International Business Machine, abbreviated as IBM, and commonly recognized as ‘Big Blue’ is an American multinational technology company headquartered in Armonk, New York. Founded 108 years ago in 1911 as ‘Computing-Tabulating-Recording Company’ and later renamed as IBM, the organization now serves over 175 countries and ranked as the 7th largest tech brand of 2020 by Investopedia. The company is known to have more patents than any other American tech company.
IBM provides a wide range of products including computer hardware and software and distinguished hosting and consultancy services in areas ranging from the mainframe computers to nanotechnology. Integrated solutions & service brand, IBM offers software & IT solutions for a wide range of uses including Healthcare, Finance, Internet Of Things (IoT), Security, and Cloud Computing.
The company has the broadest set of skills and knowledge in the industry with an enterprise-class big data platform as a part of a comprehensive information management system foundation, and analytical abilities that are interconnected to facilitate shared insights. It develops products from punch-card tabulating machines to room-sized calculators and mainframe computers.
Rich History of IBM


During the late 1880s, technological inventions kicked a greater pace which formed the backbone for the Computing-Tabulating-Recording Company. Commonly abbreviated as CTR, the company was an amalgamation of four different companies led by Charles Ranlett Flint in 1911.
They manufactured machinery for sale and lease, ranging from commercial scales and industrial time recorders, meat, and cheese slicers, to tabulators and punched cards. Later in 1914 Thomas. J. Watson joined CTR as a General Manager and within a short span of 11 months took over as the president of the company.
Watson was skilled in pioneering business practices and had his own favorite slogan named ‘THINK’ which became the main agenda for all workers of CTR. Under his leadership, the company’s revenue reached $9 million ($133 million today) in a short span of four years. Later in February 1924, Watson changed the name of the organization to International Business machine-IBM.
Major Technical Inventions & Developments
1937: Developed tabulating equipment that enabled organizations to process huge amounts of data including the United States Government which boosted the profits of the company by 81% in four years.
1956: Demonstrated the first practical example of artificial intelligence when Arthur L. Samuel programmed an IBM 704 to learn from its own experience.
1957: FORTRAN, a scientific programming language was developed which boosted the computer programming methods.
1961: Developed the SABRE Reservation System for American Airlines and introduced the highly successful Selectric typewriter.
1963: Helped NASA tracks the orbital flights of the Mercury astronauts and later its support of space exploration.
1969: Invented Magnetic Strip Card which alters substituted credit cards, driving license, and many identities and access control applications

Product Division
IBM offers a variety of products and services in vivid sectors including IT Infrastructure, Cloud Computing, Artificial Intelligence, Commerce and Data, Analytics Internet Of Things, Security, Mobile, Digital Workplace.
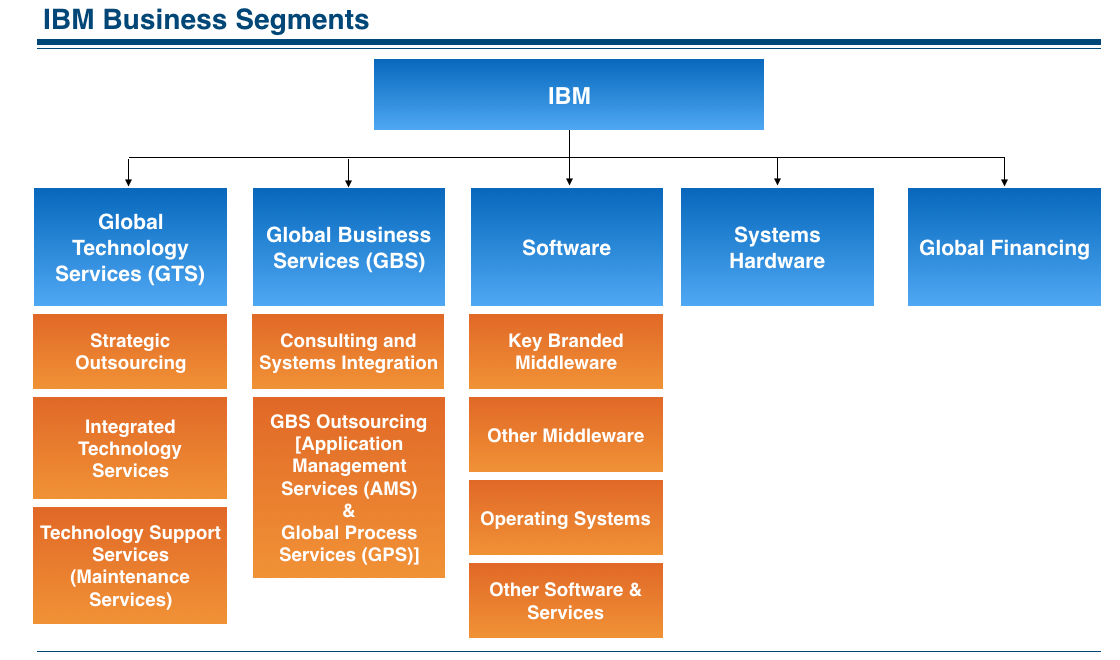
Market Segmentation
IBM operates in five different segments which are listed as follows-
Cognitive Solutions: Segment delivers a spectrum of capabilities, from descriptive, predictive and prescriptive analytics to cognitive systems.
Global Business Service: The GBS segment provides clients with consulting, application management services and global process services.
Software Technology Services & Cloud Platforms: This segment provides information technology infrastructure services including the cloud domain.
Systems Segment: Provides clients with infrastructure technologies.
Global Financing Segment: Includes client financing, commercial financing, and remanufacturing and remarketing.
SWOT Analysis Of IBM
SWOT Analysis is a framework used to identify the strengths, weaknesses, opportunities, threats to an organization thus minimizing the risks of failure and damage.
Strengths
Brand Value: IBM’s brand value ranks 6th in the world in the technology sector as per the VisualCapitalist report.
Market Share: The company accounts for 29.1% of the middleware market share and has been a leader in the segment for the 14th time in a row.
Research & Development: IBM employees have garnered over 6 Nobel Prizes, 6 Turing Awards, and many other prestigious awards. As of 2019, the company has generated more patents than any other business in each of 25 consecutive years, which is a record.
Strong Distribution Network: The organization has a strong presence in 170+ countries with trusted partners and a sustainable growing network.
Weakness
Lack of Synergy: As it is difficult to coordinate over four geographical segments, it creates a lack of synergy resulting from the series of acquisitions and divestitures.
Litigations: IBM continually involved in many litigations including the Lusacell and Bridgestone America dispute which costed a loss of over @600 million
Opportunity
Data Analytics: This field is one of the most profitable channels for IBM, hence it is an opportunity for IBM to leverage upon.
Cloud-Based Services: The increasing demand for various Cloud-based services provides an opportunity for IBM to grow its revenue by 12% in the next 10 years, as per industry reports.
Threats
Competition: IBM faces competition from Accenture, Amazon, Microsoft, Oracle, SAP, Cisco.
Global Economy: The fluctuations in currency rates and global economy serve as a major challenge for growth & development.
Also Read: Apple And The Strategies That Made It A Synonym Of Innovation And Success
Success Strategy
Repositioning: IBM is repositioning itself from a computer company to an information technology service through a series of acquisitions. Thirteen acquisitions of approximately $4.8 Billion were completed enabling the company to expand its business.
Business Model: IBM focuses on two major factors of the long-term growth strategy which include client satisfaction and long-term values to shareholders.
Jam Technology: IBM continuously evaluates and develops products and tools according to changing technological demands. It engages 50,000 employees in an online intranet discussion over a period of three days using its Jam technology. IBM has generated over 46,000 ideas through these sessions.
Data Analytics: IBM spends nearly one-third of its R&D budget on data analytics and cognitive computing.
IBM Research: IBM Research is the research and development division for IBM, which is the largest industrial research organization in the world and has twelve labs on six continents. As per the latest company data, in 2019, IBM spent 5.99 billion U.S. dollars on research and development.

To read more content like this, Subscribe to our newsletter.
Bonus: Infographic For IBM Patents
