testament to its ability to evolve, innovate, and maintain a steadfast commitment to its core values. From its humble beginnings as part of Arthur Andersen to its current status as a global technology and consulting leader, Accenture’s journey is one of transformation, expansion, and adaptation.
In a world where the business landscape is continually changing, Accenture’s ability to embrace change, stay at the forefront of technological advancements, and consistently deliver value to clients stands as a shining example for both established businesses and aspiring entrepreneurs. Accenture’s success story is not just a testament to its own growth but also a source of inspiration for the broader consulting and technology industry.
Success Factors of Accenture
Accenture is a leading global professional services company that provides strategy, consulting, digital, technology, and operations services to clients across various industries. The company has been successful in establishing itself as a trusted partner for businesses, governments, and organizations, helping them navigate the complexities of a rapidly changing world. Let’s explore the success factors of Accenture and what sets it apart from its competitors.
1. Strong Leadership: One of the key success factors of Accenture is its strong leadership. The company’s leaders have a clear vision for the future and are committed to delivering exceptional results for their clients. They have fostered a culture of innovation, collaboration, and inclusion, which has helped the company stay ahead of the curve. Under the guidance of CEO Julie Sweet, Accenture has made significant investments in emerging technologies such as artificial intelligence, blockchain, and cloud computing, positioning itself as a leader in these areas.

2. Client Focus: Accenture’s client-centric approach is another critical factor in its success. The company understands the importance of building long-term relationships with its clients and has established a robust delivery model that focuses on providing value and achieving measurable outcomes. Accenture’s experts work closely with clients to identify their specific needs and develop tailored solutions that address their unique challenges. This collaborative approach has enabled the company to build a loyal customer base and attract new clients.
3. Diverse Portfolio of Services: Accenture offers a comprehensive portfolio of services, including strategy, consulting, digital, technology, and operations. This diversity allows the company to cater to a wide range of clients across different industries, from healthcare and financial services to retail and consumer goods. By offering a broad spectrum of services, Accenture can provide end-to-end solutions that help clients achieve their business objectives. Whether it’s developing a digital transformation strategy or implementing a new technology platform, Accenture has the expertise and resources to deliver results.
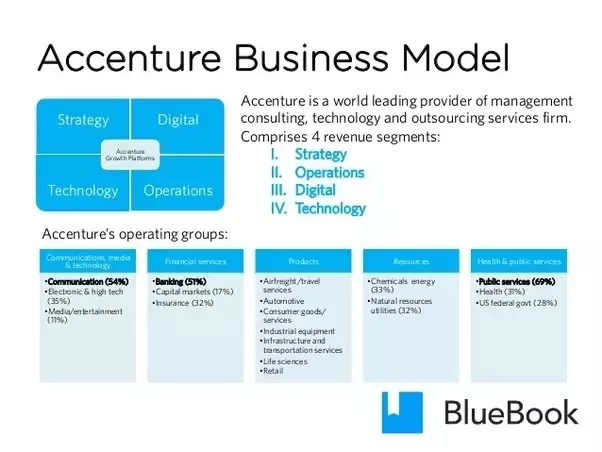
4. Global Presence: Accenture’s global presence is yet another significant advantage. With operations in over 120 countries, the company can serve clients locally while leveraging its global scale to deliver consistent service quality and best practices. This presence also enables Accenture to tap into local talent pools, bringing diverse perspectives and ideas to its clients. Additionally, the company’s global reach allows it to respond quickly to changing market conditions and capitalize on emerging opportunities.
5. Innovation and R&D: Innovation is at the heart of Accenture’s growth strategy. The company invests heavily in research and development (R&D), focusing on cutting-edge technologies like AI, machine learning, and quantum computing. Accenture’s dedicated R&D organization, Accenture Labs, explores new ideas and prototypes solutions that can be applied to real-world problems. Through its annual Accenture Technology Vision report, the company shares insights and predictions on emerging trends, demonstrating thought leadership and showcasing its commitment to innovation.
6. Talent Development: Attracting and retaining top talent is essential for any professional services firm, and Accenture recognizes the importance of investing in its people. The company offers extensive training programs, mentorship opportunities, and career advancement paths to ensure employees are equipped with the skills needed to succeed. Accenture’s commitment to employee development helps foster a high level of engagement and satisfaction among its staff, which translates into better service delivery for clients.
7. Collaborations and Partnerships: Accenture has formed numerous strategic alliances with leading technology companies, startups, and industry associations. These partnerships enable the company to expand its capabilities, offer complementary services, and stay abreast of the latest technology trends. For instance, Accenture’s partnership with Microsoft focuses on accelerating the adoption of Azure-based cloud solutions, while its collaboration with AWS combines Amazon Web Services’ cloud infrastructure with Accenture’s deep industry knowledge and implementation expertise.
8.Corporate Social Responsibility: Corporate social responsibility (CSR) is increasingly important for organizations, and Accenture takes its role seriously. The company has set ambitious targets to reduce its carbon footprint, promote diversity and inclusion, and empower communities through technology. Accenture’s CSR initiatives include Skills to Succeed, a program aimed at equipping millions of people around the world with the skills they need to thrive in the digital economy. Such initiatives not only contribute to the well-being of society but also enhance Accenture’s reputation as a responsible corporate citizen. This, in turn, can lead to increased client confidence, greater employee morale, and improved brand recognition.
9. Agile Methodology: Accenture has embraced agile methodologies to deliver projects efficiently and effectively. Agile enables Accenture to respond quickly to changing client requirements, iterate rapidly, and continuously improve solutions. By using agile frameworks such as Scrum and Kanban, Accenture’s teams can collaborate more effectively, reduce project risks, and increase transparency. This approach aligns with the company’s focus on delivering tangible outcomes and exceeding client expectations.
10. Continuous Improvement Culture: Accenture fosters a culture of continuous improvement, encouraging employees to challenge assumptions, experiment with new approaches, and learn from failures. This mindset permeates every aspect of the company’s operations, from process optimization to solution design. By constantly improving its methods and tools, Accenture ensures that clients receive the most effective and efficient services possible. This culture also promotes innovation, as employees are empowered to explore novel ways of solving complex business challenges.
11. Best Practices and Benchmarking: Accenture has developed and implemented a suite of best practices and benchmarking tools to assess performance, identify areas for improvement, and optimize processes. The company’s mature delivery methodologies, such as the Accenture Delivery Methodology (ADM) and the Accenture Project Management Methodology (APMM), provide a standardized framework for managing projects and ensuring consistency across engagements. By leveraging these methodologies, Accenture can streamline project execution, minimize risks, and maximize value for clients.
12. Thought Leadership: Accenture is recognized as a thought leader in various industries and domains, frequently publishing research reports, white papers, and case studies that provide valuable insights to clients and the broader market. The company’s experts actively participate in industry conferences, webinars, and panel discussions, sharing their knowledge and experience with peers and clients. This thought leadership helps establish Accenture’s credibility, builds trust with potential clients, and reinforces its reputation as a go-to partner for complex business challenges.
13. Strategic Acquisitions: Accenture has made strategic acquisitions over the years to bolster its capabilities, expand its offerings, and strengthen its position in key markets. For example, the company acquired Digital Kickstart to enhance its digital transformation capabilities, purchased Allen Interactions to boost its learning and development services, and acquired Clarity Insights to expand its data science and AI offerings. These acquisitions demonstrate Accenture’s commitment to staying ahead of market trends and providing comprehensive solutions to clients.
14. Robust Alumni Network: Accenture has a large and active alumni network comprising former employees who have gone on to hold senior positions in various industries. This network provides an invaluable resource for networking, referrals, and business opportunities. Many Accenture alumni have become clients, partners, or influential advocates for the company, helping to amplify its brand and reputation within their respective networks.
15. Strong Financials: Accenture has consistently delivered strong financials, with steady revenue growth, high profitability, and a healthy balance sheet. The company’s financial stability enables it to invest in new technologies, expand its operations, and pursue strategic acquisitions. This financial strength also provides peace of mind for clients, knowing that their partner is financially secure and capable of fulfilling its obligations.
By examining these 15 factors, it becomes evident that Accenture’s success stems from a combination of its consulting heritage, commitment to innovation, client-focused approach, and dedication to delivering tangible outcomes. As the company continues to evolve and adapt to changing market dynamics, it remains well-positioned to maintain its leadership status in the professional services industry.
Also Read: Marketing Strategies and Marketing Mix of Accenture
To read more content like this, subscribe to our newsletter




