What do Kylie Cosmetics, Gymshark, Fitbit, and Whole Foods all have in common? They use Shopify software to sell their products in online shops. Currently there are more than 1.7M merchants that sell goods using the Shopify platform according to Shopify Unite.
The subscription-based store builder software allows businesses to grow and succeed by providing them the easy-to-use tools to build an online store at an affordable cost.
Shopify has several eCommerce and website building competitors like WooCommerce, Squarespace, and Wix to name just a few, but has managed to provide a massive value add which leads customers to choose them.
Shopify has enabled businesses of all sizes to create a unique digital buying experience for customers online which helps them capture a large part of this big market size. Shopify’s success and impact has been great since their entry into the eCommerce industry, and their future success will be determined by their response to rapidly expanding and changing trends of the eCommerce industry.
Shopify is an online store builder and eCommerce management system that allows businesses of all sizes to create online storefronts where they can advertise, build brand strength and presence, sell products, connect with customers, and grow their business conveniently and affordable.
The company began in 2004 as an online store that sold snowboarding gear, however founders Tobias Lutke and Scott Lake realized that the success of their store wasn’t from the products they were selling, but rather the unique and efficient online storefront they had created that was unlike any other at the time.
Thus, the founders leveraged the success of this technology and Shopify was born in 2005 as an eCommerce platform that comes with tools that allow users to build websites, add inventory, sell products, track customer analytics, manage fulfillment, write blogs, and more, all on a scalable and easy-to-use platform.
By providing these services and tools, Shopify has helped millions of businesses succeed and grow in the ecommerce market and has been a key player in changing how consumers interact with businesses.
Shopify is a platform business model as it enables third-parties merchants to commercialize their products on its cloud-based eCommerce.
They make money through subscriptions and charging processing fees for every transaction.
There are different levels of subscription, the lowest level lacking selling ability ($10/month), basic Shopify ($29/month), Shopify ($79/month), and advanced Shopify ($299/month).
The transaction fees are 2% (basic), 1% (Shopify), and .5% (advanced), where a smaller transaction fee is meant to offset the cost of the monthly fee.
Shopify is also a marketplace for many applications and plugins from both Shopify and third-party developers that can be either paid services or free.
These add ons can help you with things like aesthetics, analytics, upselling, or dropshipping, a business model where a business doesn’t have any of the products that it sells in stock, but rather the store purchases the item from a third-party supplier and then has it sent directly to the customer upon a customer order.
Shopify Market Size
The website builders market was valued at USD 1.46 Billion in 2019 and is projected to reach USD 2.62 Billion by 2027, growing at a CAGR of 7.73% from 2020 to 2021 (Verified Market Research).
The market that Shopify is fighting for is extremely large. Similarly, eCommerce is only growing so Shopify is in a good position to keep growing: “Global e-commerce is expected to rise to a total of $4.89 trillion in 2021—almost a 400% increase in seven years” (Emarketer). According to SleekNote & Statista, “Shopify has nearly 11 percent of the total e-commerce market share.”
Established players & Disruptive Innovation
When Shopify entered the market in 2005, the eCommerce industry was still relatively small and mostly dominated by consumer-to-consumer businesses that facilitated the sale of products between consumers.
The majority of retail was still being done in brick-and-mortar stores, though there were a few established players in eCommerce such as online marketplaces eBay and Alibaba.
These players had immense control over the eCommerce industry at the time as businesses did not have many options and it was very difficult for small retailers to enter the industry outside of just listing products on a marketplace.
The entry barriers to creating an eCommerce brand were very high; the set up of an online store was foreign, complicated to design and operate, inflexible, and expensive, leaving businesses dependent on large marketplaces to reach their customers as online retail rapidly grew.
Shopify created a disruption when it entered the eCommerce market as it revolutionized the way retailers could facilitate sales and interactions with customers by empowering them.
Rather than having to rely on eCommerce giants at the time like eBay or Alibaba to facilitate their online sales, businesses could create their own online shop that they had almost complete control of, allowing them to strengthen their brand and grow their business.
Shopify removed and lowered technical barriers to eCommerce by providing a platform service that was affordable, convenient, scalable, and had a user-friendly set up.
Through services like end-to-end billing, inventory, and shipping, Shopify was able to provide retailers the same online shop capability as the large retailers already established in the online retail industry.
The response in the market to Shopify’s disruption was an increase of businesses of all sizes setting up online stores, rapidly expanding the size and scope of the eCommerce industry. Businesses now had feasible, affordable, scalable options to grow their business without depending on giants, which changed the way the industry operated.
Because of this expansion of eCommerce, there was also a shift to multi-channel approaches to retail. Rather than just having a brick-and-mortar store or just an online store, retailers started expanding to supporting a combination of channels at once such as online store, social media, and marketplace listings alongside physical stores.
Shopify took advantage of this response by becoming the one-stop-shop for retailers; rather than have multiple channels for commerce that they had to separately manage, Shopify provided them an omni-channel approach where they could manage all of their transactions through any channel seamlessly through their platform.
Established players at the time like eBay and Alibaba suddenly found themselves with a new competitor and a quickly changing industry after Shopify’s entrance and disruption.
Over the past 2 decades, they have been in heavy competition with each other to create new features and dominate online retail, though Shopify has kept its power by focusing their business model on the success of small businesses.
Also Read: Meesho – Leveraging Social Network To Sell Online
Strengths, Weaknesses, Opportunities & Threats
Shopify is in an interesting position in the space of eCommerce. The company has grown to an almost two hundred billion dollar company in the span of about six years.
It has had sound success that no one can deny has a bright future ahead of it. That being said, the company does have its pros and cons.
Strengths
To start off, the eCommerce giant has quite a few strengths going for it.
Firstly, it’s business model is perfectly placed for the digital world. With thousands of websites being created daily, the company is not only powering small drop shipping stores but large company websites as well. Its model of powering websites also provides a low barrier to entry for anyone to join.
Never has it been easier for one person to start their own online business.
Weakness
However with these strengths come weaknesses.
Shopify’s business model could be a victim of its own success. The giant charges fees for anything and everything extra that a user would want to add to their site.
Transaction fees, banner ad fees, locked in vendor, recurring charges for just the internal problems. Fees are essential to almost any online business model but the company needs to decide which fees are effective and necessary for growth and which are not.
Also, the model is still victim to external forces concerning logistics. A perfect example of this is the global supply chain problem that we are facing right now.
Shipping inventory from China can take as long as six weeks, a huge problem when customers are used to two day shipping.
Opportunities
Shopify does have some opportunities that come with being a leader in the eCommerce space.
The industry is on fire right now, Shopify alone is seeing yearly revenue increases of between thirty and fifty percent.
New attributes with running an online store such as wholesale and retail arbitrage, affiliate promo links for discounts, and facebook and google ads, all are fueling this cyber machine of an industry.
Shopify has the advantage of supplying the shovels for everyday people or large companies to dig for internet money, and with COVID-19 the acceleration towards a digital world has only cemented Shopify’s position to stay in the future.
Threats
There are some threats that are of concern to Shopify.
Shopify itself can become a victim of its own success as stated previously, if it continues to charge fees for little things that add up, it could be its own greatest enemy.
Shopify does have competitors that pose a threat. Amazon.com has allowed almost anyone to sell products on their site.
Almost anyone can become a seller for $25 a month. Users just have to source products and Amazon takes care of the rest.
There are alternative options that are almost identical to Shopify that provide the same service but at a lower cost for example Woocommerce. The company does almost the same exact thing that Shopify does but with fewer charges, is open source so you do not have to worry about the site going down, and even some free add-ons.
Overall Shopify undoubtedly developed a near indestructible presence in the eCommerce space.
Ultimately, as mentioned above, the growth of eCommerce and Shopify has been staggering the past couple of years.
While COVID-19 helped a lot by providing a surge of new online users, we have no reason to believe this increase will stop. Furthermore, Shopify has fortunately also solidified themselves as a main player in this market that is here to stay.
However, there is a lot of competition that needs to be fought off.
These include large influential companies such as WordPress, Squarespace, Wix, Amazon and more. Therefore, in order to remain relevant and maintain their market share, Shopify will have to be innovative with their business strategies.
Future of Shopify
For the future, we recommend that they continue to maintain their partnerships, while acquiring new ones as well.
Partnerships with companies such as Tik Tok, Google, and Facebook have been very prosperous for Shopify and a steady source of revenue.
These are companies that have a large eCommerce presence and provide a large customer base. They will need to preserve these relationships and continue their search for new companies, such as Reddit, who also have a larger online presence.
Additionally, we recommend that Shopify start charging their merchants a referral fee.
Competitors, such as Amazon, are already doing this and are even charging up to 15% per referral. By instituting this, Shopify has the opportunity to generate nearly $100 million in revenue.
This is a necessary step for them to improve their service, continue innovating, and remain competitive with their competition. This will allow them to invest in expanding even further, especially internationally.
eCommerce is increasing all around the world and there is a ton of opportunity to gain new customers abroad and capture more of the market share.
All in all, Shopify has been a key player in the eCommerce boom.
Their innovation has created opportunities for companies all over the world to conduct business online. They are now talked about in the likes of Amazon, and other influential business tycoons.
With that being said, they will need to continue to innovate, in order to stay relevant. This can be done through initiatives to create partnerships, referral fees, and overall expansion.
Shopify will need to continue to work, but they have certainly solidified themselves as a key stakeholder in the eCommerce market.
How does Shopify make money?
Shopify makes money through two revenue streams: a recurring subscription component called subscription solutions and a merchant success-based component called merchant solutions. Let’s talk about each revenue stream in detail to understand how Shopify makes such a considerable sum of money:
1. Subscription Solutions:
Shopify makes money through subscription solutions via the sale of subscriptions to its platform, including variable platform fees, through the sale of subscriptions to its POS Pro offering, the sale of themes, the sale of apps, and the registration of domain names. Subscription solutions contributed ~30% of Shopify’s revenue in 2021.
As of March 2022, Shopify has three subscription plans for merchants that are designed to meet the needs of current and prospective merchants. Offering different service and pricing levels allows entrepreneurs to scale without leaving the Shopify platform: as a merchant upgrades to the higher-priced options, they receive more powerful tools.
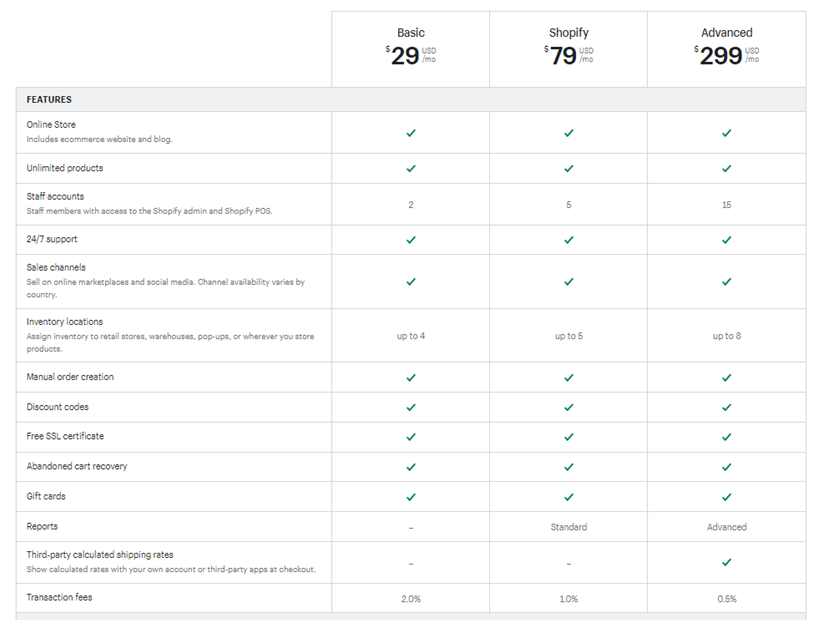
Shopify also offers one more service plan called ‘Lite,’ allowing website owners to add a Shopify store to their existing web properties. The plan costs $9 per month. For bigger-sized businesses, such as Budweiser, Tesla, or The Economist, a more advanced program like Shopify Plus is offered, which starts at $2,000.
Most merchants subscribe to Shopify’s Basic and Shopify plans. Allbirds, Gymshark, Heinz, Tupperware, FTD, Netflix, and FIGS are among the prominent 14,000 Shopify Plus merchants leveraging its commerce solution.
To attract the best developers in the world, in 2021, Shopify changed its revenue share model with app and theme developer partners to offer a zero percent revenue share on the first million dollars that they make annually on the Shopify App Store. App and theme developers pay a 15% revenue share on earnings after the first $1 million.
2. Merchant Solutions:
Shopify offers a variety of merchant solutions to augment those provided through a subscription to address the broad array of functionality merchants commonly require, including accepting payments, shipping, and fulfillment, and securing working capital. Merchant solutions contributed ~70% of Shopify’s revenue in 2021.
Let’s understand in detail how Shopify makes money through various merchant solutions –
- Shopify Payments: Shopify principally makes money in merchant solutions from payment processing fees and currency conversion fees from Shopify Payments, Shopify’s payment gateway. Based on the subscription plans, Shopify charges merchants 2.4% -2.9% of the GMV of transaction.
- Advertising: When merchants click on the apps being advertised by its partners of Shopify App Store.
- Shopify Capital: Merchants can take loans, and access Cash advances through Shopify Capital to grow their businesses. The maximum amount of money that a store owner can borrow is $2 million. However, the loan or cash advance must be repaid within 12 months. Shopify Capital charges a fixed borrowing cost to the loan. The fixed borrowing cost is the fee that the user/merchant pays to obtain a loan. To repay the loan, the merchant pays a percentage of the daily sales revenue to Shopify Capital until the full remit has been remitted.
- Shopify Shipping: It allows merchants to manage their shipments through available shipping partners on Shopify.
- Shopify POS: Shopify’s sales channel lets merchants sell their products and accept payments in person from a mobile device in a physical or retail setting.
- Shopify Email: It is an email marketing tool to enable merchants to manage their marketing campaigns. Up to a certain extent, Shopify offers the service for free and charges merchants after that.
Source: Ecommerce Business Review
To read more content like this, subscribe to our newsletter



